* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stoma
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
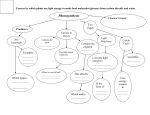
Review Question • Which mode of nutrition do the green plants carry out? A. Autotrophic nutrition B. Heterotrophic nutrition Sorry! You’re wrong! • Heterotrophic nutrition is the mode of nutrition in which organisms have to depend on other organisms or dead organic matters as their food sources. Green plants, however, can make organic food by themselves using simple inorganic substances. Very Good! • Autotrophic nutrition is the mode of nutrition in which organisms can make organic food by themselves using simple inorganic substances. • The process by which the green plants obtain nutrients is called : Photosynthesis Nature of photosynthesis • Occurs in Chloroplast • Necessary factors : Carbon dioxide Water Sunlight Chlorophyll Experiments on photosynthesis Destarching – removing starch • Reason: – To show that any starch found after the experiment is produced during the period of investigation • Method: – By placing the plant in dark for for 2 days To test a leaf for the presence of Starch boiling water turn off Bunsen burner boiling alcohol hot water iodine turn off Bunsen burner Why is the leaf first boiled in water ? Ans: Because the process can soften the leaf, break down the cuticle and kill the leaf. white tile boiling water turn off Bunsen burner boiling alcohol hot water iodine turn off Bunsen burner Why is the leaf then boiled in alcohol ? Ans: To decolourize the leaf (to remove chlorophyll). white tile boiling water turn off Bunsen burner boiling alcohol hot water iodine turn off Bunsen burner white tile Why is it important to turn off the Bunsen burner when you are heating the alcohol ? Ans: Because alcohol catches fire easily. boiling water turn off Bunsen burner boiling alcohol hot water iodine turn off Bunsen burner white tile Why is the leaf put in hot water after being boiled in alcohol ? Ans: To soften the leaf. (The leaf becomes brittle after boiling in alcohol.) boiling water turn off Bunsen burner boiling alcohol hot water iodine turn off Bunsen burner white tile What colour change can be observed if starch is present ? Ans: The leaf becomes blue-black when iodine solution is added. To show that Chlorophyll is necessary for Photosynthesis purple part green part Which part of the leaf turns blue-black when treated with iodine solution ? Ans: Only the green part. purple part green part Is chlorophyll necessary for photosynthesis ? Ans: Yes. purple part green part What is the control in this experiment ? Ans: The green part of the leaf acts as the control. To show that Carbon Dioxide is necessary for Photosynthesis sunlight A water B potassium hydroxide solution Why is potassium hydroxide solution put in one of the flasks ? Ans: To absorb all the carbon dioxide in flask B. sunlight A water B potassium hydroxide solution What happens to each leaf after testing the presence of starch at the end of the experiment ? Ans: The leaf in flask A changes to blue-black while the leaf in flask B stains brown. sunlight A water B potassium hydroxide solution What do your results suggest about the relationship between carbon dioxide and photosynthesis ? Ans: Carbon dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis. Summary of Photosynthesis 6 CO2 + 6 H20 Carbon Dioxide + water (reactants) sunlight chlorophyll C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Glucose + oxygen (products) By photosynthesis, green plants convert solar energy into chemical energy stored in glucose Route of Carbon Dioxide for Photosynthesis Chloroplast Spongy Mesophyll Cell H2O Air Space Stoma CO2 Chloroplast Palisade Mesophyll Cell H2O Air Space Stoma CO2 Mechanism of photosynthesis • • - A series of enzyme-controlled reactions Involved in 2 stages: Light-dependent stage (Light reaction) Light-independent stage (Dark reaction) Light reaction (Light-dependent stage) light water hydrogen oxygen chlorophyll Light is required Chlorophyll in chloroplast traps Light energy Light energy absorbed by chlorophyll splits water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen (photolysis) light water hydrogen oxygen chlorophyll Oxygen is formed as a by-product & released as a gas through stoma to outside Hydrogen enters light-independent stage Dark reaction (Light-independent stage) carbon' dioxide hydrogen carbohydrate water Light is not required; can take place either in light or darkness Hydrogen produced in light reaction combines with CO2 to form carbohydrates Water is formed as a by-product Summary of Photosynthesis C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H20 Light Carbon Dioxide Water H Light Reaction Oxygen Dark Reaction Glucose (C6H12O6) Fate of carbohydrate products in the plant carbon dioxide and water photosynthesis carbohydrates (e.g. glucose) release energy by respiration carbon dioxide and water photosynthesis carbohydrates (e.g. glucose) convert into other products for growth carbon dioxide and water photosynthesis carbohydrates (e.g. glucose) fatty acids glycerol combine to form lipids for use or as a food store carbon dioxide and water photosynthesis carbohydrates (e.g. glucose) mineral salts from soil (e.g. NO3-, SO42-) amino acids join together to become protein molecules carbon dioxide and water photosynthesis carbohydrates (e.g. glucose) convert into starch / lipid for storage Glucose is not a good storage molecule because Glucose is a soluble substance - it can diffuse out & lost - it affects water potential carbon dioxide and water photosynthesis carbohydrates (e.g. glucose) change into sucrose and is transported to other parts through phloem Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis Light intensity Rate of Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide concentration Rate of Photosynthesis Temperature Rate of Photosynthesis Temperature > 40℃ Rate & Stop soon If no water, stomata close no gaseous exchange photosynthesis ceases Why is Photosynthesis important ? Green plants: the only organisms capable of trapping light to manufacture food from simple inorganic substances Why is Photosynthesis important ? • Green plants are producers • It provides food for other organisms & starts the food chain Why is Photosynthesis important ? Atmospheric carbon dioxide is absorbed & oxygen is released into the atmosphere which maintains the composition of the atmosphere constant Parts of plant where photosynthesis takes place Mainly in the leaf because – it contains a lot of chloroplasts – it is well adapted for performing photosynthesis Internal Structure of Leaf cuticle upper epidermis palisade mesophyll chloroplasts spongy mesophyll intercellular space (air space) guard cell lower epidermis stoma cuticle Cross-section of a leaf of dicotyledon upper epidermis protect internal tissues from mechanical damage and bacterial & fungal invasion Cuticle • a waxy layer • prevent water loss from the leaf surface • protect the leaf mesophyll palisade mesophyll (layer) columnar cells contains many closely packed chloroplasts together absorb light more efficiently irregular cells loosely packed together to leave numerous large air some (fewer spaces than palisade allow rapid mesophyll) diffusion of gases chloroplasts for throughout the leaf photosynthesis spongy mesophyll (layer) same as upper epidermis except the cuticle is thinner lower epidermis opening which allows gases to pass through it to go into or out of the leaf stoma (stomata) guard cells control the size of stoma Stoma Guard cells thinner outer wall thicker inner wall stoma vascular bundle (vein) Internal Structure of Leaf xylem phloem xylem • to transport water and mineral salts towards the leaf • for mechanical support phloem • to transport organic substances (food/sugar/ glucose/ sucrose) away from the leaf Adaptation of leaf to photosynthesis The leaf is thin decrease diffusion distance for gases & light The leaf is broad & flattened increase surface area to absorb more sunlight Cuticle in upper epidermis is transparent Allows most light to pass into photosynthetic mesophyll tissues Palisade mesophyll cells are closely packed and contain many chloroplasts To carry out photosynthesis more efficiently Spongy mesophyll cells are loosely packed with numerous large air spaces To allow rapid diffusion of gases throughout the leaf Numerous stomata on lower epidermis To allow rapid gaseous exchange with the atmosphere Extensive vein system • Allow sufficient water to reach the cells in the leaf • To carry food away to other parts of the plant Mineral requirements in plants • In order to synthesize amino acids, nitrate ions which must be taken into the plant from the soil through the root • Other minerals are also necessary to maintain the life of the plant (N, Mg, P, K, S, etc) The importance of nitrogen • For synthesis of proteins, chlorophyll, etc • Taken in form of nitrate ions • Deficiency symptoms: – Little growth ( - no protein made) – Yellowing of leaves ( - no chlorophyll made) The importance of magnesium • Essential component of chlorophyll • Deficiency symptoms: – Yellowing of leaves (no chlorophyll made) – Poor growth (no food manufactured because of lack of chlorophyll) Use of fertilizers in agriculture • Continuous harvesting crops removes valuable mineral salts from soil Fertilizers are added to replace such loss • Two kinds of fertilizers: – Natural fertilizers – Chemical fertilizers Natural fertilizers • From manure (animal waste) • Organic compounds in it are decomposed by the bacteria in soil to form mineral salts Chemical fertilizers • Mainly nitrogenous and phosphorous compounds manufactured artificially Comparison between natural and chemical fertilizers Natural fertilizers Chemical fertilizers Contain humus which can improve soil texture No humus so cannot improve soil texture Less soluble in water so less likely to be washed away Very soluble in water so more likely to be washed away Comparison between natural and chemical fertilizers Natural fertilizers Chemical fertilizers Much cheaper Very expensive Less soluble in water so more difficult to be absorbed Very soluble in water so easier to be absorbed Time is needed for the decomposition to complete before nutrients are available to plants More readily to be used by the plants ~ END ~