* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Interpreting Microbiology Reports
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
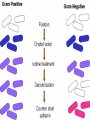
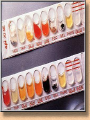
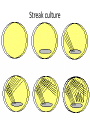
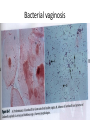
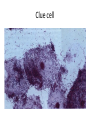
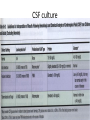
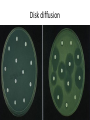
کشت نمونه های مختلف و آنتی بیوگرام Interpreting Microbiology Reports • The first step in performing cultures is to do a Gram stain of the collected sample (not for blood/urine - that is cultured first, then stained). • Gram staining results • few WBCs, no organisms seen. • many WBCs, many Gram positive cocci in clusters", or something like that Interpreting Microbiology Reports • Step 2: Identification: • Chemical tests to identify bacteria • Next the bacteria are cultured and put through biochemical tests to determine their identification. This takes a while longer than the Gram stain Interpreting Microbiology Reports • Step 3: Susceptibilities :Finally the bacteria are tested for their susceptibility to various antibiotics. • Once this data is known, we can transition from empiric to definitive therapy if the team has decided that an infection is indeed present. • The lab sometimes tests bacteria against many different antibiotics that we would never actually use - ignore them. Urine culture Urine culture Different culture methods Streak culture Female genital system infections Vaginal secretion culture Bacterial vaginosis Clue cell Blood culture Blood culture Tissue culture CSF culture catheter Susceptibility testing (disk diffusion) • Muller Hinton agar • Bacterial inoculums concentration( %5 Mc Farland) • Antibiotic disks • Pens • swap Disk diffusion Quality control of susceptibility testing (Kirby-Bauer ) Antibiotic Disk potency (by control organisms) Mueller –Hinton Agar depth (4 mm) pH (6.8-7.2) Instrument failure Inoculums concentration (0.5 Mac farland) Temperature (35-37 C) Moisture MIC determination Microdilution Agar dilution E test Gradiant