* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Food Choices: Nutrients and Nourishment
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
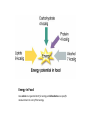
Food Choices: Nutrients and Nourishment BIOL 103 Chapter 1 What is Nutrition? • The science of foods (e.g. nutrients and other substances), including the relationships to health and disease; processes within the body (ingestion, digestion, absorption, transport, storage, functions, and disposal of end products); and the social, economic, cultural and their components, and psychological implications of eating. Factors that Influence Food Choices • • • • • Sensory Cognitive Genetics Environmental Health status Why do we eat the way we do? • Sensory (taste, texture, smell) – Flavor • Flavors: sour, bitter, salty, sweet, umami – Texture/Appearance Why do we eat the way we do? • Cognitive – Learned food habits/food reward – Social factors – Comfort/discomfort foods • Behavioral motives – Advertising – Nutrition and health beliefs Why do we eat the way we do? • Environment – Economics – Lifestyle – Availability – Cultural Influences – Religion The American Diet • “Meats and potatoes” • Americans age 2 and older consume, on average, 2157 calories (based on 2000 calories diet) • How healthful is the “American” diet? – Too little: ______________ ________________________ – Too much:_____________ ________________________ Nutrients • Definition: Any substance that provides nourishment essential for growth and the maintenance of life. • Essential vs. Non-essential nutrient – Essential nutrient: – Non-essential: • How to determine if it is an nutrient? The six classes of nutrients 1. Carbohydrates 2. Proteins 3. Lipids (fat) 4. Vitamins 5. Minerals 6. Water • Macronutrients vs. Micronutrients General Functions of Nutrients (what do they do in our body) 1. Provide ________ 2. Regulate ______________________ (ingestion, digestion, absorption, transport, storage, functions, and disposal of end products) 3. ________________________body structures How nutrients can be categorized… • Organic or Inorganic? • What is their function? Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates: “hydrate of carbon” – Made of: • Function: – energy source for cells and tissues • Dietary sources: starches and sugars found in grains, vegetables, legumes (dry beans and peas), fruits, dairy products Lipids • • • Lipids (fats, oils, cholesterol, phospholipids) – Made of: Functions: – energy storage as triglycerides – Cholesterol is a starting material for many hormones – carries fat-soluble vitamins (K, A, D, E) – provides structure for body cells Food sources: fats, oils, meat, dairy, some plants (avocado, coconut) Proteins • Made of: • Functions: – energy source – structure for cells/tissues/body structures – Regulation of body processes • Food sources: meats, dairy products, grains, legumes, vegetables. Vitamins • • • Made of: Function: – helps regulate body processes – help extract energy from carbs, fat, and proteins Food sources: meats, vegetables, grains, dairy, fats • Fat Soluble Vitamins – Vitamins K, A, D, E – Stored in larger quantities • Water Soluble Vitamins – Vitamin C/ascorbic acid – B Vitamins: thiamin (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), pyridoxine (B6), biotin (B7), folate (B9) cobalamin (B12) – Function: helpers in energy metabolism Minerals • Inorganic substances • Macrominerals vs. Microminerals or “trace minerals” • Functions: – Structure – Regulation • Food sources: all food groups Water • Most important nutrient • Functions: – temperature control – lubrication of joints – transportation of nutrients and wastes • Food sources: beverages, foods like fruits and vegetables. Energy in Food • We eat nutrients so that we can gain energy – Q: Which nutrients contain sources of potential energy? • Energy: capacity to do work • How do we measure energy in Nutrition? – Kilocalories (kcal) • 1000 calories = 1 kilocalorie • 1 kcal: the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kilogram (kg) of water by 1 degree Celsius. Energy in Food Use calorie as a general term for energy and kilocalorie as a specific measurement or unit of that energy. Problem Set #1 • A) Jeff is eating a snack with 20g of carbohydrates, 5 grams of proteins, and 3 grams of fat. What is the total amount of available energy (in kcal) in his snack? (Note: you will need to show your work for full credit in an exam). Problem Set #1 B) Determine the percentages of kilocalories of carbohydrate, protein, and fat in Jeff’s snack. Many of the leading causes of death can be avoided by good diet and exercise More than 2/3 of U.S. Adults are overweight/obese Diet and Health • Healthy: “a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being AND not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.” (WHO) • Disease – Acute – Chronic • Factors that influence Obesity: – Behavior – Environment – Genetics Diet and Health • Physical Activity – Role in long-term weight management • At least ___ mins/day of moderate activity – Weight-management • At least ___ mins/day of moderate activity – What is moderate activity? USDA – ChooseMyPlate.Gov Common Study Designs used in Nutrition Research • • • • • Cell culture studies Animal Studies Epidemiological studies Case Control Studies Clinical Trials – Randomized – Double-blind – Placebo-controlled Evaluating Information on the Internet • • • • There are no rules for posting on the internet Consider the source Keep in mind the scientific method Be on the lookout for “junk science” – May distort facts through omission of details