* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Boundaries
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
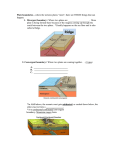
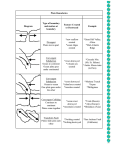
Earth’s Moving Boundaries: shaping the planet Earth’s Moving Plates Lithosphere the solid part of the Earth Tectonic plates large chunks of rock that float on the mantle Earth’s Moving Plates Transform Fault cracks along ocean ridge that allow the crust to slide Content Check-Up 1) Tectonic plates are _____. A. Large chunks of rocks that float on the mantle B. Large chunks of rocks that are in the mantle C. Sheets of magma in the core D. Part of the outer core Content Check-Up 2) The lithosphere is _____. A. B. C. D. The The The The liquid part of the Earth. Gaseous part of the Earth. solid part of the Earth. spherical part of the Earth. 3) Which is directly on a plate boundary? Earth’s Moving Plates Plate Boundaries Divergent boundary two plates move apart creating crust Plate Boundaries Divergent boundary two plates move apart creating crust Surtsey, Icelandthe newest place on earth Plate Boundaries Divergent boundary two plates move apart creating crust Surtsey, Icelandthe newest place on earth Content Check-Up 4) The type of boundary that created Iceland and the new ocean floor: A. B. C. D. Divergent Convergent Collisional Transform Plate Boundaries Divergent boundary two plates move apart creating crust Also called constructive boundaries Thingvellir, Iceland, showing a fissure zone (in shadow ) Plate Boundaries Divergent boundary two plates move apart Also called constructive boundaries mid-ocean ridge Magnetic Striping The magnetic stripes are proof of ocean-floor spreading and that the Earth’s poles have switched many times. Magnetic Striping The magnetic stripes are proof of ocean-floor spreading and that the Earth’s poles have switched many times. Ocean-Floor Spreading Can you guess where the sea floor is starting to spread? Ocean-Floor Spreading Now, can you guess where the sea floor is starting to spread? Ocean-Floor Spreading Can you guess now? Several small plates meet in the northwestern Africa Tension is causing the plates to pull apart The Breakup of Pangaea The Breakup of Pangaea The Breakup of Pangaea The Breakup of Pangaea The Breakup of Pangaea The Breakup of Pangaea Ocean-Floor Spreading Where Are We Going? Plate Boundaries Content Check-Up 4) What do the stripes on the ocean floor prove? A. That there are different currents in the ocean. B. That the sea floor is spreading evenly on both sides. C. That magnets exist. D. That there are many rocks in the ocean. Content Check-Up 5) What created the stripes on the ocean floor? A. Ocean Currents B. Mantle Currents C. Reversing magnetic poles of the Earth with moving tectonic plates. D. Moving tectonic plates Plate Boundaries convergent boundary two plates move together destroying crust Ocean crust vs. continental crust Plate Boundaries convergent boundary two plates move together destroying crust Ocean crust vs. continental crust Patagonia, Chile (not just a line of fleece for soccer mom’s) Plate Boundaries convergent boundary two plates move together destroying crust Ocean crust vs. continental crust Pachapaqui mining area in Peru Content Check-Up 6) Which of the following will not be found at a convergent boundary? A. B. C. D. E. Earthquakes Volcanoes Trenches A subducting plate A mid-ocean ridge Content Check-Up 7) Which is the best explanation for the existence of volcanoes in Washington state? A. It is a divergent boundary. B. It is a collisional boundary. C. A plate is subducting under the North American Plate. D. It is a transform boundary. Earth’s Moving Plates The Juan de Fuca Plate is Subducte d below the North Anerican Plate Plate Boundaries convergent boundary two plates move together destroying crust Ocean crust vs. ocean crust Plate Boundaries convergent boundary two plates move together destroying crust Ocean crust vs. ocean crust Aleutian Is., Alaska Plate Boundaries convergent boundary two plates move together destroying crust Ocean crust vs. ocean crust Is this a convergent boundary? Content Check-Up 8) The Aleutian Islands of Alaska were formed by a A. B. C. D. divergent boundary. collisional boundary. transform boundary. convergent boundary Content Check-Up 9) The Marianas Trench is formed by a A. divergent boundary. B. collisional boundary. C. plate is subducting under the North American Plate. D. transform boundary. E. convergent boundary Plate Boundaries convergent boundary two plates move together destroying crust Continental crust vs. continental crust (aka: collisional boundary) Plate Boundaries convergent boundary two plates move together destroying crust Continental crust vs. continental crust (aka: collisional boundary) Mt. Everest, Nepal Content Check-Up 10)The collisional boundary that formed Mount Everest is most closely related to a ____. A. divergent boundary. B. transform boundary C. convergent boundary Plate Boundaries Collisional boundary two plates move together destroying crust Continental crust vs. continental crust (aka: collisional boundary) Mt. Everest, Nepal Plate Boundaries Strike-slip boundary rocks slide past each other no rock destroyed nor created San Andreas Fault, California Content Check-Up 11) Which of the following are found a transform boundaries? A. B. C. D. Volcanoes Earthquakes Trenches Subduction Plate Boundaries 12) Which is the mantle? 13) Which is the lithosphere? 14) Which is a mid ocean ridge? 15) Which is a convergent boundary? 16) Which is a divergent boundary? 17) Which is a trench? 18) Where are the convection currents found? Add the Geological Features that will Occur Life on the Ocean Floor Alvinellid worms most heattolerant animals on the planet build their papery tubes right beside vents @ 350 C Life on the Ocean Floor Alvinellid worms most heattolerant animals on the planet build their papery tubes right beside vents @ 350 C green bacteria attached to the worm's back Life on the Ocean Floor Tube worms The red plume absorbs sulfurous water that a sac of bacteria inside the worm uses to Life on the Ocean Floor Mussels accidentally gold, owing to the make-up of their shells nutritional boost from bacteria but can also filter food directly from the Life on the Ocean Floor Amphipods These look like shrunken shrimp just fractions of an inch long travel in swarms and eat tiny animals and detritus they feed fish Life on the Ocean Floor Zoarcid fish vent fish are of the long-and-flat variety, with a long fin running the length of the spine probably rely heavily on amphipods for food Life on the Ocean Floor Zoarcid fish vent fish are of the long-and-flat variety, with a long fin running the length of the spine probably rely heavily on amphipods for food Life on the Ocean Floor Galatheid crabs litter the bottom, standing motionless on the dark rock Life on the Ocean Floor Clams8 inches, and they're late arrivals to the study site With no mud to burrow into, they anchor themselves by sticking their fleshy foot down