* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3: Observing Microorganisms Through a Microscope
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
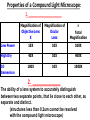
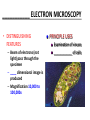
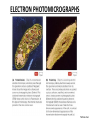
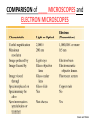
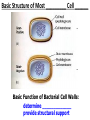
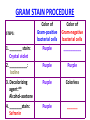
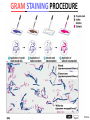
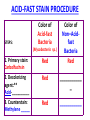
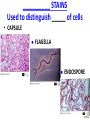
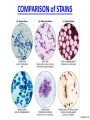
CHAPTER 3 OBSERVING MICROORGANISMS THROUGH A MICROSCOPE Dr. Reitano SUFFOLK COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Microorganisms were first observed by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, using a simple microscope. A simple microscope has only ____ _____. Cowan “Microbiology” _________ ____ as a TOOL in IDENTIFICATION Cowan “Microbiology” THE __________ SYSTEM International System of Units Equals Note: millimeters are smaller than centimeters, but there are a larger number of millimeters in a given length. http://cassfos02.ucsd.edu/physics/ph7/Units.html http://www.personal.psu.edu/hw7/Biology110/metricsystem.htm SOME TYPES of MICROSCOPES • LIGHT -uses visible light to observe specimen – Bright field • COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPE – Fluorescence • ELECTRON-uses electrons instead of visible light – Transmission – Scanning BRIGHT FIELD MICROSCOPY • DISTINGUISHING FEATURES – ______ light passes through a series of lenses which • PRINCIPLE USES ________ the specimen and – Common, multiallows fine detail to be purpose microscope observed (____________) – Used to observe live specimens and – Specimen appears darker preserved, stained – Field appears lighter (non-living) specimens – Provides fair cellular detail ____________ LIGHT MICROSCOPE Compound Light Microscopy • In a compound microscope, the image from the _____________ is magnified again by the ocular lens • Total magnification = objective lens ocular lens PATHWAY of LIGHT Figure 3.1b Properties of a Compound Light Microscope: 1. __________________ Magnification of Objective Lens X Magnification of Ocular Lens = Total Magnification Low Power 10X 10X 100X High Dry 40X 10X 400X 100X 10X 1000X Oil Immersion 2. ______________ The ability of a lens system to accurately distinguish between two separate points, that lie close to each other, as separate and distinct. (structures less than 0.2um cannot be resolved with the compound light microscope) __________ in the Compound Microscope _________ index - a measure of the light-bending ability of a medium, such as air •Air may bend the light so much that it misses the small size of the opening of the 100x objective lens •Immersion oil is used to keep light from bending Figure 3.3 ______________ MICROSCOPY • DISTINGUISHING FEATURES – Specimens are stained with fluorescent dyes – Ultraviolet light is used which causes fluorescent molecules in a specimen to emit light PRINCIPLE USES Rapid detection and identification of organisms in tissues Excellent _________ tool _____________ MICROSCOPE TYPES: _________________ TRANSMISSION __________ ELECTRON MICROSCOPY • DISTINGUISHING FEATURES • Beam of electrons (not ______) are reflected from the specimen • _______ dimensional image produced • Magnification 1,000 to 10,000x • Principle Uses • Observing _______ details of cells and _________ ___________ ELECTRON MICROSCOPY • DISTINGUISHING FEATURES – Beam of electrons (not light) pass through the specimen – ____ dimensional image is produced – Magnification 10,000 to 100,000x PRINCIPLE USES Examination of viruses ____________ of cells ELECTRON PHOTOMICROGRAPHS Tortora et al. COMPARISON of ____ MICROSCOPES and ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Cowan and Talaro MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATION • TWO TYPES of SPECIMENS: – 1. ______________ • Wet Preps, Wet __________. • Living organisms suspended in fluid-organisms have little contrast with surrounding fluid. • Used to study: size, shape, arrangement of cells, (morphology) behavior , and _______________. – 2. STAINED • Fixed Smear Preparations. • _____________organisms. • Contrast is created to allow cellular characteristics to stand out. • Used to study size, shape, arrangement of cells (morphology) but not _______________. PREPARATION of ________ SMEAR Smear: A thin film of a solution of ________ on a slide. A smear is usually fixed to ______ the microbes to the slide and to kill the microbes. Staining: ________ the microbe with a dye that emphasizes certain structures. _________ STAINING Nester et al. VARIOUS STAINING CATEGORIES _______ STAINS • _________ charge (negative stain) • Repelled by cells • _________ is stained • Ex.: India ink capsule stain BASIC STAINS • __________ charge (positive stain) • ________ to cells (which have a negative charge) • Cells are stained • Ex.: Methylene ______, Crystal Violet, Safranin, Malachite Green VARIOUS STAINING CATEGORIES _________ ____ dye Simple procedure Ex.: • Methylene Blue • Crystal Violet • Safranin • Malachite Green ______________ ____ dyes Primary Counterstain Contrast 2 cell types or parts Complex procedure Ex.: _____ Stain Acid-fast Stain SPECIAL Targets specific cell parts Such as: _________ flagella spores Ex.: India Ink Flagella Stain Spore Stain DIFFERENTIAL STAIN _______ STAIN • Developed by Dr. Hans Christian Gram in 1884 • Most widely used procedure for staining bacteria • Classify bacteria into two groups – Based on differences in CELL _____ STRUCTURE Gram ________ Gram negative Basic Structure of Most _________ Cell ______ Basic Function of Bacterial Cell Walls: determine _____________ provide structural support COMPARISON of GRAM POSITIVE and GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIA GRAM _________ BACTERIA Ex.: Staphylococcus ________ Streptococcus pyogenes GRAM ___________ BACTERIA Ex.: Escherichia ______ Klebsiella pneumoniae Nester GRAM STAIN PROCEDURE STEPS: 1. _______ stain: Crystal violet 2. __________: Iodine 3. Decolorizing agent:** Alcohol-acetone 4. _______stain: Safranin Color of Gram-positive bacterial cells Purple Color of Gram-negative bacterial cells __________ Purple Purple Purple Colorless Purple ______ GRAM STAINING PROCEDURE Tortora DIFFERENTIAL STAIN ______________ Stain • Used for bacteria with waxy, lipid (mycolic acid) material in cell wall • Several procedures* 1. ________ stain: Carbolfuchsin 2. Decolorizer: ______ Alcohol 3. Counter stain: Methylene blue • Ex.: – Mycobacterium species – Nocardia species Mycobacterium species Nester ACID-FAST STAIN PROCEDURE STEPS: Color of Acid-fast Bacteria (Mycobacteria sp.) Color of Non–Acidfast Bacteria Red 1. Primary stain: Carbolfuchsin Red 2. Decolorizing agent:** Acid-__________ Red ___________ _ 3. Counterstain: Methylene _____ Red ___________ ACID FAST STAIN Acid-fast staining of a patient’s sputum is a rapid, reliable, and inexpensive method to diagnose ___________. What is the genus and species of this organism? This is an acid-fast stain of a patient’s __________. What is the disease associated with this organism? __________ STAINS Used to distinguish _____ of cells • CAPSULE FLAGELLA ENDOSPORE Tortora COMPARISON of STAINS Cowan et al. Identify the Types of Stains Used 2 1 3 4 SOME STAINS USED in MICROSCOPY SIMPLE DIFFERENTIAL - Methylene Blue - Gram - Carbolfuchsin - __________ - Crystal Violet - __________ SPECIAL - Capsule (Negative, Acidic) - __________ - Flagella