* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 17: Blood
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
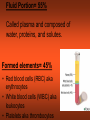
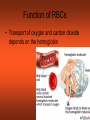
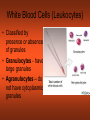
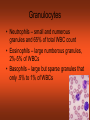
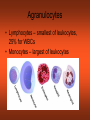
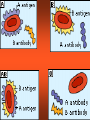
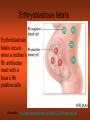
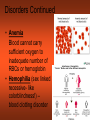
CH 17 BLOOD The Functions of Blood • (1) Transport medium that picks up food and oxygen • (2) Picks up wastes for delivery to excretory organs • (3) Transports hormones, enzymes, buffers, and other biochemical substances Fluid Portion= 55% Called plasma and composed of water, proteins, and solutes. Formed elements= 45% • Red blood cells (RBC) aka erythrocytes • White blood cells (WBC) aka leukocytes • Platelets aka thrombocytes Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) • No nucleus • Primary component is hemoglobin which gives the red color and accounts for one third of cell volume Function of RBCs • Transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide depends on the hemoglobin Formation of Red Blood Cells • Called Erythropoiesis. • Every minute you create 200 BILLION to replace an equal number destroyed at that brief time! • Formation begins in bone marrow from hematopoietic stem cells • Animation: Negative Feedback: http://health.howstuffworks.com/adam-200028.htm -If oxygen levels decrease (like at high altitude), kidneys release hormone erythropoietin, and this stimulates RBC production in red bone marrow. Red Blood Cell Destruction • Life span of RBCs is about 105 to 120 days. As they age, they break apart in the capillaries • Macrophage cells phagocytose the cells, releasing amino acids, iron, and bilirubin • ANIMATION: http://highered.mcgraw- hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter21/animation__hemoglobin_breakdown.html White Blood Cells (Leukocytes) • Classified by presence or absence of granules • Granulocytes - have large granules • Agranulocytes – do not have cytoplasmic granules Granulocytes • Neutrophils – small and numerous granules and 65% of total WBC count • Eosinophils – large numberous granules, 2%-5% of WBCs • Basophils – large but sparse granules that only .5% to 1% of WBCs Agranulocytes • Lymphocytes – smallest of leukocytes, 25% for WBCs • Monocytes – largest of leukocytes Formation of WBC • Granulocytes originate in bone marrow. • Agranulocytes originate in lymphatic tissue Platelets • Small, pale bodies that appear as irregular spindles or oval disks • Physical properties include agglutination, adhesiveness, and aggregation Function and Formation of Platelets • Play important role in hemostasis (stoppage of blood flow) and blood clotting • Form platelet plugs to stop flow of blood into tissues when damage occurs • Platelets formed in bone marrow, lungs, and spleen by fragmentation of large cells called megakaryocytes. • Life span of 7 days ABO Blood Groups U.S. Blood-type Distribution O+ 38 percent of population A+ 34 percent of population B+ 9 percent of population O7 percent of population A6 percent of population AB+ 3 percent of population B2 percent of population AB1 percent of population Writing Blood Types • Blood types are codominant genetic traits Blood Type Homozygous Genotype Heterozygous Genotype Type A I AIA IAi Type B I BIB IBi Type AB - IAIB Type O ii - Example of a Blood Type Problem • Mother is type A (remember this could be homozygous or heterozygous!) • Father is type B (remember this could be homozygous or heterozygous!) • What blood types could their children be? Rh System • Rh-positive – Rh antigen is present • Rh- negative – Rh anitgen not present • Blood does not normally contain anti-Rh antibodies, EXCEPT when an Rhnegative person is given a transfusion of Rh-positive blood or…a Rh-negative mother with a Rh-positive fetus (see next slide) Erthryoblastosis fetalis Erythroblastosis fetalis occurs when a mother’s Rh antibodies react with a fetus’s Rh positive cells. Animation: http://www.marchofdimes.com/figure2_RhDisease.swf.swf RhoGAM • All Rh-negative mothers who could carry a Rh positive baby should be treated with RhoGAM • RhoGAM stops the mother’s body from forming Rh antibodies so it prevents hurting the fetus of a Rh baby. Blood Clotting • Four Components that help clotting: are…Prothrombin, thrombin, fibrinogen, fibrin • Extrinsic – chemicals released from damaged tissue • Intrinsic – chemicals present in the blood Disorder Animations • • • • Sickle Cell Anemia: Leukemia Thrombosis Embolism (a thrombus that has moved). • Find the description of these diseases. Type them up in your own words (short definitions all on one page). Bring them in to receive 2pts for each correct definition on your test. You must be able to explain them to me at any moment that I ask you or you will lose credit. This must be your own work. No two should be exactly the same Disorders Continued • Anemia Blood cannot carry sufficient oxygen to inadequete number of RBCs or hemoglobin • Hemophilia (sex linked recessive- like colorblindness!) – blood clotting disorder