* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam Four material
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
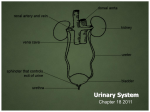
Exam Four material • Assignment due: • Exam Four: • Chapter 20 Urinary • Chapter 21 Balances Kidney • Bean shaped • Retroperitoneal: _ • Near _ Kidney • Renal pelvis: _ – Subdivided into _ • ____________________: project from _ Kidney • Inner region: _ – Contains • Outer region: – Forms _ – Granular appearance _ Kidney Function • _ • Remove __________________________ from blood • Control ___________________________ by secreting _______________________ • Regulate __________________________ by enzyme ________________________ • Activates _ Nephron • The ______________________________ of the kidney • Two sections – Renal corpuscle: • • – ________________________________: leads away from the glomerular capsule. Nephron • Renal Tubule: – – • Descending nephron loop • Ascending nephron loop – • Collecting Duct: Juxtaglomerular apparatus • Contains both – • At _________________________________, the tubule passes by arterioles, and at some point, _____________________________. This area of cells is the macula densa – Juxtaglomerular cells: _ • JG apparatus: _ Nephrons • Cortical nephron: _ – Short loops that _ • Juxtamedullary nephrons: – Shows both a cortical and Juxtamedullary nephron Urine formation • Main function nephron: – – Remove • Urine • Urine formation involves three processes: – 1. – 2. – 3. Glomerular Filtration • Fluids filtered out of __________________________ (capillaries) and into _ • Glomerular capillaries are _ Glomerular filtration • _______________________________: the ______________________ that leaves the capillaries and _ – Mostly water • Also contains glucose, amino acids, urea, uric acid and more • Filtration Pressure • _________________________________ responsible for getting material out of capillary and into glomerulus • GFR • Glomerular Filtration Rate • _________________________________ to the filtration pressure Regulation of GFR • Remains relatively constant by autoregulation • If _________________________________ vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles (leading into glomerulus) Regulation of GFR • If ____________________________ __________________________ of afferent arterioles increases filtration pressure Regulation of GFR • Renin-angiotensin system – JG cells ___________________________________ when blood pressure is_ – Macula densa senses _ – When low, _ Renin • Renin enters blood stream • Reacts with plasma protein called • • Renin • Along the _________________________________ is an enzyme called • Angiotensin I in the presence of ACE will become • Angiotensin II • Major effect on the kidneys through the adrenal cortical _ • Aldosterone: _ – ANP Atrial natriuretic peptide • Atrial natriuretic peptide – – Affects _ – ANP increases when _ – Stimulates _ – Increases Tubular Reabsorption • _________________________________. Body needs to pull some substances out of the filtrate, such as _____________________________, and ________________________________ other substances. Tubular reabsorption • • Renal tubule runs alongside Peritubular ____________________ (2) Tubular reabsorption • • Segments of the tubule are adapted to reabsorb specific substances – – Water: through _ Diuresis • Any • • • Called _ Tubular reabsorption – Amino acids: reabsorbed in_____________ by _ – Proteins: Glomerular filtrate has little protein except for small albumins: _ – Also reabsorbs: creatine, lactic, citric, uric and ascorbic acids, phosphate, sulfate, calcium, potassium and sodium Tubular reabsorption • • If more _ • Converse true as well. Tubular reabsorption • The PCT reabsorbs about 70% of water and ions. • By end of PCT the _________________________________: concentration in the __________ is same as concentration in the _ Distal Collecting Tubule • At end of PCT conditions isotonic • At beginning of _________________________________ (figure 20.22 in your text) • ____________ cells are ________________________ to water. Even if the balance is uneven, _ Antidiuretic hormone • Posterior lobe of __________________ releases ___________ when body’s water concentrations _ • ADH ________________________________ and water is moved _ • Urine volume Countercurrent system • Countercurrent Multiplier System 1) Each region has a special permeability for water, ions, and/or urea 2) Interstitial spaces accumulate ions and urea to build up a ________________________________ that increases with depth into the medulla Countercurrent system • 3) Parallel to nephrons lies a capillary network which has freely permeable walls. These capillaries passively participate in maintenance of the concentration gradient in the interstitium by removal of reabsorbed _ Tubular Secretion • Substances move from __________________ of capillary to _ – Secretes – – – Urine formation • Glomerular filtration: • Tubular reabsorption: filtrate in tubule sends _ – Glucose, water, etc • Tubular secretion: materials in _ Urine Elimination • • • • • • • Forms in _ Passes into _ Passes into _ Enters _ Enters _ Enters _ Ureter • Originates as the _ • • Layers of Ureter – Inner layer: _________________________. Continuous with renal tubules and bladder – Middle layer: ________________________ Smooth muscle fibers both circular and longitudinal – Outer layer: _____________________________ Connective tissue Peristalsis • ____________________________ enters renal pelvis and ureters • Pushed along by ______________________ to urinary bladder • _______________________: at entrance of bladder to _ Urinary Bladder • Located in _ – Male: – Female: • Like stomach, has rugae. _ Urinary bladder • ________________: ________________ area composed of – – – _________________________ of the bladder (opens to urethra) • Trigone remains _____________________________ as rest of bladder expands and contracts Bladder • Layers of the bladder – 1. Inner layer: mucous coat • – 2. Submucous coat: _ Bladder – 3. Muscular coat: _________________ muscles • • – 4. Serous coat Micturition • ______________________ reflex _ • ______________________ of the bladder stimulates _ • ______________________ muscle contracts – Aided by _ • External urethral sphincter relaxes – Bladder volume • Bladder may hold up to ____________ of urine • Urge may be present at _ • At about 300 ml, sensation _ Bladder • As bladder fills and distends, detrusor muscle contracts • Contractions may force _ – Involuntary muscle • However, in adults, urination is a ______________________________ action. Urination • Depends on control of the _ Urethra • • Contains several _ – Secrete _ Female Urethra • • • • About _______ long Travels below _ Empties between _ Empties as _ Male Urethra • Has both _ • Divided into three sections – _________________________________: passes through prostate gland – ________________________________ urethra: passes through urogenital diaphragm. Surrounded by external urethral sphincter muscle – ________________________________ urethra: passes through corpus spongiosum of penis • Ends as _ Chapter 21 • Water, Electrolyte, and acid/base balances Distribution of body fluids • Fluid compartments – Intracellular fluid compartment • All water and electrolytes _ – Extracellular fluid compartment • All fluid _ – Interstitial fluid, plasma, lymph – Transcellular fluid: _________________________________, aqueous humor, _______________________________, synovial fluid, _ Body fluid • – _________________________________ of sodium, chloride bicarbonate ions – _________________________________ of potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphate, and sulfur Body fluid composition • Intracellular fluids – Higher concentrations of potassium, phosphate, and magnesium ions – Lower concentrations of sodium, chloride, bicarbonate than extracellular fluids – Greater concentration _ Movement of fluid • Two major factors for movement – ___________________________________: pressure exerted by fluids • Fluid _ – ___________________________________: the potential pressure of a solution caused by nondiffusible solute particles in the solution Osmosis If two solutions of different concentration are separated by a semi-permeable membrane which is permeable to to the smaller solvent molecules but not to the larger solute molecules, then the solvent will tend to diffuse across the membrane from the less concentrated to the more concentrated solution. This process is called osmosis. Water balance • Adult water intake – 60% from _ – 30% from _ – 10% __________________________________: by product of metabolizing nutrients Thirst • Primary regulator: – – Related to ________________________________________ of brain – Body loses water _____________________ of the EC (extracellular) fluids _______________ Thirst • Stimulates ________________________ in the thirst center • Dry mouth: • Thirst triggered when total body water is decrease _ Quenching thirst • Drinking water _________________________________ triggers impulses to brain _ • Prevents ___________________________ Mechanism is inhibited with ________________________ of water, not ________________________ of water Water output • Loss in – – – – Evaporation and – Lungs during breathing 28% Water loss • If 2500 ml taken in on daily basis, then 2500 ml should be eliminated to maintain _ Imbalances • If not enough water taken in _ – Anti-Diuretic Hormone • DCT linings are _______________________ to water. • Blood plasma becomes _______________ due to _____________________ triggers posterior pituitary gland to release _ • ADH in bloodstream reaches ____________________ increases permeability of__________ water is _ Dehydration • EC fluid becomes _ • Change in osmotic pressure stimulates _____________________ to release ADH • ADH carried by blood to kidneys • Changes permeability of DCT • Water output _ Excess water intake • EC fluid becomes _ • Stimulates _ • Pituitary _ • Water ________________________ and collecting ducts • Removed from _ Diuretics • Alcohol, some narcotics: _ • Caffeine: inhibit _______________________ reduces reabsorption of water urine output increases Electrolyte Balance • Important electrolytes: – Sodium – – Calcium – Magnesium – – Sulfate – Phosphate – – Primarily obtained from Foods Beverages Byproducts of metabolism Electrolyte output • Body loses electrolytes – – – Greatest amount lost in _ Regulation of Sodium • Regulated through ______________________ and hormone _ – Aldosterone _ Regulation of Potassium • Rising potassium ion concentration will _ – Enhances sodium _ – Causes renal tubules to _ Regulation of Calcium • Dropping Ca concentration stimulates • – Secretes parathyroid hormone – Which _______________________________ concentrations of both calcium and phosphate ions in extracellular fluids – Also increases _ Parathyroid hormone • Causes the kidneys to – Conserve calcium ions – • Net result of PTH: – returns calcium ion concentration of EC fluid to normal levels – Maintains phosphate ion concentration Hyponatremia • – – – Diarrhea – – Drinking • Effects: – Movement of water into cells, swelling – Hypernatremia • Causes: – High fever – Diabetes insipidus • Effects: – Hypokalemia • • Causes: – – Diuretic drugs – Prolonged vomiting, diarrhea • Effects: – Muscular weakness, paralysis, _ Hyperkalemia • • Causes: – Renal disease, drugs, __________________________________ (Addison’s Disease) • Effects – – Acid Base Balance • Acids: – • Bases: – • Balance: regulation of the _ Sources of H+ • As _ • 1. – Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form carbonic acid which ionizes to release hydrogen ions and bicarbonate ions • CO2 + H20 H2C03 H+ + HCO3- Sources of H+ • 2. – Glucose in anaerobic respiration produces _______________________ which adds H+ • 3. Incomplete oxidation of _ – Produces ____________________________ which increase H+ concentration • 4. Oxidation of a.a. containing _ – Produces H2SO4 which releases H+ ions Sources of H + • 5. ______________________ of phosphoproteins and nucleic acids – These substances contain phosphorus which lends itself to _________________________ which can release H + Regulation • Acid/base regulation is essential because a shift towards more acid or more base can threaten the internal environment – Which is why we have • • • Acid Base buffer systems • • • • Bicarbonate buffer system Present in both IC fluids and EC fluids Involves _ Involves carbonic acid _ – If there is ___________________ in system: • H + will add to bicarbonate ion • H + + HCO3- H2CO3 Bicarbonate Buffer system • If there is not enough H + in system – Carbonic acid _ H2CO3 H + + HCO3- Phosphate buffer system • Present in IC and EC fluids • More important in _ • Contains H2PO4- • And HPO42- Phosphate Buffer system • If _ – Monohydrogen phosphate acts as weak base and _______________________________ to form dihydrogen phosphate • H + HPO4 –2 H2PO4 – • If conditions are too basic: – Dihydrogen phosphate will _ • H2PO4- H + HPO4 -2 Protein Buffer system • Uses _ • Review Ch 2 for protein structure and chemistry • Some proteins have a carboxyl group –COOH that _________________________ when too alkaline • Or, if conditions are too acidic, the COO- can _ Protein Buffer system • Amino acids also have amino groups: --NH2 – If conditions become too acidic: • The ________________________ will accept a H+ • --NH2 + H+ --NH3+ – If conditions become too basic: • NH3 can give up a H+ if there is an OH- group to accept it Respiratory Excretion of CO2 • Previous buffer systems good for ______________________________ …but presence of excess acid or base needs to be more completely remedied. • ______________________________ will affect more permanent changes Respiratory Excretion of CO2 • Respiratory center in brain stem – Controls _ • During exercise: – If body cells __________________________ production – Increases ________________________H2CO3 – Carbonic acid dissociates and _ – the pH starts to drop Respiratory Excretion of CO2 • Increase in H+ and increase in CO2 _ • Response: – increase ___________________ of breathing – Increase ___________________ of breathing • Result: _ Respiratory Excretion of CO2 • • • • • During rest: Concentrations of CO2 and H+ _ Breathing rate and depth falls Decreased respirations allows _ Returns pH to normal Respiratory Excretion of CO2 • Increased H+ More acidic – • Decreased H+ More basic – Renal excretion of H+ ions • Nephrons __________________________ into the urine • Kidney also regulates concentration of _ Renal excretion of H+ ions • Metabolism can result in acid formation – Amino acids when metabolized can result in • • • Kidneys will secrete _ Renal excretion of H+ • So, why if the body secretes H+ into the renal tubules doesn’t the urine have a low pH? – Some of the same buffering systems _ • Phosphate buffer system • Ammonia: NH3 + H+ NH4+ – Prevents urine from becoming acidic Rates of regulation • Acid base buffers: – Can convert strong acids and bases to _ – Considered _____________________________________ for pH shifts • Respiratory systems __________________ and renal __________________ and function more slowly – Effects of pH changes • Acidosis: – Increased _ • Depressed neuron activity • Decrease in consciousness • Alkalosis – Increased _ • Neurons become excitable • Acidosis • Results from an ______________________ or _ • Respiratory acidosis – Accumulation of _ – Decreased ventilation • Injury to _ • Obstruction in air passages • Pneumonia, emphysema Respiratory acidosis • As the H+ increases in the acidosis, the breathing rate will _ • As the body returns to normal, the acidosis is _ Respiratory acidosis • Symptoms – – – Stupor – Labored breathing – If it remains uncompensated: _ Metabolic acidosis • Due to ___________________________ (not related to respiration) or _ • Contributing conditions: – – Prolonged vomiting (including contents of small intestine) – Prolonged _ – Diabetes mellitus (fatty acids converted into ketone bodies) Respiratory alkalosis • Hyperventilation: blows off _ – Anxiety – Fever – Salicylate poisoning (aspirin) Respiratory alkalosis • Body’s response: – – Kidneys _ – Kidneys increase _ • Symptoms – Light-headedness – Agitation – Dizziness – Muscle tetany if severe Metabolic alkalosis • Results from • a_ • Increase in bases – – Prolonged vomiting _ – Diuretic drugs – Too much _ Metabolic alkalosis • Will result in a _ – Allows CO2 and H+ to recuperate