* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cytoplasmic Incompatibility
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
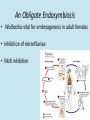
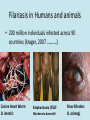
Wolbachia Google images TEM; Google images Concepts • Endosymbioses • Host manipulation • Co-evolution Google images History • One of the most infectious bacterial genera on earth • Endosymbionts • First discovered in 1924 in insects; largely unknown until the 1990s (Evade detection) • Now known to be in nematodes • Applications for bio-control and treatment of nematode diseases Diversity Google images Google images Infects over 1 million species of insects and other invertebrates! Google images Google images Google images Stevens et al, 2001 Wolbachia in insects • Maternally inherited (Usually) • Cytoplasmic incompatibility • Induced parthogenesis, functional feminization, and male killing • Protection from parasitoid wasp in pea aphids • Evolutionary implications Cytoplasmic Incompatibility (CI) Cytoplasmic incompatibility Tortora et al, 2010 Biocontrol (economic implications) • Cytoplasmic incompatibility has enormous implications for bio-control • Exp 1) The Med fly- experimentally inoculated males induced complete (CI) in target populations • Populations were “suppressed” by a single release of infected males Zabalou et al, 2004 Evolutionary Implications Experiment 2- Antibiotic treatment in wasps Hybridization! • Does Walbachia help maintain the uniqueness of it’s hosts species by impeding “hybrid” development? • How has Wolbachia influenced the evolution of insects? Google images A twist: Wolbachia is found in filarial nematodes where it is discovered to be an vital symbiont Google images Co-evolution • Strong evidence for co-evolution between endosymbiont Wolbachia and nematodes • Phylogenetic congruency • Long history of vertical transmission An Obligate Endosymbiosis • Wolbachia vital for embryogenesis in adult females • Inhibition of microfilariae • Molt inhibition Filariasis in Humans and animals • 200 million individuals infected across 90 countries (krager, 2007 ) as cited by Hoerauf Canine Heart Worm D. immitis Elephantiasis /ESLF Wuchereria bancrofti River Blindess O. ochengi Traditional Treatment (Filariasis) Traditional treatment for lymphatic Filariasis - Ivermectin Now- Effectively use chemotherapy to disrupt parasite/symbiont interactions in filarial nematodes Medical Application? Experiment 3 • A doxycyline regime can be used to treat (Ghanaian) individuals for lymphatic filariasis by targeting the host symbiont • Results: a 99% reduction in microfilaria • Implications- doxycyline as a universal treatment for filariasis in humans Ivermectin vs Doxycycline VS Google images Google images $111.17 USD/ 3 mg (Merck) $225.99 USD/100mg Neurotoxic effects Pregnancy risk factor D Annual Treatment -Kills the microfilariae not the worm 6 weeks course, makes adult worms sterile Conclusions • Wolbachia is a fundamental bacteria genus • Further study of this endosymbiont will enhance our understanding of evolutionary entomology, Nematode symbiont coeveolution, and other biological systems • Targeting Wolbachia for biocontrol and disease eradication will have huge economic and medical benifits References Hoerauf, A., Mand, S., Fischer, K., Kruppa, T., Marfo-Debrekyei, Y., Debrah, A., & ... Bättner, D. W. (2003). Doxycycline as a novel strategy against bancroftian filariasis—depletion of Wolbachia endosymbionts from Wuchereria bancrofti and stop of microfilaria production. Medical Microbiology & Immunology... Study 3 Hoerauf, A., Rao, R. U. (2007). Wolbachia: A Bug’s Life in another Bug Sofia Zabalou, Markus Riegler, Marianna Theodorakopoulou, Christian Stauffer, Charalambos Savakis, Kostas Bourtzis, John H. Law (2004). Wolbachia-Induced Cytoplasmic Incompatibility as a Means for Insect Pest Population Control. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America Vol. 101, No. 42 (Oct. 19, 2004), pp. 15042-15045....Study 1 Stevens, L., Giordano, R., & Fialho, R. F. (2001). MALE-KILLING, NEMATODE INFECTIONS, BACTERIOPHAGE INFECTION, AND VIRULENCE OF CYTOPLASMIC BACTERIA IN THE GENUS WOLBACHIA. Annual Review of Ecology & Systematics, 32: 519 Tortora, G., Funke, B., Case, C. (2010).Microbiology: An Introduction 10th Ed. 305307...Study 2 Questions