* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint to accompany
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
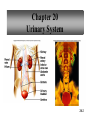
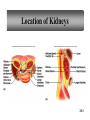
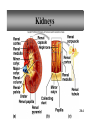
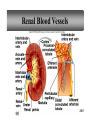
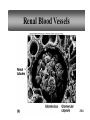
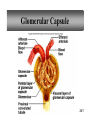
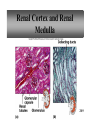
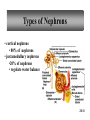
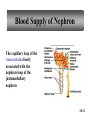
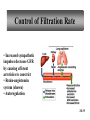
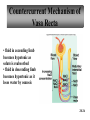
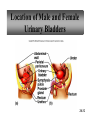
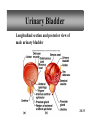
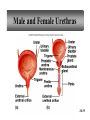
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole’s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier w Butler w Lewis Chapter 20 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 20-1 Chapter 20 Urinary System 20-2 Location of Kidneys 20-3 Kidneys 20-4 Renal Blood Vessels 20-5 Renal Blood Vessels 20-6 Glomerular Capsule 20-7 Nephron and Associated Blood Vessels 20-8 Renal Cortex and Renal Medulla 20-9 Juxtaglomerular Apparatus 20-10 • Juxtaglomerular apparatus • DCT- contains cells called the macula densa • Afferent arteriole- contains juxtaglomerular cells-release renin-in response to SNS and baroreceptors • Cells of the macula densa- responds to Na+, k, and Cl ions – Angiotensin II and Aldosterone- conserves Na and retains water by osmosis, therefore increasing BP and Blood Volume. – Vasoconstriction of both afferent and efferent, contributing to autoregulation of GFR. Types of Nephrons • cortical nephrons • 80% of nephrons • juxtamedullary nephrons •20% of nephrons • regulate water balance 20-11 Blood Supply of Nephron The capillary loop of the vasa recta is closely associated with the nephron loop of the juxtamedullary nephron 20-12 Summary of Blood Flow Through Kidney and Nephron 20-13 Urine Formation • Glomerular Filtration • substances move from blood to glomerular capsule • Tubular Reabsorption • substances move from renal tubules into blood of peritubular capillaries • glucose, water, urea, proteins, creatine • amino, lactic, citric, and uric acids • phosphate, sulfate, calcium, potassium, and sodium ions • Tubular Secretion • substances move from blood of peritubular capillaries into renal tubules • drugs and ions 20-14 Glomerular Filtration Glomerular filtrate passes through the fenestrae of the capillary endothelium 20-15 Glomerular Filtrate and Urine Composition 20-16 Net Filtration Pressure = force favoring filtration – forces opposing filtration (glomerular capillary ( capsular hydrostatic pressure hydrostatic pressure) and glomerular capillary osmotic pressure ) • GFR is directly proportional to the net filtration pressure • Sympathetic impulses constricts the afferent and GFR occurs • Constriction of the efferent, blood backs up and causes GFR • Vasodilation does the opposite 20-17 Amounts of Glomerular Filtrate and Urine average amounts over a 24 hour period • 25% of CO is received by the kidneys, 20% of plasma is filtered through the capillaries • GFR= 125ml/min=180L/24hrs • Most fluid is reabsorbed, with .6-2.5 L excreted as urine 20-18 Control of Filtration Rate • Increased sympathetic impulses decrease GFR by causing afferent arterioles to constrict • Renin-angiotensin system (shown) • Autoregulation 20-19 Control of Filtration Rate • 1. Sympathetic- If BP and BV , resulting in GFR and UO.( constriction of the afferent) • 2. Renin-angiotensin system • 3. ANP- stimulates NA excretion, and increasing GFR Tubular Reabsorption 20-20 Tubular Reabsorption of Water and Ions 20-21 Sodium and Water Filtration, Reabsorption, and Excretion 20-22 Tubular Secretion 20-23 Secretion of Ions In distal convoluted tubules, potassium ions or hydrogen ions may be passively secreted in response to active reabsorption of sodium ions 20-24 Countercurrent Mechanism • helps maintain the NaCl concentration gradient in the medullary interstitial fluid 20-25 Countercurrent Mechanism of Vasa Recta • fluid in ascending limb becomes hypotonic as solute is reabsorbed • fluid in descending limb becomes hypertonic as it loses water by osmosis 20-26 Effect of ADH on Renal Tubules • without ADH, DCT and collecting duct are impermeable to water • with ADH, DCT and collecting duct become permeable to water • with ADH, water is reabsorbed by osmosis into hypertonic medullary interstitial fluid 20-27 Urea and Uric Acid Excretion Urea • product of amino acid catabolism • plasma concentration reflects the amount or protein in diet • enters renal tubules through glomerular filtration • 50% reabsorbed • rest is excreted Uric Acid • product of nucleic acid metabolism • enters renal tubules through glomerular filtration • 100% reabsorbed • 10% secreted and excreted 20-28 Renal Clearance • the rate at which a chemical is removed from the plasma • tests of renal clearance • inulin clearance test • creatinine clearance test • paraminohipparic acid test • tests of renal clearance used to calculate glomerular filtration rate 20-29 Elimination of Urine • nephrons • collecting ducts • renal papillae • minor and major calyces • renal pelvis • ureters • urinary bladder • urethra • outside world 20-30 Ureters • 25 cm long • extend downward posterior to the parietal peritoneum • parallel to vertebral column • in pelvic cavity, join urinary bladder • wall of ureter • mucous coat • muscular coat • fibrous coat 20-31 Location of Male and Female Urinary Bladders 20-32 Urinary Bladder Longitudinal section and posterior view of male urinary bladder 20-33 Cross Section of Urethra 20-34 Male and Female Urethras 20-35 Micturition • bladder distends and stretch receptors stimulated • micturition center activated in sacral portion of spinal cord • parasympathetic nerve impulses cause detrusor muscle to contract • need to urinate is sensed • voluntary contraction of external urethral sphincter prevents urination • when decision is made to urinate, external urethral sphincter relaxes, detrusor muscle contracts, and urine is expelled 20-36 Life-Span Changes • kidneys appear scarred and grainy • kidney cells die • by age 80, kidneys have lost a third of their mass • kidney shrinkage due to loss of glomeruli • proteinuria may develop • renal tubules thicken • harder for kidneys to clear certain substances • bladder, ureters, and urethra lose elasticity • bladder holds less urine 20-37 Clinical Application Glomerulonephritis • inflammation of glomeruli • may be acute or chronic • acute glomerulonephritis usually occurs as an immune reaction to a Streptococcus infection • antigen-antibody complexes deposited in glomeruli and cause inflammation • most patients recover from acute glomerulonephritis • chronic glomerulonephritis is a progressive disease and often involves diseases other than that caused by Streptococcus • renal failure may result from chronic glomerulonephritis 20-38