* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
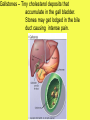
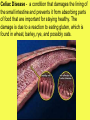
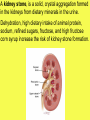
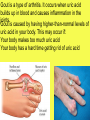
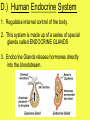
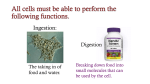
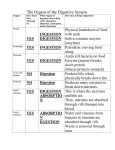
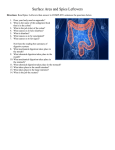
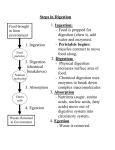
Unit 7 NUTRITION Obtaining food and breaking it down into a usable form for cells. A.) Introduction 1. There are two basic types of NUTRITION: AUTOTROPHIC NUTRITION Organisms produce their own food ex. photosynthesis HETEROTROPHIC NUTRITION Organisms obtain their food from the environment 2. The process of breaking food down is called DIGESTION 3. There are two basic types of DIGESTION: MECHANICAL DIGESTION Food is broken down into smaller pieces physically. (No Enzymes!!) CHEMICAL DIGESTION Food is broken down into end products or building blocks. (Enzymes Required!!) MECHANICAL DIGESTION CHEMICAL DIGESTION Carbohydrates (Starch) Proteins Fats Nucleic Acids Simple Sugars Amino Acids Glycerol and Fatty Acids Nucleotides 4. Some organisms digest the food within their cells. This is called Intracellular Digestion 5. Some organisms digest the food outside of their cells. This is called Extracellular Digestion Which do humans have? B.) Nutrition in Protists 1. Amoeba - (Heterotrophic) Ingestion - food is engulfed with pseudopods Digestion - intracellular within a food vacuole Egestion - indigestible material exits out through the plasma membrane 2. Paramecium - (Heterotrophic) Ingestion - food enters in through the oral groove with the help of cilia Digestion - intracellular within a food vacuole Egestion - indigestible material exits out through the anal pore 3. Euglena - (Heterotrophic & Autotrophic) Ingestion - food is absorbed in through the plasma membrane Digestion - intracellular within a food vacuole Egestion - indigestible material exits out through the plasma membrane C.) Human Digestive System 1. Basic Structure (see diagrams) 2. How is Food Digested? (see handout) 3. How are Nutrients Absorbed? (see handout) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P1sDOJM65 Bc http://kitses.com/animation/swfs/digestion .swf 4. Malfunctions of the Human Digestive System Ulcers - An ulcer is a sore in the lining of the stomach OR small intestine. Caused by an overproduction of gastric juice. Constipation - Feces is very dry and hard making egestion very difficult. Lg. Intestine reabsorbs too much water. Usually caused by dehydration Diarrhea - Feces is very wet and loose causing frequent urges of egestion. Lg. intestine does not absorb water from the wastes. There are many causes. Common cause is an intestinal pathogen Gallstones – Tiny cholesterol deposits that accumulate in the gall bladder. Stones may get lodged in the bile duct causing intense pain. Celiac Disease - a condition that damages the lining of the small intestine and prevents it from absorbing parts of food that are important for staying healthy. The damage is due to a reaction to eating gluten, which is found in wheat, barley, rye, and possibly oats. A kidney stone, is a solid, crystal aggregation formed in the kidneys from dietary minerals in the urine. Dehydration, high dietary intake of animal protein, sodium, refined sugars, fructose, and high fructose corn syrup increase the risk of kidney stone formation. Gout is a type of arthritis. It occurs when uric acid builds up in blood and causes inflammation in the joints. Gout is caused by having higher-than-normal levels of uric acid in your body. This may occur if: Your body makes too much uric acid Your body has a hard time getting rid of uric acid D.) Human Endocrine System 1. Regulates internal control of the body. 2. This system is made up of a series of special glands called ENDOCRINE GLANDS 3. Endocrine Glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream. 4. Human Endocrine Glands (see handouts) 5. Hormones are chemical messengers Most hormones are PROTEIN S Some hormones are STEROIDS (lipids) 6. Hormones in the Human Body (see handout) E.) Hormones, Receptors, and Target Cells 1. Because hormones circulate in the blood, they come in contact with most cells of the body. BUT, specific hormones only affect specific cells called TARGET CELLS 2. A TARGET CELL responds to a hormone because it bears RECEPTORS for that hormone 3. 1 Messenger Hormone Mechanisms vs. 2 Messenger Hormone Mechanisms (see handout) 4. Negative Feedback Loops -systems that regulate the levels of certain chemicals in the body. (see handout) F.) Malfunctions of the Endocrine System 1. Diabetes - Individuals maintain HIGH levels of glucose in the blood. High blood glucose levels disrupt homeostasis. Type 1 = Individual does not produce adequate amounts of INSULIN Type 2 = Individual has defect with their insulin RECEPTORS on the Liver 2. Goiter = Enlarged Thyroid Gland due to iodine deficiency