* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Major Lineages of Life
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
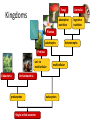
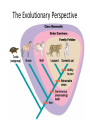
The Major Lineages of Life Molecular data challenges 5 Kingdoms Monera was too diverse 2 distinct lineages of prokaryotes Protists are still too diverse not yet sorted out Chapter 26 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life • Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a species or group of related species • The discipline of systematics classifies organisms and determines their evolutionary relationships • Systematists use fossil, molecular, and genetic data to infer evolutionary relationships • Taxonomy is the ordered division and naming of organisms 3 Domain system • Domains = “Super” Kingdoms – Bacteria – Archaea • extremophiles = live in extreme environments – methanogens – halogens – thermophiles – Eukarya • eukaryotes – – – – protists fungi plants animals Classification Eukaryote • Old 5 Kingdom system Prokaryote • Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals • New 3 Domain system – reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence • Prokaryote: Bacteria • Prokaryote: Archaebacteria • Eukaryotes – Protists – Plants – Fungi – Animals Archaebacteria & Bacteria Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaebacteria Kingdom Protista Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Plantae Kingdom Animalia Fungi Kingdoms absorptive nutrition Animalia ingestive nutrition Plantae autotrophs Protista uni- to multicellular Eubacteria multicellular Archaebacteria prokaryotes Single-celled ancestor eukaryotes heterotrophs Finding commonality in variety • Organisms classified from most general group, domain, down to most specific, species – domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species use the mnemonic! The Evolutionary Perspective Phylogenies are inferred from morphological and molecular data • To infer phylogenies, systematists gather information about morphologies, genes, and biochemistry of living organisms • Organisms with similar morphologies or DNA sequences are likely to be more closely related than organisms with different structures or sequences Cladistics • Cladistics groups organisms by common descent • A clade is a group of species that includes an ancestral species and all its descendants • Clades can be nested in larger clades, but not all groupings of organisms qualify as clades