* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Canine distemper wikipedia , lookup
Canine parvovirus wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Infectious mononucleosis wikipedia , lookup
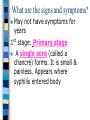
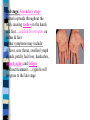
Sexually Transmitted Diseases Visit the website Life-zone.org ****come up with 5 specific facts/info you learned from the website – Homework: How can you be infected with a STD? There are 2 types of STD infections: bacterial & viral What is Chlamydia? A common STD caused by the bacteria, Chlamydia trachomatis Can damage reproductive organs & cause PID &/or infertility There are 3 million new infections in US each year Known as the silent disease 95% women & 50% men- Show no symptoms How is Chlamydia be transmitted? Vaginal sex Oral sex……(get in throat) Anal sex ---------------------------------------------- Semen Vaginal fluid What are the signs and symptoms? Symptoms show up 7-28 days after having sex w/ infected partner In men: white drip or discharge from penis, burning/pain during urination, groin pain, need to urinate more, itching around opening of penis In women: Initially infects the cervix & urethra (urine canal): a milky discharge, odor, painful urination **When infection spreads to fallopian tubes: lower abdominal pain, spotting between period, pain during sex, fever, nausea Chlamydia can be found in throats, use a__________ How is it diagnosed? A cervical sample from a female is obtained and examined A urine sample Chlamydia & Gonorrhea have similar symptoms How can it be treated? with antibiotics Abstain from sex until their partners and themselves have been treated Since most people who have chlamydia also have gonorrhea, it is recommended that people get treated for both diseases How can it be avoided? Abstinence Proper use of latex condoms with spermicides (avoid non-oxynol 9) CDC recommends yearly testing Form a monogamous faithful relationship - be tested before intimacy How can it be avoided? What is Gonorrhea? (“The CLAP”) Common infection of the urethra and cervix Caused by the bacteria, Nisseria gonorrhoeae CDC reports over 700,000 new infections in the US each year 80% of women and 10% of infected men show no symptoms What are the signs and symptoms? Symptoms usually show up 2-21 days after having sex & sometimes not @ all MEN: thick yellow, white or greenish drip from penis, pain & burning & frequent urination , tender or swollen testicles WOMEN: painful or burning urination, increased vaginal discharge, painful intercourse, bleeding between periods ……..Symptoms are usually mild and mistaken for bladder or vaginal infection Untreated gonorrhea can lead to: In women: gonorrhea is a common cause of (PID) Pelvic Inflammatory Disease About 1 million women in U.S. develop PID symptoms include: Abdominal pain & fever, damage to fallopian tubes that cause infertility or risk of ectopic pregnancy In men: can lead to sterility, damage to reproductive organs How is it transmitted/passed? Vaginal, oral or anal sex Contact with the penis, vagina, mouth or anus Mother to baby Men spread the infection more easily to women than women to men-WHY???? How can an infected mother transmit it to her baby? Babies can get Gonorrhea eye infection as they pass through the birth canal Develops into pus and potential blindness if not treated. ALL newborns receive an antibiotic ointment on their eyes immediately after birth How is it diagnosed? Testing for gonorrhea can be done with a simple urine test or Testing tissue samples from the infected area How can it be avoided? Abstinence Mutually Long Term Monogamous relationship Correct Latex condom use It is crucial that those infected alert their sexual partners to allow them to be adequately treated How can it be treated? Gonorrhea used to be 100% curable with Penicillin but has developed a resistance to this antibiotic Usually a shot of Rocephin or an extralarge dose of Zithromax will kill the bacteria and cure the disease HUMAN Papillomavirus(HPV) *The most common STI Over 40+ types of HPV 20 million people in U.S. have HPV..6.2 million new cases each yr. At least 50% of men & women will acquire an HPV infection in their lifetime HPV conti…… Most infected persons don’t realize they are infected 90% of cases, the body’s immune system clears the HPV infection naturally within 2 yrs. HPV can cause warts or cancers 2 types of HPV-(“low & high risk”) 1. “Low risk” or wart causing Genital warts are flesh-colored gray or pinkish white bumps in genital area. Warts appear after wks. or months after sexual contact.. if untreated they may go away,remain or increase in size & # How can it be treated? Visible warts can be treated at home with a prescription topical cream Laser surgery, liquid nitrogen freezing, acid treatment which remove visible symptoms but don’t get rid of the virus Warts may reoccur 2. “High risk” or cancer-causing *Most common type is cervical cancer in women-does not have signs & symptoms until it is advanced *Other cancers…vaginal, penis,& rectal cancers *Vaccination and regular pap tests are important for women *Only STD with a vaccine (for females only) Gardasil-HPV Vaccine Get vaccine before becoming sexually active Shot given 3x’s over 6 months Recommended for 11 & 12 year old girls & up to 26 yrs. old About 30% of cervical cancers will not be prevented by the vaccine- get pap tests Protects against 4 of the most common type of viruses (2 strains=70% cervical cancers) (2 strains=90% warts) How can it be avoided? Abstinence Correct condom use No skin to skin contact w/ infected area Vaccination Committed monogamous relationship What is Genital Herpes? Herpes is a viral infection of the skin Caused by the Herpes Simplex Virus 2 Types: Type 1 Infections of the mouth and lip (“fever blisters”) Not a STI but can be through mouth to genital contact Type 2 causes genital herpes…STI How can you get Herpes? Passed through kissing, intimate touching and unprotected sex …(skin to skin contact and/or infected fluids) Treatable but not curable. Virus stays in your body forever. Symptoms can come and go. 4-5 outbreaks occur within the first year……will decrease over years Stress, menstruation, fatigue, illness, or surgery trigger outbreaks What are the signs and symptoms? The first outbreak of symptoms (if any) usually occur within 2 wks. of infection. Symptoms for men & women: burning or itchy sensation 1 - 2 days before the skin rash develops, water blisters (vesicles) or open sores (ulcer), painful urination when sores are present, flu-like symptoms, fever,& swollen glands How is it transmitted? It is spread by skin-to-skin contact (even kissing) Sexual intercourse is usually the way that genital Herpes is spread How is it diagnosed? Dr. exam A culture of sores How is it treated? There is no cure for Herpes Valtrex, Zovirax, and Famvir lessen the pain and symptoms Topical creams How can it be avoided? Abstinence Correct condom use: covering all the infected skin areas Avoiding sexual activity when sores are present Limit your sex partners What is Syphilis? Caused by the bacteria Treponma Pallidum It has 3 stages…(primary, secondary,& late) Prevalent in large cities Over 36,000 cases reported 65% of reported cases in 2006 were among gay men What are the signs and symptoms? May not have symptoms for years 1st stage: Primary stage A single sore (called a chancre) forms. It is small & painless. Appears where syphilis entered body The chancre last 3-6 weeks after the chancre heals, the second stage begins………… 2nd stage: Secondary stage bacteria spreads throughout the body causing rashes on the hands and feet….reddish brown spots on palms & feet Other symptoms may include: A fever, sore throat, swollen lymph glands, patchy hair loss, headaches, muscle aches and fatigue Without treatment…..syphilis will progress to the late stage Syphilis conti…. 3rd Stage-Late stage: *occurs about 10-20 years after initial infection *It affects the brain and spinal cord, often causing mental illness, paralysis, numbness & death How is it passed/transmitted? Passed from person to person through direct contact with a syphilis sore.. usually during sex Mom to baby How can it be treated? A intramuscular injection of Penicillin/antibiotic Dosage varies according to the stage of disease Can an infected mother give this disease to her baby? YES Give it to the baby while in the womb Congenital syphilis can cause the baby to die before it is born (stillbirth) In the babies who survive, symptoms can affect the eyes, teeth, bones, liver, glands, lungs, and brain. How is it diagnosed? Taking a sample from the chancre and finding the cork-screwed shaped bacteria Blood tests Spinal fluid can be examined for the presence of syphilis during late stages of the disease 6 fluids that can transmit any STI to… any 6 openings: 6 OPENINGS *ears *nose *mouth *penis/vagina *anus *cuts/rash/open skin 6 FLUIDS *semen *vaginal *blood *amniotic fluid *breast milk *amniotic