* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tertiary Treatment: Nutrient Removal, Filtration,and
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
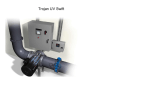
Tertiary Treatment: Nutrient Removal, Solids Removal, and Disinfection Treated Wastewater Effluent Contains… BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) • Carbon matter, depletes O2, causes biomat growth TSS (total suspended solids) • Depletes O2 NH3 (ammonia) • Toxic to fish, depletes O2, a nutrient that promotes biol. growth NO3 (nitrate) • Toxic to babies, drinking water regulated, a nutrient TP (total phosphorus) • A nutrient Pathogens (bacteria/viruses) • Disease causing First, We Must Understand Wastewater Assimilation A site’s ability to handle the amount of liquid or the amount of pollutants without causing a public health or environmental health concern In-ground or In-stream discharge Sometimes, high-quality effluent is necessary Protection of sensitive waterbodies, nearby… • Low BOD • Low fecal coliform • Low nutrients (Nitrogen and Phosphorus) • Or drinking water supplies (groundwater & wells) “Discharge” Permits In-ground dispersal • ADEM for flows of 10,000 gpd + • UIC Permit (underground injection control) • Specifies a certain effluent quantity and quality • BOD, TSS and groundwater monitoring for NO3 ADPH for smaller systems Surface dispersal • Stream Discharge NPDES Permit (specifies BOD, TSS, NH3, NO3, TP, etc.) Disinfection Required • Spray Irrigation NPDES Permit 7-10 day holding pond required Disinfection Required Why is tertiary treatment needed? To better protect public health and environment To provide additional treatment when soils or receiving waters cannot Biological Nitrogen Removal Uptake into biological cell mass Nitrification (conversion to Nitrate) Denitrification (conversion to N2 gas) Biological Nitrification Conversion of Ammonia to Nitrite (Nitrosomonas) NH4+ + 2 O2 NO2- + 2 H+ + H2O Conversion of Nitrite to Nitrate (Nitrobacter) NO2- + 0.5 O2 NO3- Nitrification (cont.) For each mg of NH4+ converted… 3.96 mg of O2 are utilized (Need Oxygen) 0.31 mg of new cells are formed 7.01 mg of alkalinity are removed Nitrification (cont.) Nitrifying bacteria are sensitive and susceptible to a variety of conditions. The following factors affect nitrification: • • • • • Conc of NH4+ and NO2BOD/TKN ratio (BOD should be gone/removed) Dissolved oxygen conc (need oxygen) Temperature pH (7.5 to 8.6) Nitrification Processes Suspended Growth Separate Stage Nitrification Single State Nitrification Nitrification Processes Attached Growth Attached Growth Nitrification following Act. Sludge Biological Denitrification A modification of aerobic pathways (no oxygen) • Same bacteria that consume carbon material aerobically Denitrifying bacteria obtain energy from the conversion of NO3- to N2 gas, but require a carbon source NO3- + CH3OH + H2CO3 C5H7O2N + N2 + H2O + HCO3Organic matter Cell mass Denitrification Need low (no) oxygen (< 1 mg/L) Need carbon source (BOD in Wastewater) Neutral pH (pH 7) Conc of nitrate Denitrification (cont.) Separate denitrification reactor or Combined Carbon Oxidationnitrification-denitrification reactor • A series of alternating aerobic and anoxic stages • Reduces the amount of air needed • No need for supplemental carbon source Combined Nitrification/Denitrification (note alternating regions of aerobic and anoxic) Phosphorus Removal Chemical Precipitation • Calcium (lime) addition at high pH (>10) Reacts with alkalinity • Alum (Aluminum Sulfate) precipitation • Iron precipitation Disinfection Selective destruction of diseasecausing organisms 1. Chlorine 2. UV Light 3. Ozone (gas) Chlorine Disinfection Liquid chlorine 2. Sodium hypochlorite (tablets) 1. Note: not allowed to discharge chlorine (it must be removed after disinfection) * chlorine removed with either… a. sulfur dioxide b. sodium bisulfite Tablet Chlorinator (Calcium Hypochlorite) Chlorine Disinfection To be effective… • Chlorine concentration • Contact time • Proper mixing • Temperature • Number and type of organisms Chlorine Dose UV Disinfection UV Light • Specific wavelengths have biocidal properties (~254 nm) • Quartz, mercury-vapor lamps • Cleaning required • No residual UV Disinfection a specific wavelength of light UV Disinfection Ozone Disinfection O3 a gas, must be generated on-site Bubbled into a basin effluent (or pipeline) with treated Great disinfectant! No residual…ozone degrades to oxygen, O2 Costs More, Need equipment and electricity Ozone Disinfection Flow Diagram Ozone Generation