* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STIpresentation
Rochdale child sex abuse ring wikipedia , lookup
History of human sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Sexual ethics wikipedia , lookup
Female promiscuity wikipedia , lookup
Human female sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Sexual dysfunction wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Human sexual response cycle wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Slut-shaming wikipedia , lookup
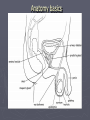
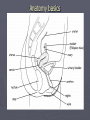
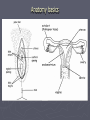
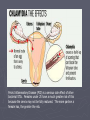
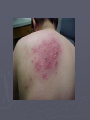
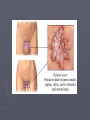
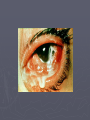
STI: Sexually Transmitted Infections Anatomy basics Anatomy basics Anatomy basics Chlamydia ► Caused by a bacteria ► Spread sexually by an infected partner, A/O/V ► An untreated mother can transmit chlamydia to her unborn baby ► Most females have no symptoms – 70%, 50% of males have no symptoms ► Two of the possible symptoms: can cause burning during urination discharge from the vagina or penis ► can be cured by antibiotics ► tested for through a family physician or public health clinic ► Can lead to infertility caused by Pelvic Inflammatory Disease in females and infertility in males (damages the epididymis and urethra) Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) is a serious side effect of other bacterial STIs. Females under 25 have a much greater risk of this because the cervix may not be fully matured. The more partner a female has, the greater the risk. Herpes caused by two types of virus – HSV1, HSV2 ► Transmitted through A/O/V sexual contact. ► HSV1 – contact with saliva is the most common mode to spread the virus ► HSV2 – usually by sexual contact with a person with the blisters or sores ► Can be passed as well by someone with no symptoms ► A mother can pass the virus to her baby during childbirth ► Symptoms can include recurring, painful blisters on mouth or genitals ► NO cure for herpes ► Medication can help the blisters to heal faster but cannot cure them ► HIV/AIDS ► Spread by a virus that is blood borne ► Spread through sexual contact (anal sex particularly risky) with an infected person (A/O/V) ► Spread by sharing needles – for drugs, tattooing or piercing ► A mother can transmit the virus to her baby during pregnancy, childbirth, and breastfeeding ► some symptoms: acute flu-like illness, high fever (2 weeks) , chronic diarrhea (3 weeks), extreme tiredness ► there is no cure for HIV/AIDS - good treatments exist for those who can afford it Genital Warts ► caused by a virus (HPV) - papillomavirus ► spread by sexual contact ► the warts can appear 1-20 months after sexual contact with an infected person ► warts are sometimes soft and pink, others are hard, yellow-grey ► there is no cure for genital warts, but the warts can be treated ► There is a vaccine against HPV ► HPV is the leading cause of cervical cancer Hepatitis B ► caused ► virus is by a virus found in blood, semen, vaginal fluids and saliva ► spread by sexual contact with an infected partner, or infected blood in used needles (drugs, tattoo, piercing), sharing toothbrushes or razors ► mothers can pass hepatitis B on to their babies ► symptoms can include tiredness, not hungry, yellow skin ► most people get better and can no longer pass on the virus, others do pass on the virus ► Hep B has a safe and effective vaccine Gonorrhea Caused by a bacteria ► Spread by sexual contact (A/O/V) with an infected partner ► A mother can pass gonorrhea to her baby during childbirth ► More than 50% of men and women have no symptoms, often do not know they have the STI ► Symptoms include pain during urination, discharge from the vagina or penis ► Can be cured by antibiotics ► Can lead to infertility caused by Pelvic Inflammatory Disease in females and infertility in males (damages the epididymis and urethra) ► Syphilis ► Caused by bacteria ► Transmitted by sexual contact with an infected person (A/O/V) and to an unborn child from their mother (leads to stillbirth or death shortly after birth) ► Can be treated with antibiotics ► Stages – 1 – a sore on the genitals or mouth, 2 – a skin rash and sore throat followed by a “hidden” phase (may last for years), 3- serious damage (e.g. blindness) Trichomoniasis ► Caused by a protozoan parasite ► Transmitted by sexual contact with an infected person where fluids are exchanged (can be passed on by fingers) ► Can be treated with antibiotics ► Leads to vaginitis (inflammation of the vagina and vulva) and urethritis (inflammation of the urethra) – symptoms include (female) discharge, pain, itching and (male) discharge, pain with urination ► If women are pregnant with trich, it may result in miscarriage, pre-term birth. In Summary: • Be conscious of the symptoms of STIs • Pain when urinating • Unusual discharge from genitals • Genital pain, abdominal pain • Sores or blisters • Remember: some very harmful infections have NO NOTICEABLE SYMPTOMS! •The ONLY 100% way to prevent STI infection is abstinence Some local statistics ► In Waterloo Region, the teen pregnancy rate is 30.8 per 1000 females 15-19 - highest of all urban areas in Ontario. ► includes live births, miscarriages and abortions. ► rate is higher than Toronto (27.4) and Ontario average (25.7). ► In WR, the number of teens who say they have had sexual intercourse is lower than the Ontario average (36.9% of boys, 35.1% of girls) – ages 15-19. ► Chlamydia – 263 confirmed cases a year (80% female) – 1,212 out of 100,000 – ages 15-19 , rate increasing yearly Some local statistics ► Interesting (scary!) note: in 2010 there were over 5000 cases of chlamydia reported in WR – almost 4 times the number of cases of the flu! ► Gonorrhea rates are lower ► HIV rates in WR are currently at 7 per 100,000 (no age descriptor given) ► Rates of HIV are declining in Ontario ► Younger women remain a higher risk category