* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Urinary system
Interstitial cystitis wikipedia , lookup
Urethroplasty wikipedia , lookup
Kidney stone disease wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
IgA nephropathy wikipedia , lookup
Kidney transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Chronic kidney disease wikipedia , lookup
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease wikipedia , lookup
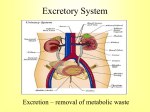
Urinary system Lab 7 Announcements • Urinary system • Lab Practical Week after Spring Break • Practical Review this Sunday 23rd at 3-5 pm Functions of Urinary System • Kidneys carry out four functions – Filter nitrogenous wastes, toxins, ions, etc. from blood to be excreted as urine. – Regulate volume and chemical composition of blood (water, salts, acids, bases). – Produce regulatory enzymes. • Renin – regulates BP/ kidney function • Erthropoeitin – stimulates RBC production from marrow. – Metabolism of Vitamin D to active form. Urinary System • Two Kidneys – Perform all functions except actual excretion. • Two Ureters – Convey urine from Kidneys to Urinary Bladder • Urinary Bladder – Holds Urine until excretion • Urethra – Conveys urine from bladder to outside of body Complete System Kidney general info • Lie against posterior abdominal wall at level of T12-L3. • Right kidney is lower than left kidney due to the shape of the liver. • Lateral surface of kidney is convex while medial is concave. – Concave side has a cleft – Renal Hilus – Inside hilus is Renal sinus • Where kidneys receive renal vessels and nerves. Kidney External Anatomy • Average size – 12cm x 6cm x 3 cm • Weights 150 grams or 5 oz • Surrounded by three membranes (deep to superficial) – Renal capsule – fibrous barrier for kidneys. – Adipose capsule – fatty tissue designed for protection / stability. – Renal fascia – dense fibrous CTP anchors kidneys/ adrenals/ membrane 1 and 2 to surroundings. Kidney Anatomy • • • • • • • • • Renal arteries and veins Renal cortex Renal medulla Nephron Renal pyramids (6-10) Renal papilla Calyx (ces) Renal pelvis Ureter Kidney- External Anatomy • Lateral surface- convex • Medial is concave– Renal Hilum • Opening to Kidney – Renal Sinus • Space within hilus • Kidneys receive blood vessels and nerves. Kidney Internal Anatomy I • Renal arteries and veins – Bring blood in and out of kidney • Renal cortex – Outer layer of Kidney • Renal medulla – Inner layer of Kidney • Nephron Kidney Internal Anatomy II • Renal Pyramids • Renal Columns – Space between pyramids within the medula • Renal Papilla – Narrow end of pyramid • Calyx (ces) – Collecting tubes • Renal Pelvis – Collecting vessel prior to ureter Human Kidney Nephron • Blood processing unit which serves to produce urine • 1 million per kidney • Consists of a glomerulus and tubules Nephron: Vascular System • • • • Afferent arteriole Glomerulus Efferent arteriole Peritubular capillaries – Capillary beds reabsorb in cortex • Vasa recta – Capillary beds reabsorb in medulla Nephron • Tubular system – Glomerular Capsule – Proximal convoluted tubule – Loop of Henle (nephron loop) • Descending limb • Ascending limb – Distal convoluted tubule – Collecting duct Nephron Dynamic Human Gross Anatomy Urinary system Kidney Nephron Urine Formation I • Glomerular filtration • Water, ions, amino acids, and glucose get into capsular space from blood • Proteins stay in blood – too big to leave capillaries. Urine Formation II • Proximal convoluted tubule and Peritubular capillary • Na+ goes down gradient and brings glucose, amino acids, etc. back into blood stream (cotransport). • Reabsorbs about 65% of filtrate. Urine Formation III Countercurrent Multiplication in the Nephron Loop • Descending limb • Ascending limb • Goes into medulla - increasing salt gradient • Water leaves • Fluid concentrates • Goes up toward cortex - decreasing salt gradient • Na+ pumped out • Fluid relatively diluted Nephron Loop Urine Formation IV • • • • Collecting duct Travels down into medulla Water leaves tubule and enters blood Urine becomes concentrated and enters renal papilla • ADH controls water channel • ADH – Antidiuretic hormone Collecting duct Dynamic Human Urine Formation Micturition • Ureters – 25 cm long – Enters on the floor of bladder • Urinary Bladder – – – – Muscular sac on floor of pelvic cavity Muscle layer formed by detrusor muscle Average bladder volume is 500 ml Max capacity is 700-800 ml Micturition • Urethra – – – – – – Conveys urine out of body Female urethra – 3 - 4 cm Opens into external urethral oriface Lies between vaginal oriface and clitoris Male urethra – 18 cm 3 regions • Prostatic urethra – 2.5 cm • Membranous urethra – 0.5 cm • Penile urethra – 15 cm Micturition Reflex Bladder with >= 200 ml of urine Sensory input to parasympathetic system Contraction of detrusor muscle and relaxation of internal urethral sphincter Relaxation of external urethral sphincter Micturition Kidney stones • A hard granule of calcium, phosphate, uric acid and protein. • Form in renal pelvis and get lodged in pelvis or ureter. • Caused by urinary tract infections, dehydration, pH imbalances, or an enlarged prostate gland. • Treated with stone dissolving drugs, surgical removal, or lithotripsy (ultrasonic vibrations) Dynamic Human Visualizing the Urinary System Intravenous pyelography Ultrasound Dissection • Be able to identify layers of the kidney on human material • Be able to locate kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra on cat. Next Week – Spring Break Week After - Practical II • Material over lymphatic, respiratory, and urinary systems • Review Sunday (end of break) at 3-5pm • Remember – some questions will be based on identifying structures on the cats.