* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Are eukaryotes that depend on another host for their nutrients
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
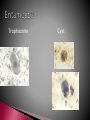
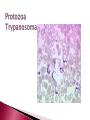
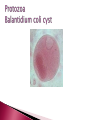
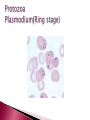
Are eukaryotes that depend on another host for their nutrients and metabolic activities. Divided to 1-Protozoa: Unicellular. 2-Helminths: Multicellular. 3-Arthropods: Multicellular. Common stages of life cycle 1- Trophozoite: active growing stage 2- Cyst: resting non active stage Can infect all major tissues and organs of the body Transmission of protozoan parasites by 1- injection via bites of blood sucking insects 2- ingestion of infective stages Protozoa move by : Psuedopod: (extending part of protoplasm towards direction of movement) Example: Entamoeba species Flagella : Example: Trypanosoma species, Giardia Lamblia Cilia: Example: Balantidium coli non motile: Example : Plasmodium species Trophozoite Cyst Multicellular organisms with organ systems as digestive, nervous , excretory system. Have complicated life cycle Mostly have different stages of life cycle which are: ova(egg), larvae (Adult) Adult worms can measure centimeters or even meters long Extracellular parasites Are classified according to shape into: 1- Nematodes (round worms) cylindrical thin Example: Ascaris lumbricoides 2- Cestodes ( tape worms)flat long worms Example: Tenia saginata,tenia solium 3- Trematodes( Flukes)leaf like flat worms Example: Schistosoma species Are insects such as bugs ,fleas, biting flies, mosquitoes etc. Harmful effects of parasites Discomfort, transmission of diseases( malaria, yellow fever, typhus), cause disease(amoebic dysentery, bilharzias), damage to crops. Heterotrophic eukaryotes Saprophytes: obtain nutrients from dead organic material Nucleated achlorophyllous organisms Reproduce sexually and asexually Surrounded by true cell wall 2 groups Yeast and mold Grow within a wide range pH(acidic-alkaline) Grow at room temperature (can grow at cold temp) Prefer moist or humid atmospheres Can be cultured in Sabouraud Dextrose agar media (SDA) or potato dextrose agar (PDA) that contains a source of protein (peptone) and a source of carbohydrate (dextrose) The commonest microscopic examination of fungi is LACTO-PHENOL- COTTON BLUE tease mount or reagent (LPCB) Benefits of fungi: important in baking , pharmaceutical(antibiotic),brewing industries. Also as saprophytes and as food. Harmful effects: cause a lot of diseases in skin, hair, nail and systemic diseases. Yeast Unicellular, round or oval( tear drop)shape Multiply asexually by budding resulting in production of 2 cells Molds Multicellular branching hyphea forming a mycelium. Fungi Molds using LPCB x40 Alternaria species Fungi Molds using LPCB x40 Penicillium Fungi Molds using LPCB x40 Aspergillus species Iron needles made from iron because fungi dig into agar thus it is difficult to culture them with wire loop Virus in Latin means poison All viruses are obligate intracellular parasites( can multiply only in living cells) Possess a single type of nucleic acid either DNA or RNA (Ss or Ds) Nucleic material is enclosed in a protein coat called capsid. ( both capsid and nucleic acid are called nucleocapsid) Vary in size from 20-300nm Cannot be seen by bright field microscope Can be examined by Electron microscope Can infect humans, animals, plants and bacteria Viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages Isolation of viruses : a- animal inoculation b- embrynoted egg inoculation c- cell culture Cytopathic effects are morphological changes in cell lines due to virus infection.