* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download American Heart Association meeting, Fall 2007
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
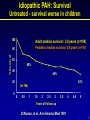
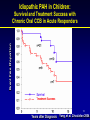
Bringing Proteomics to the Clinic: From Discovery to Validation November 4, 2007 “Biomarkers of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension” Frank J. Accurso, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Colorado Disclosures: None Support: NHLBI, NIDDK, NCRR, AHA, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Acknowledgements – Dunbar Ivy, MD; Steve Abman, MD 1 Biomarkers of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH): Overview • PAH in adults and children • PAH and biomarkers • Exploratory protein biomarker studies in PAH in children Take home messages: 1. Improved biomarkers are needed to quickly “test” new treatment approaches. 2. Biomarker studies should be incorporated into clinical trials and investigations in PAH. 2 PAH - definition • Sustained elevation of mean pulmonary arterial pressure to > 25 mm Hg at rest or >30 mm Hg with exercise, with a mean pulmonary capillary and left atrial pressure < 15 mm Hg at rest. • “fixed” (structural) and “reactive” components • Better treatments are needed. Rubin, Chest supplement, 2004 3 WHO Classification of PH (Venice, 2003) Former Primary Pulmonary Hypertension (PPH) – idiopathic or unknown cause OR Secondary Pulmonary Hypertension (SPH) – all other causes Current 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. WHO (Venice, 2003) Pulmonary arterial hypertension Pulmonary hypertension with left heart failure PH with lung diseases and/or hypoxemia PH due to chronic thrombotic and/or embolic diseases Miscellaneous Simonneau G, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol , Supplement, 2004. 4 PAH (WHO Group I) • Idiopathic (IPAH) • Familial (FPAH) • Associated with (APAH) – Collagen vascular disease – HIV infection – Congenital systemic-to-pulmonary shunts – Drugs/toxins – Portal hypertension – Other • Associated with significant venous or capillary involvement – Pulmonary veno-occlusive disease (PVOD) – Pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis (PCH) • Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn Simonneau G, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol , Supplement, 2004. 5 PAH: Diagnostic Evaluation • Physical • Physiologic* - Lung function - Exercise testing • Blood • Imaging • EKG • Sleep study • ECHO • Right Heart Catheterization • History* * Difficult in young children ? Biochemical biomarkers of disease 6 Idiopathic PAH: Survival Untreated - survival worse in children 100 Adult median survival: 2.8 years (n=194) Pediatric median survival: 0.8 years (n=16) % Survival 80 60 68% 40 48% 20 34% (n=194) 0 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 Years of Follow-up D’Alonzo, et al. Ann Internal Med 1991 7 PAH: Acute vasodilator response depends on age Barst et al. 8 PAH: Treatment Approaches • Pathophysiology - “fixed” – structural, associated with proliferation - “reactive” – amenable to vasodilator treatment - treatments based on known pathways of vasoactivity • Calcium channel blockers – vasodilators • Prostacyclin – vasodilator, antiproliferative • Nitric oxide – vasodilator, antiproliferative • Endothelin – vasoconstrictor, proliferative – need antagonist • Vascular reactivity is a favorable prognostic sign 9 Idiopathic PAH in Children: Event Free Proportion Survival and Treatment Success with Chronic Oral CCB in Acute Responders 10 Years after Diagnosis Yung, et al. Circulation 2004 Complex, long-term PAH treatment strategies have been developed Yes Acute Vasodilator Response No Epoprostenol Nitric Oxide CHF No Yes Epoprostenol Treprostinil Incomplete response Trial of Calcium Channel Blocker Incomplete response Trial of : Bosentan Ambrisentan Sildenafil Iloprost Treprostinil Epoprostenol Biomarkers would be helpful in adding treatments. Adapted from Rashid A, Ivy D. 2006: Current Paediatrics 11 Biomarkers of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) • PAH in Adults and Children • Biomarkers and PAH • Exploratory Biomarker Studies in PAH in Children 12 Outcome Measures Clinical efficacy measures: A characteristic or variable that reflects how a patient feels, functions, or survives. Surrogate endpoint: A laboratory measurement or physical sign that is used in therapeutic trials as a substitute for a clinically meaningful endpoint that is a direct measure of how a patient feels, functions, or survives and is expected to predict the effect of therapy. Biomarker: A characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal biologic process, pathogenic process, or pharmacologic response to a therapeutic intervention. Pulmonary Hypertension Review : Snow and Kawut, 2007 ; Hamblett et al, 2007 13 Biomarker Need in PAH Need Current biochemical biomarker Diagnosis - Early identification - Staging No No Prognosis - Rapid progression of disease - Ongoing structural Injury - Predict complications Treatment - Select treatment - Response to treatment - Toxicity with treatment - Clinical Trials a. Stratification b. Proof of concept c. Efficacy No No No No No No No No No 14 Value Added: Proof of Concept 15 The specific goals of the Clinical Proteomics Program are to: (1) design panels of candidate proteins for disease areas (2) develop high throughput analytic methods (3) assess the predictive value of these proteomic measurements using biological specimens and clinical data from existing study populations (4) establish procedures and standards for quality control http://www.mc.vanderbilt.edu/root/vumc.php?site=proteomics 16 Approaches to Protein Biomarkers Single/Few Protein Assay(s) (Hypothesis) Multiplex Protein Assay(s) (Hypothesis/ Discovery) Candidate - Single - Panel Validation Value Added Proteomics (Discovery) 17 Candidate Biomarker Pathways in PAH Candidate Natriuretic peptide (BNP) Troponin T Source myocytes myocytes Uric acid Endothelin-1 Serotonin Angiotensin system ubiquitous endothelium platelets vascular wall NO related products Cyclic nucleotides endothelium vascular wall, smooth muscle Fibrinogen related products Cytokines, Growth factors Acute Phase Reactants fibrin variety liver Aubert, Swiss Med Weekly, 2007 18 Caveat: Different Reagent Sources Serum Il-6 • Controls Agree • Duplicate Clinical samples do not agree • A second analytical method is needed for validation. Brand Y • Standards Agree Brand X 19 Biomarkers of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH): Overview • PAH in adults and children • PAH and biomarkers • Exploratory protein biomarker studies in PAH in children Take home messages: 1. Improved biomarkers are needed to quickly “test” new treatment approaches. 2. Biomarker studies should be incorporated into clinical trials and investigations in PAH. 20 Characteristics of biomarkers • Is the outcome measure specific to a process occurring either early or late in the disease process? • Is the biomarker in the causal pathway of the drug? • How is the biomarker expected to change in response to the drug? • How long will it take to see an expected change in response to the drug? 21