* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
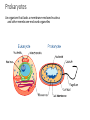
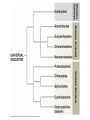
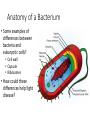
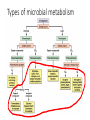
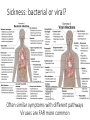
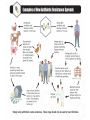
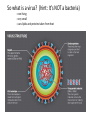
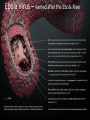
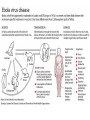
Microbes (Prokaryotes!) Laboratory 8 Biology 101 Three domains of life: two are prokaryotic Prokaryotes An organism that lacks a membrane-enclosed nucleus and other membrane-enclosed organelles Prokaryotes An organism that lacks a membrane-enclosed nucleus and other membrane-enclosed organelles Bacteria • Unicellular microorganisms • a few micrometers in length • Numbers… • 40 million bacterial cells in a gram of soil • 1 million in a milliliter of freshwater • Approximately 10x as many bacterial cells as human cells in the human body – most on skin & digestive tract • Approximately 5 nontrillion (5 x 1030) on earth! 5,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 Where are bacteria found? • EVERYWHERE! • In the soil and water • On and in our bodies • In the air we breathe • Critical to nutrient cycling as decomposers • Some cause disease • Vast majority are harmless, but half of all human diseases are caused by bacteria Anatomy of a Bacterium • Some examples of differences between bacteria and eukaryotic cells? • Cell wall • Capsule • Ribosomes • How could these differences help fight disease? Types of microbial metabolism Sickness: bacterial or viral? Often similar symptoms with different pathways Viruses are FAR more common Antibiotic Resistance – take all of your antibiotics, or else…. So what is a virus? (hint: It’s NOT a bacteria) - non-living - very small - uses lipids and proteins taken from host Ebola Virus – named after the Ebola River Today in lab: Bacterial Shapes Colony Shape Colony Color