* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Role of Nutrients
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
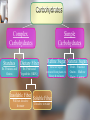
The Role of Nutrients Benefits of Good Nutrition 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Growth, Development, and Function Fitness Job Performance Appearance Less Risk of Illness Long-term Health Malnutrition Malnutrition = Poor nutrition over a prolonged period What is a Calorie (kilocalorie)? It is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kilogram of water 1° Celsius It is how we measure the amount of energy we put into our body. Six types of Essential Nutrients 1. Carbohydrates - Body’s main source of energy. Examples: Grains, potatoes, & vegetables. 2. Fats - Concentrated source of energy Examples: Butter, dressings, baked goods. 3. Protein – Helps build, repair and maintain body tissue. Examples: Poultry, eggs, milk, and beef. 4. 5. Vitamins – Chemicals that help regulate many vital body processes and aid other nutrients. Examples: Vitamins C, D & E Minerals – Non-living substances that help the body work and can become part of body tissue. Examples: Calcium & Potassium 6. Water – Essential to life. Nutrient Deficiency – Nutrient shortage produces many possible symptoms depending on the nutrient. Carbohydrates Complex Carbohydrates Simple Carbohydrates Starches Dietary Fiber Ex. Potatoes and Grains Ex. Fruits and Vegetables (SKIN)_ Refine Sugar Natural Sugars These are sugars extracted from plants ex. Honey & molasses Insoluble Fiber Soluble Fiber Will not dissolve In water Dissolve in water Fruit – Fructose Grains – Maltose Dairy - Lactose Protein Complete Protein Incomplete Protein Supplies all 9 of the Essential Amino Acids Ex. Meat, eggs, & dairy Lacking one or more Essential Amino Acids All food from plant sources Role of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Dietary Fiber – a mixture of plant materials that is not broken down in the digestive system. DRI’s – (Dietary Reference Intakes) Standards used for assessing nutrients needs among people of different age and gender groups. RDA’s – (Recommended Dietary Allowances) The amounts of a nutrient needed by 98% of the people in a given area and gender group. AI’s - (Adequate Intakes) Used when a lack of RDA cannot be established. Can malnutrition exist where food is abundant? YES Why? – Due to poor diet or a medical condition What four factors determine the number of calories your body needs? 1. 2. 3. 4. Activity level Age Weight Gender