* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint: Market Equilibrium & Disequilibrium
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
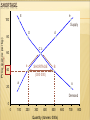
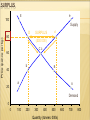
MARKET EQUILIBRIUM & DISEQUILIBRIUM EQUILIBRIUM where the supply and demand curves meet equilibrium price: P where QD = QS equilibrium quantity: Q where QD = QS DISEQUILIBRIUM (QD ≠ QS) shortage QD exceeds QS fix: P surplus QS exceeds QD fix: P SHORTAGE QD exceeds QS fix: P SHORTAGE E e 100 Price (pence per kg) Supply d D 80 Cc 60 b 40 SHORTAGE B (300 000) a A 20 Demand 0 0 100 200 300 400 500 Quantity (tonnes: 000s) 600 700 800 SURPLUS E e 100 Price (pence per kg) Supply D 80 SURPLUS d (330 000) Cc 60 b 40 B a A 20 Demand 0 0 100 200 300 400 500 Quantity (tonnes: 000s) 600 700 800 THE MARKET S Price (£) A shift in the demand In an attempt to get curve to the left will rid ofreduce surplus stock, the demand to producers 300 from will 500accept at a lower prices. Lower price of £5. Suppliers prices turn the attract do notinhave some consumers to to information or time buy. Thesupply process adjust continues untiland thestill immediately surplus disappears and offer 600 for sale at equilibrium is once £5. This results in a again reached. market surplus (S > D) Surplus £5 £3 D1 300 450 600 D Quantity Bought and Sold (000s) The Market S1 Price (£) A shift in the supply curve to the left The shortage in the would lead to less market would drive products being up prices as some available forare sale at consumers every price. prepared to pay Suppliers more. Thewould price will only be able to offer continue to rise 100 units for sale at until the shortage a price of competed £5 but has been consumers away and astill new desire to purchase equilibrium position 600.been This reached. creates a has market shortage. (S < D) £8 £5 S Shortage D 100 350 600 Quantity Bought and Sold (000s) GOVERNMENTS IMPACT MARKET EQUILIBRIUM price floor sets min. P above PE price ceiling sets max. P below PE