* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aminoglycosides(氨基糖苷类)
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Thermal shift assay wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Disinfectant wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
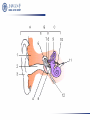
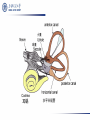
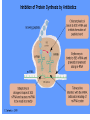
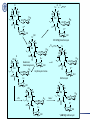
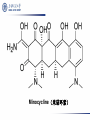
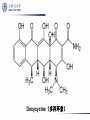
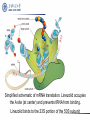
Aminoglycosides(氨基糖苷类), Macrolides(大环内酯类)and others 2011.12 Aminoglycosides(氨基糖苷类) Tuberculosis, still severe infection now 1882, Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch discovered M. tuberculosis (结核分枝杆菌) 1940’s, Merck supported S.A. Waksman’s lab, Rutgers university, NJ 1940, actinomycin(放线菌素), toxic 1942, streptothricin (链丝菌素),still toxic 1942, Albert Schatz, PhD student Aminoglycosides(氨基糖苷类) 1943.6 returned from army Oct 19, 1943, streptomycin isolated 1944, Mayo clinic 1946, graduated and patent left in Rutgers 1947, succeeded in TB treatment Law suit 1952, Nobel Prize to Waksman Streptomycin(链霉素) Individual aminoglycosides Streptomycin(链霉素) Gentamycin(庆大霉素) Amikacin(氨苄卡星) Tobramycin(妥布霉素) Netilmycin(奈替米星) aminoglycosides Common characters: Potent effect on Gram- bacteria, including Pseudomonas, Mycobacterium tuberculosis Ineffective against anaerobic bacteria Not absorbed orally Untoward effects: >5 days; high dose; elderly; renal insufficiency ototoxicity(2%-10%): vertigo(眩晕), ataxia(共 济失调), loss of banlance nephrotoxicity(6%-10%) neuromuscular blocking (co-administered with general analgesics or muscle relaxants) Toxicity Their undesirable side effects: severe ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. 18 of 21 actress showing “qianshou guanyin” were caused deafness by aminoglycosides. 小囊 球囊 耳蜗 水平半规管 血管纹 前庭阶 中阶;蜗管 鼓阶 aminoglycosides Mechanism: binding to the S12 Protein of the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, interfering with the binding of formyl-methionyl-tRNA to the 30S subunit Resistance to aminoglycosides aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes (钝化酶) Phosphoryltransferases(磷酰转移酶) Acetyltransferases(乙酰转移酶) Adenylyltransferases(腺苷酰转移酶) Polymyxins 多黏菌素 Polymyxins(多粘菌素类) Cyclic peptide with a long hydrophobic tail polymyxins detergents, selectively toxic for Grambacteria due to their specificity for the lipopolysaccharide(脂多糖) molecule strong nephrotoxic renewed interest duo to antimicrobial resistance Macrolides(大环内酯类) Macrolides(大环内酯类) 1949, Abelardo Aguilar soil samples to Eli Lilly Erythromycin from Streptomyces erythreus (红色链霉菌) 1952, clinical uses 1970’s, clarithromycin (克拉霉素),acid instability overcome azithromycin, … Erythromycin 红霉素 O N OH OH OH OH N O O HO O O O O OH OH O N O O O HO O OH O O N O OH O O OH O ÂÞºì ùËØ¡¡ Roxithromycin OH OH O OH O O O HO O O HN OH OH O O HO O OH O O N OH O HO O O O O Erythromycin Oxime O OH O Dirithromycin O O OH O O N O N O Beckmann Rearraangement OH O N N OH HN OH OH OH OH OH »¹ Ô- N O O OH O HO O O N O ¼×»ù»¯ O O HO O O O O O OH O OH °¢Æë ùËØ¡¡ Azithromycin macrolides Antibacterial spectrum: similar or wider anti-bacterial spectrum than penicillin (replacing penicillin for allergic patients) some G- bacteria: Legionella pneumophila (嗜肺军团菌),now >50 lines, >70 serum types Mycoplasma pneumoniae (肺炎支原体) Legionella pneumophila (嗜肺军团菌) Mechanism of macrolides binding to the 50s subunit of the bacterial 70s rRNA complex →interfering with aminoacyl translocation →preventing the transfer of the tRNA bound at the A site of the rRNA complex to the P site of the rRNA complex Resistance to macrolides Reduced permeability of the cell membrane or active efflux Production of esterases that hydrolyze macrolides Modification of the ribosomal binding site by chromosomal mutation or by a macrolideinducible or a constitutive methylase Clinical uses of macrolides First choice: Legionaire’s disease(军团病) diphtheria(白喉),eradicated through widespread vaccination 1976.7,费城一旅馆退伍军人会议 近200人罹患前所未见呼吸道感染,29人死 全身不适、头痛、恶心呕吐、腹泻、肌肉疼痛、 发烧、咳嗽。干咳,渐咳灰色或血色浓痰,死于 肺炎及其他并发症 数月调查,耗200万美元 鉴定:嗜肺军团菌(源于首次在退伍军人发现) 空调系统的水箱、管道是该菌的理想繁殖地 Clinical uses mycoplasmal pneumonia(支原体肺炎),小 儿多见 chlamydial Infection(沙眼衣原体、鹦鹉热衣 原体感染):沙眼、性病性淋巴肉芽肿 Azithromycin(阿奇霉素):mostly replacing erythromycin Lincomycin(林可霉素) Lincomycin(林可霉素) clindamycin lincomycin (林可霉素) Actinomyces Streptomyces lincolnensis Mechanism, spectrum, uses and untoward effect of clindamycin Mechanism, spectrum and structure similar to erythromycin Also effective against other species as well i.e. actinomycetes(放 线菌), mycoplasma(支原体), and some species of Plasmodium (疟原虫) reserved for patients who are either allergic to penicillin or where bacteria has developed resistance Anaerobic infections Sensitive gram-positive bacteria infections (first choice for S. aureus induced osteomyelitis(骨髓炎) malaria acne(痤疮) methicillin-resistant Staphylocuccus aureus (MRSA) infections(耐 甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌感染) untoward effect: Clostridium difficile (艰难梭菌 )-associated diarrhea (main cause of pseudomembraneous colitis, 假膜性肠炎) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Tetracyclines 四环素类 1945, Benjamin Duggar, Aureomycin (金霉素) 1950, Lloyd Conover (Pfizer), tetracycline Tetracycline(四环素) tetracyclines Sources: Actinobacteria, Streptomyces genus (链霉菌) natural: oxytetracycline(土霉素), seldom used tetracycline(四环素), seldom used semi-synthetic: doxycycline(多西环素) minocycline(米诺环素) metacycline(美他环素) Minocycline(米诺环素) Doxycyclne(多西环素) Pharmacokinetics of tetracyclines deposited and staining developing teeth (even when taken by the mother during pregnancy) causing permanent teeth discoloration (under children of 8) Antibacterial spectrum Antibacterial spectrum wide, but most of microorganisms resistant to tetracyclines now Mechanism Bacterial – 70S (50S/30S) Mammalian – 80S (60S/40S) • High levels may interact with mammalian ribosomes Binding to 30s subunit • Aminoglycosides • tetracyclines Binding to 50s subunit • chloramphenicol • Macrolides, erythromycin, clarithromycin, azithromycin, … 30s subunit mRNA 50s subunit protein Clinical uses first-line(一线): Rocky Mountain spotted fever (Rickettsia)落基山斑 疹热 (Coxiella burnetii,科克斯属立克次体 ) Q fever (Chlamydia) Psittacosis(鹦鹉热) Lymphogranuloma venereum(性病淋巴肉芽肿) eradicating nasal carriage(鼻腔带菌) of meningococci(脑膜炎球菌) acne(痤疮);rosacea(酒糟鼻) Since wide resistance to tetracyclines, not used often Coxiella burnetii 四环素牙 Chloramphenicol(氯霉素) Streptomyces Venezuelae, isolated by David Gottlieb 1949, introduced into clinical practice First synthetic antibiotic Chloramphenicol(氯霉素) chloramphenicol wide spectrum Gram-positive bacteria (including most strains of MRSA) Gram-negative bacteria anaerobes potent inhibitor of the cytochrome P450 isoforms CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 Mechanism and resistance binding to 50S ribosomal subunit preventing the docking of amino-acylated tRNA Bacterial resistance: reduced membrane permeability mutation of the 50S ribosomal subunit chloramphenicol acetyltransferase protein synthesis inhibitors Bacterial – 70S (50S/30S) Mammalian – 80S (60S/40S) • High levels may interact with mammalian ribosomes Binding to 30s subunit • Aminoglycosides • tetracyclines Binding to 50s subunit • chloramphenicol • Macrolides, erythromycin, clarithromycin, azithromycin, … 30s subunit mRNA 50s subunit protein Therapeutic uses Originally, typhoid(伤寒) Now, Staphylococcal and other bacterial brain abscesses(脓肿) and meningitis(脑膜炎) Vancomycin-resistant enterococcus infections Adverse drug effects Aplastic anemia(再生障碍性贫血): 1/30000-1/50000 Idiosyncratic 特发性; unrelated to dose Gray baby syndrome: lack of glucoronyl transferase (葡糖醛酸转移酶) Linezolid 利奈唑胺 Linezolid(利奈唑胺) discovered in the 1990s approved for use in 2000 first oxazolidinone(噁唑烷酮 ) antibiotic linezolid effective against all clinically important Gram-positive bacteria (including vancomycin-resistant enterococci and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, etc. 2005, 中国细菌耐药监测网:金葡菌感染患者 MRSA分离率占69.2%。 Simplified schematic of mRNA translation. Linezolid occupies the A site (at center) and prevents tRNA from binding. Linezolid binds to the 23S portion of the 50S subunit