* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic characterisation of PHARC
Periodontal disease wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Ankylosing spondylitis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis signs and symptoms wikipedia , lookup
Neuromyelitis optica wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
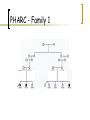
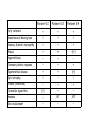
PHARC – en ny sykdom med ny sykdomsmekanisme Laurence Bindoff Eikholt – Fagkonferanse August 2011 Oversikt Bakgrunn PHARC syndrom Egen For studiet Kliniske funn Utredning Jakt etter genet Sykdomsmekanisme Personal background Neurologist Clinical & research interests mitochondrial disease other inherited neurological diseases Mitochondrial Medicine & Neurogenetics (MMN) group Studying genetic disease in Norway Geographical factors Natural barriers to movement Dark nights Large families? Concentrated gene pool Plague (1349) (from England?) 30 - 70 % population lost Famine 1800’s (English blockade) Good records Genealogical records back to 1500’s Helge Boman Limited time! Norwegians decide to move to towns Norwegians have found the Mediterranean (again) Background for PHARC PHARC ascertained as “Refsum’s like” Refsum’s Disease Demyelinating neuropathy; ataxia & retinitis pigmentosa Also cataract, anosmia, deafness, icthyosis, skeletal abnormalities, cardiac involvement PHARC - Family 1 Patient V:1 Patient V:2 Patient V:4 Early cataract + + + Sensorineural hearing loss + + + Sensory & motor neuropathy + + + Ataxia + ++ +(+) Hyperreflexia − + − Extensor plantar response − + + Tapetoretinal disease + + (+) Optic atrophy + − − Tremor (intention) − + + (+) + − Anosmia − NT NT Skin involvement − − − Cerebellar dysarthria Summary Patients present with: visual problems hearing impairment gait disturbance develops late either cataract or retinal disease combination of peripheral & central dysfunction Neurological impairment Peripheral neuropathy is present early but symptoms develop late! both pyramidal and cerebellar disease PHARC - acronym Peripheral neuropathy Hearing loss Ataxia & pyramidal tract (not all) Retinal pigmentation Cataract PHARC - Investigations Normal: phytanic & pristanic acid VLCFA peroxisomal β-oxidation α- oxidation vitamin E PHARC - Investigations Normal: Metabolic screening inc. lactate Muscle biopsy Various gene tests SCA7 Frataxin mtDNA ATPase 6 So far: Found a new disease But, no evidence of which biochemical pathway involved Question How to find the cause? PHARC - Linkage Assumptions Autosomal recessive disorder Parents distantly related Common ancestral couple linking the 2 sibs to affected third cousin occurred 6-7 generations back. Identity by descent Patient homozygous for deleterious mutation Used homozygosity mapping (2007) 400 microsatellite markers Locus 20p11.21-q12 LOD score 6.3 ~16Mb (12 cM) >130 genes Sequenced 21 Did not give up! Found further 5 families with similar disease Used 250K SNP chip Reduced region from 16 to ca. 6 Mb ~60 genes sequenced 23 Homozygous indel mutation in exon 3 in the ABHD12 gene (c.337_338delGAinsTTT) Enter the rest of the world Mutations in ABHD12 Norwegian - frameshift leads to a premature stop codon (p.Asp113PhefsX15). Emirates - 14 Kb deletion of promoter region and exon 1 Algerian - 7 bp duplication in exon 9 (p.His285fsX1). USA - nonsense mutation (c.1054C>T) in exon 12 All mutations considered NULL 19 patients from 3 continents Finding Yes No ? Age Comment S/M neuropathy 19 - - ?from birth demyelinating 100% Pes cavus 19 - - early = Neuropathy Deafness 16 2 1 teens range 6->30 Cataract 16 3 - teens/20 range 15->40 Retinal disease 12 3 4 >20 late phenomenon Ataxia (sensory 14 > central) 4 1 2->40 earlier M. East families Pyramidal tract 14 2 3 late mild - moderate MRI cerebellar atrophy 11 5 3 3 – late mild - both vermis & hemispheres Summary PHARC A clinically distinct syndrome Caused by mutations in ABHD12 World-wide distribution First neurodegenerative disorder linked to endocannabinoid metabolism ABHD12 Codes for an α,β hydrolase (ABHD) Currently 17 ABHD known, but function not known for all Only known disease associated with ABHD5 Chinarin Dorfman (fat storage disorder) ABHD12 - only known substrate is endocannabinoid 2arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) Not the only enzyme involved in 2-AG degradation What do endocannabinoids do? CB1 & CB2 are G-protein coupled receptors i.e. involved in signalling Where is ABDH12 found in the cell? Where is ABDH12 expressed? ABDH12 and microglia? CB2-receptors Immune modifying effect Over-expressed in some neurodegenerative diseases Do endocannabinoids modulate function of microglia & glial cells? Migration, activation Phagocytosis Secretion of cytokines Further work Antibodies to ABHD12 confirm localisation Urine, blood, macrophages Study metabolites of 2-AG etc Animal model? Study PHARC-like disorders other defects in endocannabinoid related disorders? Thank you for your attention! Bergen Collaborators Genetics Neurology T. Fiskerstrand; P. Knappskog; H Boman; S. Johansson; B.I. Haukanes; V.M. Steen C. Vedeler Ophthalmology C. Bredrup Mutasjon i ABHD12-genet!