Chapter 15: Financial Markets and Expectations
... Managerial economics provides a wide variety of practical techniques that we can use to reduce costs and eliminate wastes and maximize profits. Managerial economics provides a link between economic theory and the decision sciences in the analysis of managerial decision making. Economic theory: - MI ...
... Managerial economics provides a wide variety of practical techniques that we can use to reduce costs and eliminate wastes and maximize profits. Managerial economics provides a link between economic theory and the decision sciences in the analysis of managerial decision making. Economic theory: - MI ...
Economics of Business-VE II - Kings County Office of Education
... This course introduces students to the study of Economics within the context of entrepreneurship and business administration. Students will learn the fundamental concepts of economics as they relate to scarcity, supply and demand, choices and effective decision-making, and economic systems. They wil ...
... This course introduces students to the study of Economics within the context of entrepreneurship and business administration. Students will learn the fundamental concepts of economics as they relate to scarcity, supply and demand, choices and effective decision-making, and economic systems. They wil ...
Lab #7 Chapter 7 — Utility and Demand
... 25) Ron starts out in consumer equilibrium, consuming two goods, X and Y. The price of Y rises. At this point, A) MUX /PX > MUY/PY, and Ron should decrease his consumption of Y. B) MUX /PX > MUY/PY, and Ron should increase his consumption of Y. C) MUX /PX < MUY/PY, and Ron should decrease his consum ...
... 25) Ron starts out in consumer equilibrium, consuming two goods, X and Y. The price of Y rises. At this point, A) MUX /PX > MUY/PY, and Ron should decrease his consumption of Y. B) MUX /PX > MUY/PY, and Ron should increase his consumption of Y. C) MUX /PX < MUY/PY, and Ron should decrease his consum ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... of Economic Research Volume Title: Import Competition and Response
... International Economic Studies, University of Stockholm. He has published on international economics, macroeconomics, and consumer theory in American Economic Review, Economica, Economic Journal, European Economic Review, Oxford Economic Papers, and Quarterly Journal of Economics. This paper was beg ...
... International Economic Studies, University of Stockholm. He has published on international economics, macroeconomics, and consumer theory in American Economic Review, Economica, Economic Journal, European Economic Review, Oxford Economic Papers, and Quarterly Journal of Economics. This paper was beg ...
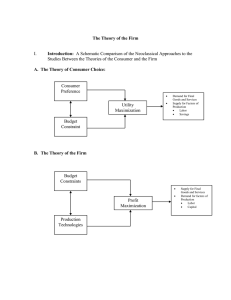
B. The Theory of the Firm
... (c) From the isoquant equation above, derive the general equation for the marginal rate of substitution. Use this equation to verify that at the optimal input combination (25, 15) the marginal rate of technical substitution of labor for capital is 0.3. What does this number inform us? (d) For the ab ...
... (c) From the isoquant equation above, derive the general equation for the marginal rate of substitution. Use this equation to verify that at the optimal input combination (25, 15) the marginal rate of technical substitution of labor for capital is 0.3. What does this number inform us? (d) For the ab ...
Chapter 1 Questions
... 25. Every school day Brain eats lunch at school. He only eats ice cream, C, and apple wedges, A. Brain’s utility function for these two commodities is represented by U(C, A) = CA. a. If an ice cream costs $0.50 and an apple wedge costs $0.25, how will Brain maximize his utility with the $2.00 his m ...
... 25. Every school day Brain eats lunch at school. He only eats ice cream, C, and apple wedges, A. Brain’s utility function for these two commodities is represented by U(C, A) = CA. a. If an ice cream costs $0.50 and an apple wedge costs $0.25, how will Brain maximize his utility with the $2.00 his m ...
Economics, by R. Glenn Hubbard and Anthony Patrick O`Brien
... Appendix 10A: Using Isoquants and Isocosts to Understand Production and Cost CHAPTER 10: Technology, Production, and Costs ...
... Appendix 10A: Using Isoquants and Isocosts to Understand Production and Cost CHAPTER 10: Technology, Production, and Costs ...
Ahliman Abbasov Microeconomics (Qrup 1023-1024)
... Test 3 51. Define the following terms and give an example of each: private goods, public goods, common ...
... Test 3 51. Define the following terms and give an example of each: private goods, public goods, common ...
CHAPTER 6 CONSUMPTION AND THE COST OF LIVING I. Socially
... prices, remains fixed, what one would find is that at very low income levels all of the consumer's income would go toward the purchase of necessities. But as income increases the fraction allocated toward the purchase of necessities decreases, while the fraction allocated toward luxuries increases. ...
... prices, remains fixed, what one would find is that at very low income levels all of the consumer's income would go toward the purchase of necessities. But as income increases the fraction allocated toward the purchase of necessities decreases, while the fraction allocated toward luxuries increases. ...
The Principle of Diminishing Marginal Utility
... goods and services An individual’s consumption bundle is the collection of all the goods and services consumed by that individual An individual’s utility function gives the total utility generated by his or her consumption bundle. The unit of utility is a util ...
... goods and services An individual’s consumption bundle is the collection of all the goods and services consumed by that individual An individual’s utility function gives the total utility generated by his or her consumption bundle. The unit of utility is a util ...
Value of Marginal Product
... the wage rate paid to the workers but also the costs of fringe benefits and employment taxes such as social security, unemployment insurance, and workers’ compensation. The true price of an hour of labor to an employer is often much greater than the money wage paid to the employee. ...
... the wage rate paid to the workers but also the costs of fringe benefits and employment taxes such as social security, unemployment insurance, and workers’ compensation. The true price of an hour of labor to an employer is often much greater than the money wage paid to the employee. ...
Principles of Economics Third Edition by Fred Gottheil
... slope up in Exhibit 7? • The curve is upward sloping because the higher the wage rate, the more willing are workers to supply greater quantities of labor. Their opportunity costs are met at higher wage rates. © 2013 Cengage Learning ...
... slope up in Exhibit 7? • The curve is upward sloping because the higher the wage rate, the more willing are workers to supply greater quantities of labor. Their opportunity costs are met at higher wage rates. © 2013 Cengage Learning ...
Factor Markets and Vertical Integration
... • A monopoly operates in the elastic section of its downward sloping demand curve, so its demand elasticity is less than -1 and finite: 1 . At any given price, the monopoly’s labor demand, p(1 1/ ) MPL , lies below the labor demand curve, pMPL , of a competitive firm with an identical ...
... • A monopoly operates in the elastic section of its downward sloping demand curve, so its demand elasticity is less than -1 and finite: 1 . At any given price, the monopoly’s labor demand, p(1 1/ ) MPL , lies below the labor demand curve, pMPL , of a competitive firm with an identical ...
ADAM SMITH: THE WEALTH OF NATIONS
... forty-eight thousand pins in a day. Each person, therefore, making a tenth part of forty-eight thousand pins, might be considered as making four thousand eight hundred pins in a day. But if they had all wrought separately and independently, and without any of them having been educated to this pecul ...
... forty-eight thousand pins in a day. Each person, therefore, making a tenth part of forty-eight thousand pins, might be considered as making four thousand eight hundred pins in a day. But if they had all wrought separately and independently, and without any of them having been educated to this pecul ...
adam smith: the wealth of nations
... forty-eight thousand pins in a day. Each person, therefore, making a tenth part of forty-eight thousand pins, might be considered as making four thousand eight hundred pins in a day. But if they had all wrought separately and independently, and without any of them having been educated to this pecul ...
... forty-eight thousand pins in a day. Each person, therefore, making a tenth part of forty-eight thousand pins, might be considered as making four thousand eight hundred pins in a day. But if they had all wrought separately and independently, and without any of them having been educated to this pecul ...
CONSUMER CHOICE
... that provide a consumer with equal utility Different individual will naturally rank market baskets differently ...
... that provide a consumer with equal utility Different individual will naturally rank market baskets differently ...
Managerial Economics
... Common Entry Barriers • Economies of scale • When long-run average cost declines over a wide range of output relative to demand for the product, there may not be room for another large producer to enter market ...
... Common Entry Barriers • Economies of scale • When long-run average cost declines over a wide range of output relative to demand for the product, there may not be room for another large producer to enter market ...
Chapter 1
... the ‘pleasure’ (in economic terms utility) these would bring to the purchaser. In the property market this price is the rental that a household pays to the landlord. In effect, every household in the urban area is purchasing the flow of services derived from the characteristics of the property per p ...
... the ‘pleasure’ (in economic terms utility) these would bring to the purchaser. In the property market this price is the rental that a household pays to the landlord. In effect, every household in the urban area is purchasing the flow of services derived from the characteristics of the property per p ...
chapter 15 wage rates in competitive labor markets
... The labor supply curve is upward sloping. The higher the wage rate, the greater the quantities of labor workers are willing to supply. Shifts in the supply curve of labor occur as a result of changes in alternative employment opportunities, changes in population size, and changes in wealth. The inte ...
... The labor supply curve is upward sloping. The higher the wage rate, the greater the quantities of labor workers are willing to supply. Shifts in the supply curve of labor occur as a result of changes in alternative employment opportunities, changes in population size, and changes in wealth. The inte ...
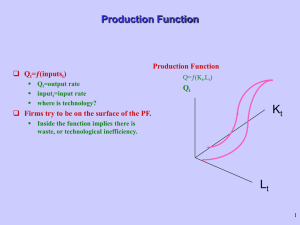
Production Function - National Bureau of Economic Research
... There is a relationship between the productivity of the average worker, and the productivity of the marginal worker. Think of a batting average. Think of your marginal productivity in the most recent game. Think of average productivity from beginning of year. ...
... There is a relationship between the productivity of the average worker, and the productivity of the marginal worker. Think of a batting average. Think of your marginal productivity in the most recent game. Think of average productivity from beginning of year. ...
14DEMAND AND SUPPLY IN FACTOR MARKETS
... run than in the long run. The elasticity of demand for labor depends on the: ♦ Labor intensity — the greater the proportion of the total cost accounted for by wages, the more elastic is the demand for labor. ♦ Elasticity of demand for the product — the greater the elasticity of demand for the produc ...
... run than in the long run. The elasticity of demand for labor depends on the: ♦ Labor intensity — the greater the proportion of the total cost accounted for by wages, the more elastic is the demand for labor. ♦ Elasticity of demand for the product — the greater the elasticity of demand for the produc ...
ge14 Yeaple
... pay their workers higher wages, and are more likely to be engaged in international trade and investment (Bernard, Redding, and Schott, 2011). These well documented empirical regularities raise several critical questions. First, what is the source of the competitive advantages of large multiproduct fi ...
... pay their workers higher wages, and are more likely to be engaged in international trade and investment (Bernard, Redding, and Schott, 2011). These well documented empirical regularities raise several critical questions. First, what is the source of the competitive advantages of large multiproduct fi ...
office of independent study
... will help you understand how people within the institutional structures developed by society make decisions concerning (1) what the society should produce; (2) how to produce the goods and services that satisfy the society’s wants; (3) how to distribute the goods and services that are produced withi ...
... will help you understand how people within the institutional structures developed by society make decisions concerning (1) what the society should produce; (2) how to produce the goods and services that satisfy the society’s wants; (3) how to distribute the goods and services that are produced withi ...
utlity and demand 1 Ch 7 Utility and Demand I. Household
... utility from movies by more than it decreases the total utility from soda, so total utility increases. b) Similarly, if MUS/PS > MUM/PM,then moving a dollar from movies to soda increases the total utility from soda by more than it decreases the total utility from movies, so total utility increases. ...
... utility from movies by more than it decreases the total utility from soda, so total utility increases. b) Similarly, if MUS/PS > MUM/PM,then moving a dollar from movies to soda increases the total utility from soda by more than it decreases the total utility from movies, so total utility increases. ...