* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13 Study Notes Volcanoes
David A. Johnston wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Types of volcanic eruptions wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
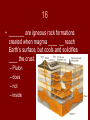
Chapter 13 Study Notes Volcanoes 1 • A _______ cone is rarely more than a few hundred meters high, with slope angles up to 40°, and formed from ______ eruptions. – cinder – explosive 2 • A large circular depression that forms when the magma chamber below a volcano partially empties, causing the ground above it to sink, is called a ______. – caldera. 3 • A _______ forms on the ocean floor in a _________ zone. – trench – subduction 4 • An area of volcanic activity ____ from a tectonic plate boundary is called a ________. – far – hot spot. 5 • Any activity that includes the movement of ______ to Earth’s surface is called ________. – magma – volcanism 6 • ________ volcanoes are also known as _________. – Composite – stratovolcanoes 7 • _______ eruptions are produced by ____, sticky lava with high viscosity and a high volume of trapped gases. – Explosive – thick, 8 • ______ is cut by a fissure breaking it into two parts. – Iceland 9 • If the temperature of rock rises ______ the melting point of the minerals the rock is composed of the rock will ____. – above – melt. 10 • _____ plutons that can cover an area as large as 100 km2 are called ________. – Large – batholiths. 11 • ____ is magma that flows onto Earth’s _____. – Lava – surface. 12 • ____ is liquid rock produced _____ Earth’s surface. – Magma – under 13 • Magma that is rich in _____ and silica is called ______. – feldspar – felsic 14 • Magma that is rich in ______ and iron is called ___. – magnesium – mafic. 15 • _____ lava forms on a _________ ridge. – Pillow – mid-ocean 16 • _______ are igneous rock formations created when magma ____ __ reach Earth’s surface, but cools and solidifies ____ the crust. – Pluton – does – not – inside 17 • Pyroclastic material ___ than 0.25 mm in diameter is called volcanic ______. – less – dust 18 • _____ eruptions are produced by _____ lava with low viscosity and few trapped gases. – Quiet – runny 19 • The eruption of Mount _________ was an ________ eruption. – St. Helens – explosive 20 • The Pacific ____ __ ____ is both a major earthquake zone and volcano zone. – Ring – of – Fire 21 • Three type’s volcanoes are _______, _____, and ______ cone. – composite – shield – cinder 22 • Volcanic ___, ____, blocks, _____, and lapilli are all _______ materials. – ash – dust – bombs – pyroclastic. 23 • Volcanic _____ may be signaled by a change in ______ activity. – eruptions – earthquake 24 • When an ______ volcano erupts, the magma cools quickly, forming _____ lava. – underwater – pillow 25 • When lava cools rapidly, a crust forms on the surface of the flow. If the flow continues, the crust _______ and forms volcanic rock known as ________. – wrinkles – pahoehoe. 26 • When oceanic lithosphere _____ beneath oceanic lithosphere, an island ____ forms. – subducts – arc The End!!!