* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Play your cards right!
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
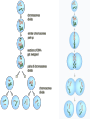
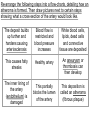
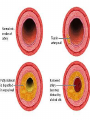
Infection Treatment Cholera bacterium is ingested and enters the small intestine. Oral rehydration solution (ORS) is given to the infected patient. Cholera bacterium secretes enterotoxin subunit B. ORS contains glucose and sodium, and also bicarbonate and potassium ions. Enterotoxin subunit B attaches to a receptor on the cell membrane of the small intestine microvilli. The presence of glucose and sodium in the small intestine causes the carrier protein to co-transport these into the small intestine cell. This causes the release of enterotoxin subunit A inside the small intestine cell This changes the water potential and water flows back into the small intestine cell by osmosis. This causes ion channels to open and sodium ions flow back from the bloodstream into the small intestine lumen. Water also flows back into the small intestine lumen by osmosis, causing rice water (diarrhoea). Water, glucose, sodium and the other ions now diffuse into the bloodstream. The patient is cured! However, the bacterium has been known to survive upto 50 days in faeces, so Colin the cholera and co. may now have infected someone else… Homework • Answer the past exam questions on coronary heart disease and cancer. (We will be learning about these two topics today) Due in: Friday 3rd October (Day 3, Period 5) • BHF animation Play your cards right! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ThMIAHxdawI&feature=related For each picture that appears, say whether it would HIGHER or LOWER your risk of developing CHD or cancer You have been warned! Cancer and CHD • Aims: • To know how lifestyle can affect your risk of developing some diseases - In particular, cancer and coronary heart disease (CHD) • To understand how specific risk factors can contribute to (not cause!!) cancer and CHD How much do you already know…? • What are the differences between meiosis and mitosis? • Which of these two types of cell division do you think is involved in cancer? • What is the name given to an agent that causes cancer? • Name the two types of tumour caused by cancer. • How many cancer treatments do you know of? http://www.cancerquest.org/images/Documentary/En glish/DocInterfaceEng.swf Cancer Treatment • Chemotherapy – stops the cancer cells from replicating themselves • Radiotherapy – damages DNA so that the cell destroys itself • Surgery – removal of the tumour and surrounding tissue. On a lighter note! • 80% of most cancers are curable if diagnosed early • Science has already made vast improvements already in treating cancer, and continue to do so • You are now aware of the risk factors which make you more susceptible to getting cancer (and CHD), so YOU have the choice to change your bad habitats now! CVD – cardiovascular disease • Most common form is Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) • In economically developed countries, the main cause of CHD is atherosclerosis. • http://uk.youtube.com/watch?v=fLonh7ZesKs • http://uk.youtube.com/watch?v=EQVEdFSlUG U • Complete the following activity on atherosclerosis… Re-arrange the following steps into a flow-charts, detailing how an atheroma is formed. Then draw pictures next to certain steps showing what a cross-section of the artery would look like. The deposit builds up further and hardens causing arteriosclerosis Blood flow is restricted and blood pressure increases White blood cells, lipids, dead cells and connective tissue are deposited This causes fatty streaks Healthy artery An aneurysm or thrombosis can then develop The inner lining of the artery (endothelium) is damaged This partially blocks the lumen of the artery This deposition is called an atheroma (fibrous plaque) Atherosclerosis Aneurysm Thrombosis (make your own notes here from my explanation) A burst blood vessel associated with an aneurysm, blood clot or head injury can cause a … Stroke Blockage or severe narrowing of one of the coronary arteries that supply the heart can lead to angina pectoris, or more severely, a ‘myocardial infarction’ Cholesterol • Diet high in saturated fats causes excess cholesterol in blood • Part of the fatty deposits in atheromas • Accelerates atherosclerosis High Blood Pressure • Hypertension • Excessive salt intake, saturated fats, lack of exercise, stress, smoking, high alcohol consumption • Increased risk of damage to the artery wall through increased pressure • Heart has to work harder to pump blood around the body – could cause a myocardial infarction Smoking and CHD CO Nicotine Carboxyhaemoglobin (reduced O2 capacity) Stimulates adrenaline Heart pumps faster Hypertension Angina during exercise Increased heart rate b.p., reduces arteries ability to dilate Increased risk of CHD & stroke RBC ‘sticky’ Increased risk of thrombosis Stroke/myocardial infarction True or False In the UK, one person has a heart attack every two minutes