* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download First cells ppt The first cells ppt
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
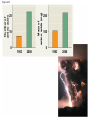
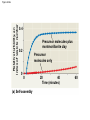
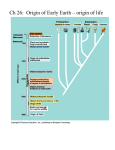
The First Cells Conditions on Earth • Planet formed 4.6 billion years ago • For the first few hundred million years. . . • • • • Huge chunks of ice and rock bombarded the planet Intense heat vaporized all available water Asteroids began to melt the Earth’s crust Radioactive core produced intense volcanic eruptions spewing molten lava and gases So then what happened? • Gaseous H20 from meteorites and the Earth’s crust began to rise and combine with CO2 creating dense clouds • These shielded the Earth from the sun’s radiation eventually causing cooling • Then. . .RAIN! • Creating lakes and rivers Chemical makeup of the atmosphere • Most early scientists believed that the atmosphere was “reducing” (electron adding) made up of: – Very little O2 – Thick water vapor – Volcanic gases such as methane (CH4) and ammonia (NH4) Abiogenesis • The idea that some small organic molecules (the basic building blocks of living organisms) could have been created from inorganic compounds under the right conditions. • These then went on to evolve into diverse life forms over MANY years. Scientists hypothesize that simple cells could have been produced through a series of 4 main stages. 1. The abiotic (nonliving) synthesis of small organic molecules (amino acids and nitrogenous bases). 2. The joining of these into macromolecules (proteins and nucleic acids). 3. Packaging these into protocells = droplets with membranes that maintained an internal chemistry different from that of their surroundings. 4. The origin of self-replicating molecules that made inheritance possible The Miller- Urey Experiment • Assumed: – A reducing atmosphere – Energy supplied by lightning and intense UV radiation • Let’s look – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mF9U5x6Nxn w Controversy Not everyone agrees about the composition of early Earth’s atmosphere. Was it more “neutral”? Were there only “pockets” of reducing substances such as near volcanoes and deep sea vents? In 2008, the experiments were repeated under volcanic-atmosphere conditions. . . Number of amino acids 20 10 Mass of amino acids (mg) Figure 24.3 0 1953 2008 200 100 0 1953 2008 Alien invasion? • 2nd source of organic molecules may have been meteorites. • Fragments of a 4.5 billion year old meteorite that fell in 1969 was found to contain 80 amino acids, some lipids, simple sugars and nitrogenous bases! Small organic molecules to macromolecules • 2009 experiment showed spontaneous synthesis of RNA monomers. • By dripping RNA nucleotides or solutions of amino acids on hot clay, polymers formed. • These could then have acted as catalysts for further chemical reactions. The next step • Vesicle formation • Vesicles form spontaneously when lipids or other organic materials are added to water. • Think oil or soap in water! • Furthermore, it has been found that these vesicles: – Can reproduce by simple division – Grow – Absorb particles on which RNA and other organic materials may have been attached. Figure 24.4b 20 m (b) Reproduction • The rate of vesicle assembly and polymer formation increases on montmorillonite- a soft mineral clay derived from volcanic ash! Relative turbidity, an index of vesicle number Figure 24.4a 0.4 Precursor molecules plus montmorillonite clay 0.2 Precursor molecules only 0 0 (a) Self-assembly 40 20 Time (minutes) 60 Homework • In 50 words, or fewer (total for both), answer each of the 2 questions below: – What is the difference between abiogenesis and spontaneous generation? – What do scientists believe was the first genetic material? RNA or DNA? Why? You will turn this in at the beginning of the period.