* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fetal Development Lecture Notes Page
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
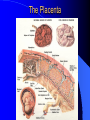
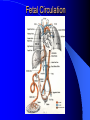
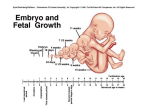
Fetal Development RC 290 The Placenta Placental Structure Purple and pancake shaped 6 inch diameter, 1 inch thick 13-16 square meter surface area Attaches to upper 1/3 of uterus Maternal side: Decidua Basalis Fetal side: Chorion (attaches to amniotic membrane) Placental Functions Primary function is to act as organ of respiration and to be the pathway for exchange of nutrients and waste products between mother and fetus Physical protection Hormone synthesis Iron and Glycogen storage Some metabolic functions Antibodies Maternal-Fetal Circulation Note: Maternal and fetal blood do not come into direct contact! Maternal-Fetal Circulation Blood comes to IV spaces (maternal side) from uterine arteries Blood in villi (fetal side) comes from umbilical arteries After exchange of O2 and CO2, the “fresh blood” returns to the fetus via the umbilical vein Umbilical Cord 2 arteries 1 vein Surrounded by Wharton’s jelly Amniotic Sac The outer layer of the umbilical cord forms the amniotic sac around the fetus Fetus is in amniotic sac containing amniotic fluid – Amniotic fluid made up of maternal serum and fetal urine and fetal lung fluid 3 Functions of amniotic fluid: – Shock absorption, temperature stability, sterile environment Blood Gas Values Hence, fetal PO2 is 25-30 mmhg! Why is fetal PO2 low? Placental O2 consumption Admixture and shunting – Like the lung, the IV space and the villi are not perfectly matched Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) – More of it (when compared to adult blood) and has greater affinity for O2 – Concentration is 17-18 grams% – Made up of alpha and gamma chains of amino acids – HbF is present for up to two months after birth Fetal O2 consumption is about twice what an adults is Fetal Circulation OOOPS! This is fecal circulation! Fetal Circulation Fetal Circulation UV goes into liver and portal circulation Most of blood shunts across the Ductus Venosus into the inferior vena cava As inferior vena cava empties into right atrium, most blood shunts across the Foramen Ovale into the left atrium where it enters the systemic circulation from the left ventricle – The heart and brain get the best blood first! Blood from superior vena cava goes into right ventricle and then to pulmonary artery Most of this blood flow shunts across the Ductus Arteriosus into the aorta – DA is in the descending aorta after the arch Pre-ductal blood may have a higher PO2! – Hence, only 3-10% of fetal cardiac out put perfuses the fetal lings Summary: Fetal Circulation 3 Shunts: Ductus Venosus, Foramen Ovale, and Ductus Arteriosus Placental Circulation Only 3-10% of fetal cardiac output actually perfuses the fetal lungs Fetal Lung Development Lung buds appear at 3.5 weeks Tracheo-bronchial tree formed by 16 weeks Alveoli start forming at 20-24 weeks – Surfactant also starts to form Capillary networks starts forming and approaching alveoli at 26-28 weeks Lungs and surfactant mature at 35 weeks Normal term is 40 weeks Surfactant Reduces surface tension so alveoli don’t collapse with each exhalation Is a phospolipid made up of dipalmityllecithin and sphingomyelin Produced through two enzymatic pathways: – Methyl transferase – Phosphocholine transferase This is the major pathway and has a longer half-life Matures last Respiratory Problems at Birth! Immature lung architecture if born premature And/or: Surfactant levels may not be adequate if: – Premature birth – Production inhibited if significant hypoxia, hypothermia, or hypoglycemia