* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prescribing in Disease
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Neuromyelitis optica wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatoid arthritis wikipedia , lookup
Ankylosing spondylitis wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
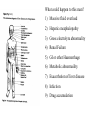
Prescribing in Disease Clive Roberts So what are drugs good at treating (or preventing)? • • • • • • • • • • Pain Inflammation Infection Fluid retention Heart problems High blood pressure Epilepsy Parkinsonism Asthma / COPD Peptic ulcer disease • • • • • • • • • Diarrhoea/constipation Depression Anxiety/sleeplessness Psychosis Metabolic /endocrine diseases Malignant disease Degenerative disease Haematological problems Etc Etc What could happen to this man? 1) Massive fluid overload 2) Hepatic encephalopathy 3) Gross electrolyte abnormality 4) Renal Failure 5) GI or other Haemorrhage 6) Metabolic abnormaility 7) Exacerbation of liver disease 8) Infection 9) Drug accumulation And so the risks of drug use in decompensated liver disease • Precipitate encephalopathy – CNS effect – Electrolyte effect – GI effect • Worsen metabolic effect/features of hepatic failure – – – – – Fluid retention Sodium retention Electrolyte abnormality Hypoglycaemia Clotting abnormalities Continued: • Profound pharmacokinetic disturbance leading to drug accumulation and dose related adverse effects – – – – – – – Decreased systemic clearance of lipid soluble drugs Increased bioavailability of drugs with high extraction ratio Decreased plasma protein binding Altered apparent volume of distribution Associated impairment of renal function Failure of pro-drugs Hepatic blood flow reduction • Worsened hepatic state – Hepatotoxic drugs Some examples from the BNF table • • • • • • • • • Anticoagulants Antidepressants, anxiolytics and hypnotics Anti-psychotics NSAIDs Diuretics Phenytoin, Carbamazepine Glibenclamide Opioids Rifampicin • Co-amoxyclav, clarythromycin, erythromycin, ketoconazole, isoniazid • Chloramphenicol • Clopidogrel • Cyclophosphamide, methotrexate • Lignocaine • ACE inhibitors • Metformin • Verapamil and some dihydropyridine Ca blockers • Statins • Antacids • Theophylline Other risk situations • • • • • • • • • • • • Renal disease The Elderly Need for many drugs Allergy Lung disease Heart disease Gastrointestinal disease Inherited diseases Blood diseases Bone disease Skin disease Pregnancy The renal patient • Pharmacokinetic disturbance – Mainly affecting drug clearance – Also protein binding • Increased sensitivity • Poor tolerance of adverse effects • Decreased effectiveness of some drugs Drugs in the elderly • Multiple indications leads to polypharmacy • Pharmacokinetic disturbance of metabolism, excretion, protein binding and drug distribution • Increased sensitivity to the actions of drugs on CVS, CNS, GIT • Poor tolerance of adverse effect Other risk situations • • • • • • • • • • • • Renal disease The Elderly Need for many drugs Allergy Lung disease Heart disease Gastrointestinal disease Inherited diseases Blood diseases Bone disease Skin disease Pregnancy Remember • Every disease represents a potential contraindication to particular drugs • Prescribing any drug should only follow a decision that potential benefit outweighs potential risk