* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Markets Perfect Competition - DSS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
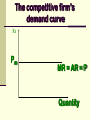
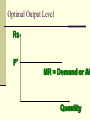
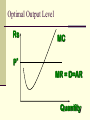
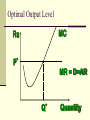
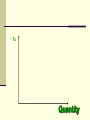
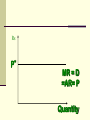
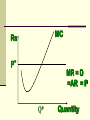
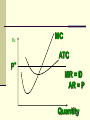
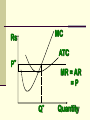
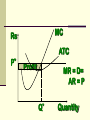
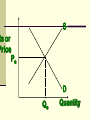
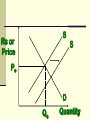
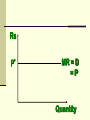
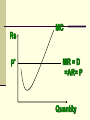
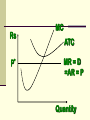
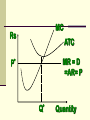
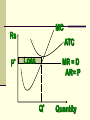
Perfectly Competitive Market Sunitha.S Assistant Professor School of Management Studies, National Institute of Technology (NIT) Calicut MARKETS AND ITS FORMS The four distinct market models are; Perfect Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Pure Monopoly PERFECT COMPETITION Characteristics Large number of Buyers and Sellers Standardized/Homogeneous Product Price Takers Free Entry and Exit Perfect knowledge about the market condition EQUILIBRIUM OF A PRICE TAKER FIRM IN SHORT RUN In short run the number of firms is fixed in the industry and firms can only change its output level by changing the variable cost. A Firm’s equilibrium point can be ascertained by the following two ways. Total Revenue & Total Cost Approach Marginal Revenue & Marginal Cost Approach EQUILIBRIUM OF A PRICE TAKER FIRM IN SHORT RUN “TR & TC APPROACH” A firm is in equilibrium and earns maximum profit when the difference between TR and TC is highest. At any point, where TR touches TC curve, it will be a Break-even point and here firm will earn Normal Profit. Normal profit does not mean Economic profit. The Profit Motive and the Results of Competition The competitive firm’s demand curve Perfect Competition: Price & Revenue No: Output 1 Price Total Revenue Average Revenue Marginal Revenue 10 10 10 2 10 20 10 10 3 10 30 10 10 4 10 40 10 10 Hence we say under perfect competition, Price=AR=MR The competitive firm’s demand curve Rs Quantity The competitive firm’s demand curve Rs Pm MR = AR = P Quantity The optimal level of output for a competitive firm is determined where Marginal Revenue (MR) is equal to Marginal Cost (MC). Optimal Output Level Rs Quantity Optimal Output Level Rs P* MR = Demand or AR Quantity Optimal Output Level Rs MC P* MR = D=AR Quantity Optimal Output Level MC Rs P* MR = D=AR Q* Quantity Average Total Cost (ATC) can be added to the graph to demonstrate the firm’s profit potential. Average Total Cost The per unit cost of producing a specific good. The difference between ATC and product’s price equals the profit per unit of product. Average Total Cost Rs Quantity Average Total Cost Rs ATC Quantity Average Total Cost Price - ATC = Profit per unit of output Note: Price > ATC indicates a profit EQUILIBRIUM OF A PRICE TAKER FIRM IN SHORT RUN “MR & MC APPROACH” MR & MC approach states that a price taker firm is in equilibrium at a point where “MR or Price = MC”. The firm’s equilibrium point does not ensure that it is producing that level of output which gives firm maximum profit. In short run, a firm is faced with four types of product prices in the market which give rise to following results; A firm earns Supernormal Profit A firm earns Normal Profit A firm incurs Losses but does not Close Down A firm minimizes Losses by Shutting Down Rs Quantity Rs P* MR = D =AR= P Quantity MC Rs P* MR = D =AR = P Q* Quantity Rs MC ATC P* MR = D AR = P Quantity MC Rs ATC P* MR = AR =P Q* Quantity MC Rs ATC P* Profit MR = D= AR = P Q* Quantity Profit Price - ATC = Profit per unit of output Note: Price < ATC indicates a loss Profit It is important to note that profit in a perfectly competitive market will lead to firms wanting to enter that market If enough firms enter, then the market supply curve will shift to the right. S Rs or Price Pe D Qe Quantity S Rs or Price S Pe D Qe Quantity Profit With the increase in Supply, price will be driven down. With the lower price, profits will be driven out. Rs Quantity Rs P* MR = D =P Quantity Rs P* MC MR = D =AR= P Quantity Rs P* MC ATC MR = D =AR = P Quantity MC Rs ATC MR = D =AR= P P* Q* Quantity MC Rs P* ATC Loss MR = D AR= P Q* Quantity Price S Pe D Qe Quantity Price S S Pe D Qe Quantity Summarise Perfect competition s a myth an not a reality Firm is in equilibrium when MC =MR Firm maximizes the profit when the price exceeds the AC. In the short run firms earn either supernormal profits(when AR exceeds AC),losses(when AC exceeds the AR)or will be forced to shut down(when AR falls short of AVC) Long Run Equilibrium Long run shows the entry and exit of the firms into the industry. If firms make supernormal profits in the SR, new firms will enter the industry till the excess profits get wiped out. Similarly, If firms are making losses ,existing firms will quit the industry so that the remaining ones will be able to make at least normal profits. Thus, under long run , firm and industry under perfectly competitive market will earn only normal profits.