* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Plant disease resistance wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
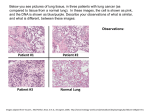
Biotechnology Applications The 1950’s GM Firebird III Public Health - Sanitation Public Health - Vaccination Polio Allergy and Asthma Epidemic in Developing Countries Devereux G. 2006. Nature Rev Immunol 6;869-874. Hygiene Hypothesis early childhood infections inhibit the tendency to develop allgergic disease Helminth Infections & Allergies: Inverse Correlation Helminth infections are associated with a decreased incidence of allergic disease in industrialized areas % Population* Helminth Infection** Allergic Disease*** Globally ~ 25% ~ 2% United States < 1% ~ 13% * United States Census (www.census.gov) ** Clin Exp Immunol, 2002. 128(3): p. 398-404 *** Lancet, 1998. 351(9111): p. 1225-32 The Hygiene Hypothesis Hygiene Hypothesis - Infection history makes a difference Many Helminth Species Have an Obligate Lung Stage Filariasis Schisto ASCARIS Malaria HOOKWORM Geohelminths SCHISTOSOMA INFECTION Skin penetration L3 larvae enter circulation Reach lungs within a day PULMONARY PHASE L3 molt into L4 Larvae Spend less than 48hrs in lung Crawl/coughed up trachea Swallowed down esophagus ADULT PHASE L4 reach small intestine Molt into adult stage worms Patency by day 7 RESOLUTION Normal BALB/c will expel the worms within 11 days SCID maintain infection Outline • Part I: Innate responses to Nb in the lungs - Gene array, PCR • Part II: Persistent alterations in the immune environment of the lung Flow cytometry • Part III: Molecular basis for helminth-induced dampening of inflammation Innate Immune Responses to Nb in the Lung Experimental Design Major Gene Array Platforms Bead Array Illuminia Spotted Array Agilent GeneChip Affymetrix General Scheme Affymetrix GeneChip Array DNA RNA Protein >5,500,000 features per chip Image Courtesy of Bioteach Innate Source of Th2 Cytokines in the Lung lung intestine lung intestine Nb Infection Innately Induced AAM Genes lung intestine lung intestine Polymerase Chain Reaction - PCR Thermal Vents Thermus aquaticus T. aquaticus DNA Polymerase 30 rounds of amplification = >1,000,000,000 molecules Real Time RT PCR results Alternatively Activated Macrophage Alternatively Activated Macrophages T Cell Help is Required for AAAM Maintenance Observations: Nb induces cellular/molecular changes through day 12 PI Helminth-induced suppression of reactivity to secondary challenge (Wohlleben et al. 2004; Wilson et al. 2005; Yang et al. 2006) Hypotheses: • Helminth infection results in permanent alterations to the lung’s immunological environment Nb Induces an Altered Lung Environment Experimental Design 2-4 13-15 36 Granular Macrophages Contain Surfactant day 36 PI Flow cytometry antibody-based detection of surface molecules Day 36 PI AMs are CD11c+, F4/80+, Mrc1mid & MHC IIhi day 36 PI Surface Phenotype of CD11c+ AAAM Day 0 2 4 8 13 MHC I CD11c+ AAAM up-regulate: MHC I & II PDL-1 CD80/CD86 CD40 MHC II PDL-I PDL-2 CD80 CD86 CD1d CD40 ICAM-1 CD1d AAAM are Highly Phagocytic Nb+ 0.02 Nb- 0.07 Ova- CD11c APC CD11c APC 22.5 9.2 Ova+* CD11c APC CD11c APC 3.5 5.2 Ova+* CytoB Ova-Alexa 448 at 2 μg/ml for 30 min CD11c APC CD11c APC CytoB - cytochalasin B at 800 μg/ml CD11c+ AM Expression Profile Up-regulated >2-fold AAM (arg1, fizz1, Ym1/2, trem2b) Scavenger Receptors (clecsf5/6/8/10, marco, day 2 PI mgl1/2, msr1/2) Chemokines (ccl4/8/9/11/12/17/24) Cell Cycle Lipid Metabolism (ppar gamma, cd68, apobec1, ch25h) 194 797 76 day 4 PI (1,674) (606) 277 59 524 392 day 8 PI (1,252) Altered Lung Environment: Hypotheses: • The Nb-altered lung environment results in a modulation in responses to secondary challenges - HDM allergen challenge • Gene array, PCR, histology, lung function Similar Numbers, Different Genes are Up-regulated Nb-Altered Lung Down-Regulates Many More Genes Nb-Altered Lung Decreases Airway Hyperresponsiveness Altered Lung Environment: Dampened Responses to Allergen Key Findings: • Persistent changes resulted in a reduction in the overall inflammatory response to allergen challenge in the lungs of Nb-infected animals • Distinct gene expression profiles in the lungs of NbHDM vs HDM mice • Lower fold-increase of transcription of Th1 & Th2 cytokines in NbHDM mice • Resistance in the airways is significantly depressed in the lungs of NbHDM mice Hygiene Hypothesis early childhood infections inhibit the tendency to develop allgergic disease Alternatively Activated Alveolar Macrophages (PDL 1/2 ?) CD1d ? IL-6 NKT IL-21 ? Acknowledgments Scott Lab Josh Reece Mark Siracusa Kiwon Park Sarah Coffman Ellen Tarr JHU Sabra Klein Mike Overstreet Fidel Zavala Mark Soloski Bill Spannhake Wayne Mitzner Jon Fallica Doug Norris Vern Carruthers Brian Schofield Paul Fallon Theresa Southard Cory Brayton JHU Gene Array Core Facility Anne Jedlicka Meg Mintz Jason Bailey Amanda Dziedzic Collaborators Joe Urban (USDA) Andrea Keane-Myers (NIH) Jamie Lee (Mayo Clinic) Funding / Support NIH NHLBI (U01 HL66623) NIH Training Grant (T32AI007417) Hegner, Cort Root Memorial Scholarship Martin Frobisher Fellowship