* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Urinary System
Urethroplasty wikipedia , lookup
Interstitial cystitis wikipedia , lookup
Kidney stone disease wikipedia , lookup
IgA nephropathy wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Kidney transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Chronic kidney disease wikipedia , lookup
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease wikipedia , lookup
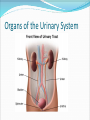
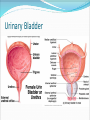
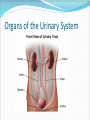
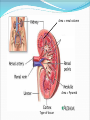
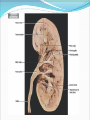
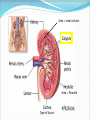
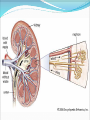
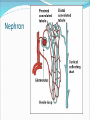
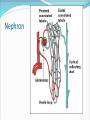
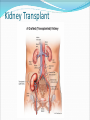
Try to Control Your Urge to Learn! Organs of the Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System Kidneys – filter blood to produce urine Ureters – drain urine from kidneys Bladder – temporary storage for urine Trigone – between 3 holes Urethra – carries urine out of body Internal & external sphincters Urinary Bladder Organs of the Urinary System Kidney Covered in fat and anchored with connective tissue Connected to abdominal aorta by renal artery Connected to inferior vena cava by renal vein ADD Renal artery & vein to drawing! Kidney – Internal Structure Renal pelvis – cavity in center collects urine Types of tissue around pelvis Renal medulla found in pyramids Renal cortex found outside of pyramids and in columns Area = renal column Area = Pyramid Type of tissue Kidney – Internal Structure Nephron – functional unit of kidney Urine formation Overlaps medulla & cortex Over 1 million in each kidney Calyx – directs urine from nephrons to renal pelvis ADD Calyces to picture! Area = renal column Area = Pyramid Type of tissue Kidney – Nephron Structure Renal corpuscle – Bowman’s capsule & glomerulus Renal tubule – Loop of Henle & collecting duct Nephron Kidney Functions – Urine Formation Filtration Almost everything pushed from glomerulus to Bowman’s capsule Reabsorption Anything you might need pulled from renal tubule into bloodstream Secretion Balancing act from blood into renal tubule Nephron Micturition Urine accumulates in bladder, stretching the walls Signal sent to brain to relax internal urethral sphincter You get “the urge…” Voluntary relaxation of external urethral sphincter Kidney Stones Hard mass of chemicals unable to pass through ureter Can be very painful Treatment varies Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) Can be anywhere in tract but often in trigone Often caused by intestinal bacteria Symptoms vary based on location of infection Cranberry juice?? Kidney Transplant Dialysis Starts when you lose 85% - 90% kidney function