* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wednesday 5/29/13
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
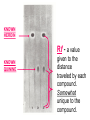
Wednesday 5/29/13 • AIM: how can we be successful on our post assessment exam? • DO NOW: Grab a text book and define criminalistics and evidence. • Explain the difference between class and individual characteristics • HOMEWORK: Review sheet • a shoe print is left at a burglary scene. Identify each of the following as individual or class characteristics. – Manufacturer of shoe – Pattern of print – Sole imprint – Size of shoe Criminalitics • the application of science to the physical evidence • bloodstains • DNA • bullet trajectories – includes the psychological angle – studying crime scenes for motives, traits, and behavior. Evidence:establishes or disproves a fact – Testimonial Evidence – Any witness accounts of the crime – Physical – any material items that would be present on the crime scene – Hard evidence left at the crime scene – Fingerprints, blood or semen samples, hair samples etc. Individual vs Class • Individual evidence: can be connected to one single person – DNA, fingerprints, hair if there is a follicle, glass, bite marks • Class evidence: related to an entire group – Glass, hair, blood Locard’s Exchange Principle – • It was Locard’s belief that when a criminal came in contact with an object or person, a crosstransfer of evidence occurred. • The exchange of materials between two objects that occurs whenever two objects come into contact with one another. Crime Labs – 1915: Edmond Locard – Lyon France – His only instruments were a microscope and spectrometer – 1923: Los Angeles Police Department – First Crime lab in the US – Current Day FBI has the LARGEST crime lab in the WORLD United States crime labs • Currently there are 320 in the US alone – Operate on different levels – Federal – State – County – Municipal – Crime Labs may function as part of the police department or the District Attorney’s office – Medical examiner or coroner Criminalist or Forensic analyst • JOB is to analyze evidence and testify about the facts – Provide an expert opinion – NO BIAS NO OPINIONS • 1960’s supreme court began depending on scientific evidence • 1990’s DNA profiling was discovered – Creation of a National DNA profile system • Today FBI has the largest forensics lab in the world Legal terms to know • • • • Stare decisis Corpus delecti Nolo contendere Pro bono • Corpus delicti: the principle that a crime must have been proven to have occurred before a person can be convicted of committing that crime. • Stare decisis: "the decisions remains" or words to that effect, It says that once a decision is made it becomes a precedent and the courts have a bias toward respecting and preserving that precedent. It is necessary to ensure that the law be predictable and consistent and not change every time a different judge or bench looks at an issue • Pro bono: work taken voluntarily. • Nolo contendere: refers to a pleas of no contest. An alternative to pleading guilty or not guilty. Crime Scene Analysis • 1- Seal off the crime scene • 2- each piece of evidence is packaged separately • 3-begin to mentally document the scene • 4- check the body if there is one • 5- isolate witnesses • 6- observe the scene for evidence Maintain a chain of custody • A list of each person who comes in contact with the evidence • Makes sure evidence is not tampered with in order to be admitted into court • NO CHAIN OF CUSTODY NO COURT ADMISSION Branches of a crime unit – Physical Science Unit • Chemistry • Drug test – Biomolecular evidence • Physics – Trajectory • • • • Geology Soil Rocks mineral Basic services of a crime unit • • • • • • • Biology Firearms Questioned document: checks, diacritics Photography Odontology Latent fingerprint Polygraph diacritics • marks such as an accent or a tilde that indicate the correct pronunciation of a letter or combination of letters which, without the mark, would be pronunced differently. • Crossing of t dotting of i Optional Services of a crime unit – Toxicology unit • • • • – – – – – Usually under the medical examiners direction Drugs,alcohol, poisons Fingerprint unit Polygraph unit Voiceprint analysis Telephone threats or taped messages Voiceprint: transforms speech into visual graphic Evidence Collection unit Cyber bullying • Voiceprint Analysis Unit - The sound spectrograph is an instrument that transforms speech into a visual graphic display called a voiceprint. Forensic entomology • Observes the development of bugs Forensic Pathology • This field involves the investigation of sudden, unnatural, unexplained, or violent deaths,disease • Rigor mortis • Algor mortis • Liver mortis 1- Algor Mortis: Time of death • Check the body core temperature • At the scene, a thermometer is inserted into the liver • Body temperature drops about one degree Celsius per hour after death 1- Algor Mortis Time of death continued • Body Temperature cools until it reaches room temperature • Rate of cooling is determined by – Location and size of body – Victim’s clothing – Weather conditions – General rule; body looses 1-1.5 degrees every hour 2- Stiffening of the body • Rigor Mortis: Muscles relax and then become rigid • Joints of body stiffen and lock – Sets in within 30 minutes to 3 hours after death – Goes away 24-36 hours after it begins 3- Liver Mortis • Blood settles in parts of the body closest to the floor • Happens 6 hours after death • More efficient in determining cause of death Forensic anthropology • Analyzes bones – Age, sex, race, height NOT weight • Sutures: determine age Fingerprints • Should be developed within 24 hours of the crime, found on any surface NOT ON A BODY • 3 types of prints • Visible, plastic, latent Fingerprint patterns Loops whorls arches % in general population 60 - 65 30 - 35 5 Visualizing a human fingerprint • MOST REACT with sweat oils • Development is based on the surface it is found on • Cyanoacrylate ester: found in super glue • Can visualize a print on a porous surface • Ninhydrin: white powder or clear liquid – Reacts with the amino acid in skin – Turns purple when amino acid is present • Iodine: drawback is when the vapors disappear the print disappears Hairs and fibers • • • • Human hair characteristics Cuticle Cortex Medulla: 1/3 of the hair shaft diameter other animals about 1/2 • ACT: anagen, catagen, telogen Fiber patterns • Wayne Williams Natural fibers are derived in whole from animal & plant sources Coton, wool REGENERATED FIBERS use CELLULOSE from plant materials mixed with a solvent to produce a fiber rayon, acetate, triacetate Drugs • Analgesics: relieve pain • Spot tests • Blood alcohol content: alcohol is dissolved in the blood and leaves the body unchanged in breath, sweat and urine COLOR TESTS: for screening only A drug is mixed with a reagent which turns colors. Bullet caliber • Caliber is a measurement of the diameter of the gun Human blood • Class characteristic • Determined by the antigen present – 3 alleles but only 2 antigens • Blood type A has antigen A • To determine if a sample is human, precipitin tests are used – Basically antigen antibody response Fire: parts of a fire • Fuel + oxygen= carbon dioxide, water, heat and flame Terms to know • CODIS: Combines DNA Index System • AFIS: Automated Fingerprint Identification system • IBIS: Integrated Ballistics • IAFIS: Integrated Automated Fingerprint Chromatography • Capillary action • Retention time • Rf value UNKNOWN SAMPLES KNOWN SAMPLES KNOWN HEROIN Rf - a value KNOWN QUININE given to the distance traveled by each compound. Somewhat unique to the compound. Comparison Microscope • Used to compare unknown samples to known samples • Places samples side by side