7 UTILITY AND DEMAND
... 30) In the table above, which of the following is true? A) Jim and Sally have increasing marginal utility. B) Jim has increasing marginal utility and Sally has diminishing marginal utility. C) Jim has diminishing marginal utility and Sally has increasing marginal utility. D) Jim and Sally have dimin ...
... 30) In the table above, which of the following is true? A) Jim and Sally have increasing marginal utility. B) Jim has increasing marginal utility and Sally has diminishing marginal utility. C) Jim has diminishing marginal utility and Sally has increasing marginal utility. D) Jim and Sally have dimin ...
Chapter 7: Utility and Demand
... quantity of sodas consumed. There is an upward movement along the negatively sloped demand curve for soda. The demand curve for movies, a substitute for soda, shifts rightward. ♦ Movies and soda are normal goods, so an increase in income increases the consumption of both products and thereby increas ...
... quantity of sodas consumed. There is an upward movement along the negatively sloped demand curve for soda. The demand curve for movies, a substitute for soda, shifts rightward. ♦ Movies and soda are normal goods, so an increase in income increases the consumption of both products and thereby increas ...
Utility
... The analysis of rational choice begins with the premise that rational individuals want as much satisfaction as they can get from their available income. Rational means that people prefer more to less and will make choices that give them as much satisfaction as possible. ...
... The analysis of rational choice begins with the premise that rational individuals want as much satisfaction as they can get from their available income. Rational means that people prefer more to less and will make choices that give them as much satisfaction as possible. ...
Chapter 7: Consumer Behavior - jb
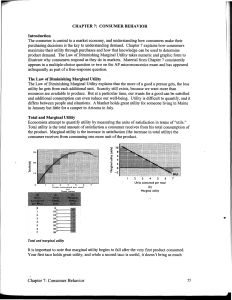
... illustrate why consumers respond as they do in markets. Material from Chapter 7 consistently appears in a multiple-choice question or two on the AP microeconomics exam and has appeared infrequently as part of a free-response question. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility The Law of Diminishing Ma ...
... illustrate why consumers respond as they do in markets. Material from Chapter 7 consistently appears in a multiple-choice question or two on the AP microeconomics exam and has appeared infrequently as part of a free-response question. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility The Law of Diminishing Ma ...
Chapter 21: Consumer Behavior and Utility Maximization
... is, consumers compare the extra utility from each product with its cost. 4. As long as one good provides more utility per dollar than another, the consumer will buy more of the first good; as more of the first product is bought, its marginal utility diminishes until the amount of utility per dollar ...
... is, consumers compare the extra utility from each product with its cost. 4. As long as one good provides more utility per dollar than another, the consumer will buy more of the first good; as more of the first product is bought, its marginal utility diminishes until the amount of utility per dollar ...
Choice, Change, Challenge, and Opportunity
... Different decisions appear to activate different areas of the brain. Some decisions are made In the pre-frontal cortex where memories are stored and data analyzed and might be deemed rational. In the hippocampus where memories of anxiety and fear are stored and might be deemed irrational. © 2010 Pea ...
... Different decisions appear to activate different areas of the brain. Some decisions are made In the pre-frontal cortex where memories are stored and data analyzed and might be deemed rational. In the hippocampus where memories of anxiety and fear are stored and might be deemed irrational. © 2010 Pea ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES CONSUMPTION? Andrew Paciorek
... by the CPI, for 168 metropolitan areas over the 1982-2007 time period. ...
... by the CPI, for 168 metropolitan areas over the 1982-2007 time period. ...
PDF
... demand for Promised Land white and chocolate milk; (3) estimate own- and cross-price elasticities for Promised Land white and chocolate milk; (4) To identify substitutes and complements of Promised Land white and chocolate milk. Data and Methodology Promised Land’s “home region” was identified to be ...
... demand for Promised Land white and chocolate milk; (3) estimate own- and cross-price elasticities for Promised Land white and chocolate milk; (4) To identify substitutes and complements of Promised Land white and chocolate milk. Data and Methodology Promised Land’s “home region” was identified to be ...
COM231 Business Economics-I
... business economics. Managerial Economics became a separate branch of economics, more particularly after 2nd world was and growth of global business through corporate organization, larger scale of operations and rapid improvements and progress in technology vis-à-vis production and distribution. Mode ...
... business economics. Managerial Economics became a separate branch of economics, more particularly after 2nd world was and growth of global business through corporate organization, larger scale of operations and rapid improvements and progress in technology vis-à-vis production and distribution. Mode ...
MRP L - Dwi Retno Andriani, SP.,MP
... demand for labor curve. When the wage rate falls to $15, the MRP curve shifts, generating a new point C on the firm’s demand for labor curve. Thus A and C are on the demand for labor curve, but B is not. ...
... demand for labor curve. When the wage rate falls to $15, the MRP curve shifts, generating a new point C on the firm’s demand for labor curve. Thus A and C are on the demand for labor curve, but B is not. ...
MRP L - Nuhfil Hanani
... demand for labor curve. When the wage rate falls to $15, the MRP curve shifts, generating a new point C on the firm’s demand for labor curve. Thus A and C are on the demand for labor curve, but B is not. ...
... demand for labor curve. When the wage rate falls to $15, the MRP curve shifts, generating a new point C on the firm’s demand for labor curve. Thus A and C are on the demand for labor curve, but B is not. ...
Interest, Rent, and Profit - Choose your book for Principles of
... • Economists believe that capital is productive in precisely the same way that people are. • We calculate the productivity of capital the same way we calculate the productivity of people. Gottheil - Principles of Economics, 4e © 2005 Thomson ...
... • Economists believe that capital is productive in precisely the same way that people are. • We calculate the productivity of capital the same way we calculate the productivity of people. Gottheil - Principles of Economics, 4e © 2005 Thomson ...
all,c,COM
... V1BAS from file BASEDATA header "1BAS"; V2BAS from file BASEDATA header "2BAS"; V3BAS from file BASEDATA header "3BAS"; V4BAS from file BASEDATA header "4BAS"; V5BAS from file BASEDATA header "5BAS"; V6BAS from file BASEDATA header "6BAS"; ...
... V1BAS from file BASEDATA header "1BAS"; V2BAS from file BASEDATA header "2BAS"; V3BAS from file BASEDATA header "3BAS"; V4BAS from file BASEDATA header "4BAS"; V5BAS from file BASEDATA header "5BAS"; V6BAS from file BASEDATA header "6BAS"; ...
all, c,COM
... V1BAS from file BASEDATA header "1BAS"; V2BAS from file BASEDATA header "2BAS"; V3BAS from file BASEDATA header "3BAS"; V4BAS from file BASEDATA header "4BAS"; V5BAS from file BASEDATA header "5BAS"; V6BAS from file BASEDATA header "6BAS"; ...
... V1BAS from file BASEDATA header "1BAS"; V2BAS from file BASEDATA header "2BAS"; V3BAS from file BASEDATA header "3BAS"; V4BAS from file BASEDATA header "4BAS"; V5BAS from file BASEDATA header "5BAS"; V6BAS from file BASEDATA header "6BAS"; ...
Chapter 12 - lenses is not covered
... technological constraint faced by producers, and with isoprofit curves depicting their “tastes” for profit. We also demonstrated an alternative “indirect” approach to profit maximization – one in which producers first investigate the cost side of their operations before bringing revenues into the an ...
... technological constraint faced by producers, and with isoprofit curves depicting their “tastes” for profit. We also demonstrated an alternative “indirect” approach to profit maximization – one in which producers first investigate the cost side of their operations before bringing revenues into the an ...
The Logic of Individual Choice: The Foundation of Supply and
... – This rule leads to focal point equilibria in which a set of goods is consumed, not because the goods are objectively preferred to other goods, but because they have become focal points to which ...
... – This rule leads to focal point equilibria in which a set of goods is consumed, not because the goods are objectively preferred to other goods, but because they have become focal points to which ...
CHAPTER 8
... 5. Explain why economists can believe there are many explanations of individual choice but nonetheless focus on self-interest. It is impossible to create a universal theory of choice owing to the multitude of tastes a population may have. Therefore, economists focus on the individual and what makes ...
... 5. Explain why economists can believe there are many explanations of individual choice but nonetheless focus on self-interest. It is impossible to create a universal theory of choice owing to the multitude of tastes a population may have. Therefore, economists focus on the individual and what makes ...
3_Consumer_Theory
... Ordinal utility: rational consumer behaviour ─ The consumer achieves optimal state in the point where the budget line is actually a tangent line to the ...
... Ordinal utility: rational consumer behaviour ─ The consumer achieves optimal state in the point where the budget line is actually a tangent line to the ...
PDF
... dropped. Because Iterative Zellner (IZEF) for complete demand systems is equivalent to maximum likelihood, estimates made by IZEF will also be invariant. A problem arises in considering how to treat households who do not consume any of the three beef products. For this case the expenditure on each i ...
... dropped. Because Iterative Zellner (IZEF) for complete demand systems is equivalent to maximum likelihood, estimates made by IZEF will also be invariant. A problem arises in considering how to treat households who do not consume any of the three beef products. For this case the expenditure on each i ...
Principles of Economics Third Edition by Fred Gottheil
... • Due to diminishing marginal utility and the abundance of water, the marginal utility of water is lower than for diamonds. Gottheil - Principles of Economics, 4e © 2005 Thomson ...
... • Due to diminishing marginal utility and the abundance of water, the marginal utility of water is lower than for diamonds. Gottheil - Principles of Economics, 4e © 2005 Thomson ...
Interpreting economic data: estimating the elasticity of demand
... first column of Table 2. From the table we see that all but two of these slope estimates are positive. The two exceptions are the demand for Fuel and Power and the demand for Tobacco. If we again interpret these slope coefficients as estimates of the slope of the Engel curves then we would interpret ...
... first column of Table 2. From the table we see that all but two of these slope estimates are positive. The two exceptions are the demand for Fuel and Power and the demand for Tobacco. If we again interpret these slope coefficients as estimates of the slope of the Engel curves then we would interpret ...
chapter 09
... 27) Workers who are unemployed but are not actively looking for jobs are referred to as: A) laid off workers. B) laid back workers. C) abandoned workers. D) discouraged workers. Answer: D Difficulty: Easy AACSB: Analytical Thinking Topic: Calculating the Unemployment Rate 28) Workers who are undere ...
... 27) Workers who are unemployed but are not actively looking for jobs are referred to as: A) laid off workers. B) laid back workers. C) abandoned workers. D) discouraged workers. Answer: D Difficulty: Easy AACSB: Analytical Thinking Topic: Calculating the Unemployment Rate 28) Workers who are undere ...
Chapter 18
... Factor market analysis could not be complete without some characterization of a. product-market demand. b. the marginal productivities of the different factors. c. market prices for final goods and services. d. All of the above are correct. ANSWER: d. All of the above are correct. TYPE: M DIFFICULTY ...
... Factor market analysis could not be complete without some characterization of a. product-market demand. b. the marginal productivities of the different factors. c. market prices for final goods and services. d. All of the above are correct. ANSWER: d. All of the above are correct. TYPE: M DIFFICULTY ...
Why Minimum Wage Hikes May Not Reduce Employment
... for labor is inelastic and the level of employment will be fairly unresponsive to changes in the wage. Conversely, the more elastic each firm’s demand for labor is and the flatter the market labor demand curve is, the more employment will fall when the wage increases. Similarly, if a wage floor alre ...
... for labor is inelastic and the level of employment will be fairly unresponsive to changes in the wage. Conversely, the more elastic each firm’s demand for labor is and the flatter the market labor demand curve is, the more employment will fall when the wage increases. Similarly, if a wage floor alre ...
marginal utility - Yuli Andriansyah
... The Principle of Diminishing Marginal Utility • The marginal utility of a good or service is the change in total utility generated by consuming one additional unit of that good or service. The marginal utility curve shows how marginal utility depends on the quantity of a good or service consumed. • ...
... The Principle of Diminishing Marginal Utility • The marginal utility of a good or service is the change in total utility generated by consuming one additional unit of that good or service. The marginal utility curve shows how marginal utility depends on the quantity of a good or service consumed. • ...