* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1: Human Misery
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
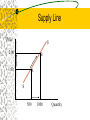
Chapter 2: Economic Systems & Resource Allocation Basic Economic Questions What to Produce (guns vs. butter) How to Produce (labor-intensive vs. capitalintensive technology) For Whom to Produce (rich vs. poor) Economic Systems Tradition & Custom Economy Command & Control Economy – Central Planning Market Economy – Pure vs. Mixed – Competitive vs. Non-competitive Market System Network of buyers & sellers who transact in the market Buyers “demand” goods & services Sellers “supply” goods & services Advantage of Market Economy Free interactions between buyers & sellers Full information to make decisions Free to choose between alternatives Demand Definition: quantities of a good or service consumers are able to buy at various prices Law of Demand: price and quantity are negatively related Movement along demand is caused by a price change Demand Schedule Demand for Pepsi Price Quantity Demanded $1.50 1,500 $2.00 1,000 $2.50 500 Demand Line Price D A 2.00 B 1.50 D 1000 1500 Quantity Shift in Demand Shift in demand is caused by a change in – – – – Consumer income & tastes Consumer expectations (price, income) Number of consumers Price of related goods (substitute, complementary) Increase in Demand Price D’ D A 2.00 C B D’ D 1500 2000 Quantity Supply Definition: quantities of a good or service producers are able to sell at various prices Law of Supply: price and quantity supplied are positively related Movement along supply is caused by a price change Supply Schedule Supply for Pepsi Price Quantity Supplied $1.50 500 $2.00 1,000 $2.50 1,500 Supply Line Price S 2.00 B 1.50 A S 500 1000 Quantity Shift in Supply Shift in supply is caused by an change in – – – – production cost & technology number of firms price of related goods price expectations Increase in Supply Price S S’ B A 1.50 C S S’ 500 1000 Quantity Equilibrium A condition at which the independent plans of buyers and sellers exactly coincide in the marketplace. At equilibrium: Demand = Supply to determine equilibrium price & quantity Market Equilibrium Equilibrium in Pepsi Market Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied $1.50 1,500 500 $2.00 1,000 1,000 $2.50 500 1,500 Demand-Supply Interaction Price 2.50 D Surplus S Equilibrium 2.00 B 1.50 Shortage S 500 D 1000 1500 Quantity Stability Shortage: at a price below equilibrium quantity demanded > quantity supplied Surplus: at a price above equilibrium quantity supplied > quantity demanded Price adjustments eliminate shortages & surpluses Increase in Demand: Price D’ D S Higher Price Larger Quantity B P’ P A D’ D S Q Q’ Quantity Increase in Supply: Price D S S’ A P P’ B S Lower Price Larger Quantity D S’ Q Q’ Quantity Increase in Demand & Supply: Price D’ D S S’ P’ B Here: Higher Price Larger Quantity A P D’ S S’ Q D Q’ Quantity Market: Command Economy Price D’ S B D P’ P Shortage=AC if price is fixed C A D’ D Q Q’ Quantity





























![[A, 8-9]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006655537_1-7e8069f13791f08c2f696cc5adb95462-150x150.png)



