* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Firm - Course
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
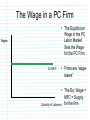
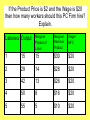
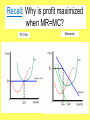
The Firm in PC Labor Markets Objective(s) • 3. Students should be able to explain why a firm hires labor until MFC=MRPL and identify this point on a cost chart and the graph of a factor market. • 5. Students should be able to graph the supply and demand of perfectly competitive labor firms and specifically recognize: – that the demand curve is derived from MRPL. – that the supply curve (MFC) is set by the market. – that the intersection of MFC and MRPL represents the profit maximization quantity of labor. – that certain variables can cause shifts in the supply and demand of labor firms. A review… • How many graphs are needed to show changes to a PC firm that produces and sells its goods in a PC Market? • 2! One for the market and one for the firm. • The firm is a “Price-Taker”. PC Firm’s Take their Wage from the PC Labor Market PC LABOR MARKET We are studying Perfectly Competitive Labor Markets PC Labor Markets PC Product Markets • Many Firms- No Barriers to Entry • Many Firms- No Barriers to Entry • Firms are Wage Takers • Firms are Price Takers • Firms are DEMANDERS • Firms are SUPPLIERS What is marginal cost? • The cost of increasing output by one unit. Marginal Factor Cost (MFC) • The cost of each additional factor employed by a firm. With labor, it is: • Change in Total Factor Cost of Laborers Change in Laborers • This equals wage in the PC industry So if this is my situation… Laborers Total Factor Cost 1 20 2 40 3 60 4 80 Marginal Factor Cost The firm is a “Wage-Taker” The Wage in a PC Firm • The Equilibrium Wage in the PC Labor Market Sets the Wage for the PC Firm Wages S= MFC • Firms are “wagetakers” • The Eq. Wage = MFC = Supply Quantity of Laborers for the firm Recall: What is MRP? MRP: Marginal Revenue Product of Labor. What is it? Marginal Revenue Product of Labor (MRP) MRP= MPL (Marginal Product of Labor) X P (Price of the Good) The Firm’s Demand Curve & The Market Demand for Laborers • The market’s demand for labor is equal to all firms in the market’s demand for labor. Wages • D= MRP • The firm hires workers at a wage that does not exceed their marginal revenue product of labor. Quantity of Laborers If the Product Price is $2 and the Wage is $20 then how many workers should this PC Firm hire? Explain. Laborers Output Marginal Product of Labor Marginal Revenue Product Wage= MFC 1 15 15 $30 $20 2 29 14 $28 $20 3 42 13 $26 $20 4 50 8 $16 $20 5 55 5 $10 $20 Recall: Why is profit maximized when MR=MC? PC Firm Monopoly Supply and Demand for a Firm in a PC Labor Market • Demand is equal to MRP Wage Add the MRP curve S=MfC Eq.W • You maximize Profit/ Minimize Costs where MFC=MRP D=MRp Eq. Q Quantity of Laborers – Hire workers until MFC=MRP – Hire less if MRP < MFC – Hire more if MRP > MFC The Whole Thing Together PC Labor Market PC Firm in Labor Market Compare and contrast PC Labor markets and firms to PC Product market and firms. Practice… 1. How many workers should this firm hire? 2. How do you know this? Price= $10 Wage=$60 Labor Units Total Output 1 5 2 20 3 30 4 35 5 35 Marginal Product of Labor MRP MFC