* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Shortage vs. Surplus
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
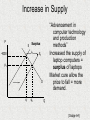
Shortage vs. Surplus Shortage vs. Surplus Let’s start with some basic concepts… • “A shortage exists at a market price when the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied.” (i.e., excess demand) • “A surplus exists at a market price when the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded.” (i.e., excess supply) (Dodge 62) Increase in Demand P S 17 2.79 Shortage D1 D q q1 Q Winter Blizzard! The price of rock salt “skyrockets” to $17/bag. Initial equilibrium price was $2.79/bag. “With the forecast of a blizzard, consumers expect a lack of future availability for” rock salt. Result = an increase in the demand for rock salt creating a shortage. Market cure = a higher equilibrium price $17/bag (Dodge 63) Decrease in Demand P Surplus S 18,000 p1 D D1 q1 q Q Recession caused a decrease in the demand for cars (a normal good) Manufacturers discounted sticker prices and offered a zero interest rate, along with other incentives. When the demand fell there was a surplus of cars at the original price. Market cure = lower the equilibrium price; resulting in fewer cars being purchased and sold. (Dodge 63) Remember! • “When demand increases, equilibrium price and quantity both increase.” P & Q • “When demand decreases, equilibrium price and quantity both decrease.” P & Q (Dodge 64) Increase in Supply P S “Advancement in computer technology and production methods” Increased the supply of laptop computers = surplus of laptops Market cure allow the price to fall = more demand. Surplus 4000 S1 p1 D q q1 Q (Dodge 64) Decrease in Supply P S p1 S1 20 D Shortage q q1 Q “Geopolitical conflict in the Middle East usually shows the production of crude oil.” A decrease “in the global supply of oil” = “a shortage of crude oil in the global market” Result = higher prices (Dodge 64) Remember! • When supply increases, equilibrium price decreases and quantity increases. P & Q • When supply decreases, equilibrium price increases and quantity decreases. P & Q Works Cited • Dodge, Eric R. “5 Steps to a 5 AP Microeconomics/ Macroeconomics”. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. 2005.