* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
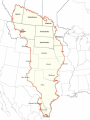
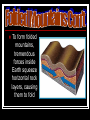
Answer the following questions in complete sentences, in your science notebook: 1. Name at least 1 specific example of each type of mountain. 2. Name at least 1 specific example of a plateau in the US. 3. Name the two types of plains – give a specific example of each one. 4. What is another name for the Great Plains? This ball was once a glowing mass Of mixed and superheated gas, Till it cooled to liquid, shrank in girth, Solidified and turned to earth. For several thousand endless ages It muddled through its early stages Of heat, eruptions, floods, and quakes And other infant bellyaches. Surviving all such pains and notions, It settled down as land and oceans. In eras that are known as “glacials” The planet then got several facialsWhich filled its unbecoming dimples And leveled off some rocky pimples. If, sometimes, there’s a recrudescence, It’s due, no doubt, to adolescence, But in the main, we are now able To say the Earth is fairly stable And, in most geologic features, Better balanced than its creatures. By Joseph S. Newman * Recrudescence – return of a disease Objectives: You will learn to discuss the differences between plains and plateaus. You will learn to describe folded, upwarped, fault-block, and volcanic mountains. Do not copy the words typed in this color Plains Coastal Interior Plateaus Mountains Folded Upwarped Fault-block Volcanic Large, flat areas, often found in the interior regions of continents Have thick, fertile soils and abundant, grassy meadows suitable for grazing animals Plains also are home to a variety of wildlife, including foxes, ground squirrels, and snakes When plains are found near the ocean, they’re called ______________ A coastal plain is often called a _________ because it is lower in elevation, or distance above sea level, than the land around it This area has low rolling hills, swamps, and marshes The ____________ _____________ is a good example of this type of landform How do coastal plains form? Coastal plains form when sea level drops and the seafloor is exposed The central portion of the United States is comprised largely of _______________ A large part of the interior plains is known as the ________________ It is a flat, grassy, dry area with few trees The ________________ are also referred to as _______________ Do now Study vocab words on 1st pg of packet The world’s highest mountain peak is _________________ in the Himalayan Mts. — more than 8,800 m above sea level 4 types: folded upwarped fault- block volcanic Appalachian Mountains and the The ___________________________ Rocky Mountains in Canada are ____________________ comprised of folded rock layers In _____________, the rock layers are folded like a rug that has been pushed up against a wall To form folded mountains, tremendous forces inside Earth squeeze horizontal rock layers, causing them to fold southern Rocky Mtns. in The _________________________ Colorado and New Mexico are upwarped mountains High peaks and sharp ridges are common to this type of mountain Form when blocks of Earth’s crust are pushed up by forces inside Earth Made of huge, tilted blocks of rock that are separated from surrounding rock by faults These ________ are large fractures in rock along which mostly vertical movement has occurred When these mountains formed, one block was pushed up, while the adjacent block dropped down This mountain-building process produces majestic peaks and steep slopes SAN ANDREAS FAULT _____________________ _____________________ Begins to form when molten material reaches the surface through a weak area of the crust The deposited materials pile up, layer upon layer, until a cone-shaped structure forms _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ Flat, raised areas of land made up of nearly horizontal rocks that have been uplifted by forces within Earth They are different from plains in that their edges rise steeply ________ from the land around them 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. ________ Plains are large, flat landforms that are usually found in the interior region of a continent. __________ Plateaus are flat, raised areas of land with horizontal rocks that were uplifted. Folded mtns form when horizontal rock layers are _______________ squeezed from opposite sides. () Upwarped mtns form when blocks of Earth’s crust __________________ are pushed up by forces inside Earth. Fault-block mtns form from huge, tilted blocks of ___________________ rock that are separated by faults. When molten material reaches Earth’s surface through a weak area, ____________ volcanic mountains begin to form. Describe the difference between the formation of folded mountains and fault-block mountains. Study for Quiz on 1.1 Monday!!! 1. 2. 3. 4. In your notebooks, answer the following review questions in complete sentences: What are the three basic types of landforms? What are the three types of mountains? What are the three types of map projections? What are topographic maps used for? 1. 2. 3. The imaginary line representing 0º Prime Meridian longitude is the ______________. What imaginary line separates Earth into the northern and southern hemispheres? ________ Equator What is the transition line for calendar International Date Line days called? ___________________ Objective: Compare and contrast map projections and their uses. Analyze information from topographic, geologic, and satellite maps. Maps are models of Earth’s ______ surface maps for various reasons Scientists use _____ such as: locating various places and showing the distribution of various features or types of materials A _____________ is made when points and lines on a globe’s surface are paper transferred onto _____ All types of projections distort _____ the shape/size of landmasses or their areas 3 types: _______________ _______________ _______________ Used mainly on ______ ships Project correct shapes _______ of continents, but the areas are distorted Lines of longitude _________ are projected onto the map parallel to each other When longitude lines are projected as parallel, areas near the poles appear _______ bigger than they are Shows accurate continent shapes and more accurate land areas Lines of _________ longitude curve just like on a globe Often are used to produce maps of _____ small areas Well suited for middle latitude regions weather Road or ________ maps Made by projecting points and lines from a globe onto a _____ cone Models the changes in elevation of Earth’s ________ surface Also indicate cultural features such as roads, cities, dams, and other structures built by people A line on a map that connects points of ______ equal elevation The difference in elevation between two side-by-side contour lines is called a ________ contour interval _________ In mountainous areas, the contour lines are close together ______ However, if the change in elevation is slight, the contour lines will be ________ far apart index Some contour lines, called ______ _________, contours are marked with their elevation The relationship between the distances on the map ____ and distances on ______ Earth’s surface ________ Explains what symbols the ________ used on the map mean Includes maps that have the same latitude and ________ longitude dimensions of _______ Show the arrangement and types of _____ rocks at Earth’s surface Using geologic maps and data collected from rock exposures, a geologist can infer how rock layers might have looked below Earth’s surface The block diagram is a 3D model that illustrates a solid section of Earth The top surface of the block is the __________ Side views of the block are called cross sections, which are derived from the surface map To visualize Earth three dimensionally, scientists often rely on computers Using computers, information is digitized to create a three-dimensional view of features such as rock layers or river systems Digitizing is a process by which points are plotted on a coordinate grid To determine New Zealand’s location relative to Canada, you probably would examine a ____________________ or a _____________________ To travel across the country, you would rely on a road map, or _______________ To climb the highest peak in your region, you would take along a _______________ Remote sensing is a way of collecting information about Earth from a distance, often using satellites 2 types: Landsat Global Positioning System (GPS) One way the Earth’s surface has been studied is with data collected from Landsat satellites These satellites take pictures of Earth’s surface using different wavelengths of light The images can be used to make maps of snow cover over the United States or to evaluate the impact of forest fires The Global Positioning System, or GPS, is satellite-based, radio-navigation system that allows users to determine their exact location anywhere on Earth GPS technology is used to navigate, to create detailed maps, and to track wildlife 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. map projection is the projection of points A ______________ and lines of a globe’s surface onto paper. __________________ Topographic maps show the changes in elevation of Earth’s surface by using contour lines. _______________ Geologic maps show the arrangement and types of rocks at Earth’s surface. ________________ Remote sensing is a way of collecting information about Earth from a distance, often by using satellites. Distant planets can be mapped using satellites ________. Study for Chapter 1 Test!!! In your notebooks, answer the following question: What is the scientific method? If you are not sure, take a guess!!! Objective: List and describe steps used in the scientific method. The Scientific Method How do scientists do what they do? Well, YOU know because you’re a scientist too! Observation is an important part – in fact it’s the part at the very start. For it’s observation that causes you to wonder why earthworms do what they do and clouds form in the sky. Your hypothesis is a “best guess” based on what you know about how things work – now you’re ready to go! Experimentation lets you test the hypothesis you’ve made – to see if your best guess can make the grade. And because variation is found in nature everywhere, repeated trials should be done, and done with care. And don’t forget to decide what variables you’ll test. You change the independent variables, but not the rest. Recording your data is very important, too; so you can analyze the results and others can repeat what you do. When you’ve summarized your results and your experiment is done, You’ll have more information about nature and you’ll have some fun. So, now you know that the scientific method is really cool, and that scientists don’t just measure – they RULE!!! Determine the problem 2. Make a hypothesis Test your hypothesis or a prediction that can be tested 4. Analyze your results 5. Draw conclusion 1. 3. Science is my thing today. When you do science – here’s the way: First ask questions – why or how? Then hypothesize – do it now! Experimentation is next in line. You get results that are SO fine! Analyzing data comes up next. Then graph your data, to show it best. Being a scientist – it’s a trip! It’s not square – it’s really hip! 1. What are the five steps in the scientific method? 2. Define the term hypothesis. 3. When completing a __________, using the scientific method becomes helpful.