* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Theory of Plate Tectonics Chapter 1 Section 5
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
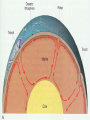
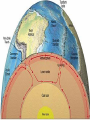
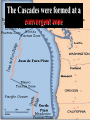
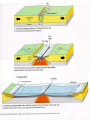
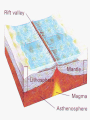
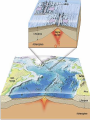
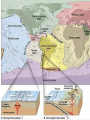
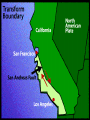
Vocabulary • • • • • • • • Plate Scientific theory Plate tectonics Fault Transform boundary Diverent boundary Rift valley Convergent boundary The Theory of Plate Tectonics Chapter 1 Section 5 What is Plate Tectonics? In 1965, J Tuzo Wilson put together Wegner’s theory of continental drift and Hess’ theory about sea-floor spreading into one big theoryPlate Tectonics Plate Tectonics is the theory that states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. Confused? I’ll explain. These pieces of the lithosphere are called plates or tectonic plates. The plates are always moving in slow motion. So what moves them? Scientists think that convection currents inside the mantle do! Plate Tectonics is the theory that states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. As the plates move around they collide, pull apart and grind past each other! Plates collide at convergent zones The Cascades were formed at a convergent zone Many volcanic islands are formed at convergent zones. So were the Himalayas! Do you see how? Plates move apart, or divide, at divergent boundaries. The mid- ocean ridge is a divergent boundary. Plates slide past each other at transform boundaries. Crust is neither created or destroyed at transform boundaries. 3 boundaries are convergent, divergent and transform!