* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Embryonic and Fetal Development
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
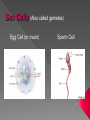
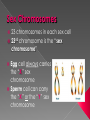
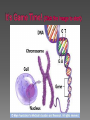
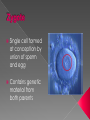
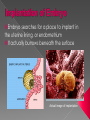
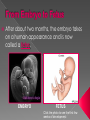
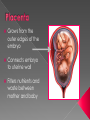
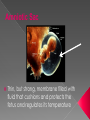
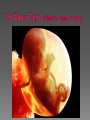
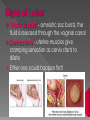
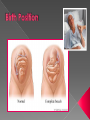
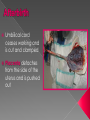
Sex Cells (Also called gametes) Egg Cell (or ovum) Sperm Cell Sex Chromosomes 23 chromosomes in each sex cell 23rd chromosome is the “sex chromosome” Egg cell always carries the “X” sex chromosome Sperm cell can carry the “X” or the “Y” sex chromosome Which sex cell determines the gender of the baby? Genes found pass on chromosomes genetic traits to offspring will be expressed if one of the parents has the gene for that trait. will be expressed only if both parents carry the trait. Definition: the process of becoming pregnant including fertilization Starts with two tiny cells (sperm and egg) that join together to grow into a baby Fertilization The strongest, fastest healthiest sperm have the best chance of fertilizing the egg Or maybe the most charming… Clip How does a woman know if she is pregnant? Missed period Breast tenderness or fullness Nausea and sometimes vomiting Changes in appetite Urination Tiredness Pregnancy Tests Urine test – tests for pregnancy hormone, HCG Pelvic exam – checks for enlarged cervix Single cell formed at conception by union of sperm and egg Contains genetic material from both parents From Zygote to Embryo Zygote divides into a multi-celled mass called an embryo as it travels down the fallopian tubes Embryo searches for a place to implant in the uterine lining, or endometrium It actually burrows beneath the surface Actual image of implantation After about two months, the embryo takes on a human appearance and is now called a fetus. EMBRYO FETUS Click the photo to see the first few weeks of development. Formation of Twins Identical One egg and one sperm Zygote divides and separates into two Each have the same DNA Fraternal Two eggs and two sperm Each have different DNA Grows from the outer edges of the embryo Connects embryo to uterine wall Filters nutrients and waste between mother and baby Grows between placenta and baby Provides baby with oxygen and nutrients Amniotic Sac Thin, but strong, membrane filled with fluid that cushions and protects the fetus and regulates its temperature How can smoking during a pregnancy affect the baby? After birth: In the womb: Low birth weight Stillborn baby Increased risk of birth defects Premature birth Asthma and breathing problems Increased risk of SIDS Affects physical and intellectual growth Behavioral problems Did You Know? Pregnant women who use drugs such as heroin, cocaine, marijuana, PCP, methadone, and/or amphetamines may give birth to drug-addicted babies. How does alcohol use affect the baby? Increased risk of miscarriage Birth defects Fetal Alcohol syndrome (FAS) - facial abnormalities - malformations of the heart - growth retardation - mental disorders “Water breaks” - amniotic sac bursts, the fluid is released through the vaginal canal Contractions - uterine muscles give cramping sensation as cervix starts to dilate Either one could happen first! Birth Natural birth - Baby is pushed out through birth canal (vagina) Caesarian section – Baby is removed from uterus via surgery Click the photo to see how the baby makes its way out of the womb. First Breath The hole in the heart will close, changing the heart from a one-pump heart to a two-pump heart. The linking passage outside the heart will close off and force oxygenated blood to the lungs so the baby can take its first breath. Umbilical cord ceases working and is cut and clamped Placenta detaches from the side of the uterus and is pushed out
























![miracle_of_life_guided_notes [2/10/2017]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009279968_1-a1e93e7997d9f4bf0c1e68e426c1356a-150x150.png)