* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Medication Administration
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
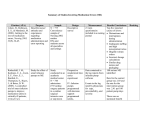
Medication Administration Part 1 Keith Rischer, RN, MA, CEN, CCRN Today’s Objectives State the primary use and nursing implications for drugs in each major classification Describe the characteristics of any drug that the nurse is responsible for administering –Onset, peak, duration and half-life –Mechanism of action>SE>Nsg Implications Calculate fractional dosages of drugs Using drug reference text correctly fill out clinical paperwork related to medication administration Nurse’s Responsibility How many patients die each year because of medication errors in US hospitals? 500 5000 7000 25,000 How many patients are injured as a result of medication errors annually? 100,000 500,000 1,000,000 1,500,000 Pharmacological Concepts Drug Names Chemical name – name of a drug as the chemist knows it. Describes the constituents of the drug Ex: – N-acetyl-para-aminophenol (Tylenol) – 2-(acetyloxy)benzoic acid. (Aspirin) Pharmacological Concepts Drug names Generic names Name given to a drug before it becomes official. Name is often listed in the USP as the official name Ex: Furosemide, Acetaminophen, Atorvastatin Brand name Trademark or name given by drug manufacturer. More that one manufacturer may make the same drug EX: Lasix, Tylenol, Lipitor Reading Medication Labels Nursing implications Implications related to administration and assessment/monitoring RN responsible for V/S Timing with meals Labs I&O Dilute? Crush? Classifications/Nursing Implications Anti-hypertensive Beta Blockers Calcium channel blockers Diltiazem Nifedipine ACE Inhibitors Atenolol Metoprolol Propranolol Captopril Enalapril Lisinopril Diuretics Loop of Henle (Furosemide) Distal tubule-(Hydrochlorothiazide-HCTZ) Classifications/Nursing Implications Analgesics Mild-NSAIDS Moderate-Opiod Narcotics po Tylenol #3, Vicodin, Percocet Severe-Opiod Narcotics IV Tylenol, Ibuprofen, Aspirin Morphine, Dilaudid, Fentanyl Anti-bacterial Penicillins Cephalosporins Amoxicillin Keflex Sulfa Bactrim DS Classifications/Nursing Implications Anti-inflammatory Anti-coagulant Heparin Coumadin Anti-platelet NSAIDS Prednisone Aspirin Plavix Laxative Sennakot, Metamucil Routes of Administration Oral Capsules/tablets Syrup/solution Inhalation Rectal suppository Topical Patch ointment Parenteral IV (intravenous) Sub-q (sub-cutaneous) IM (intra-muscular) ID (intra-dermal) Medication Administration Oral 60-100 mL of fluid Contraindications NPO GI CVA Prevent aspiration (Table 35-16 p.717 P&P) Medication Administration Topical Remove old patch before applying new Date and time new patch Use gloves Make sure skin is clean and dry Examples: Fentanyl Nitroglycerin Nicoderm Medication Administration Nasal Eye Ear Medication Administration Inhalers Albuterol/Advair Spacer Vaginal Rectal Types of Medication Action Therapeutic/Mechanism of action Side effects Allergic reactions Idiosyncratic reactions Toxic effects Adverse reactions Amiodarone Tolerance Opiate narcotics Time/Action Profile Onset Peak Duration Trough Serum Half life Morphine IV Vicodin po Interpreting Drug Orders Abbreviations - Pickar “Do not use” of abbreviations list – Pickar MS 2 mg IV q4 hours p.r.n for pain Lantus insulin 20u qd Maalox 15cc q6 hours prn Formula Method D X Q = X H Desired Have X Quantity = Amount Formula Method Heparin subq order for 12,000u due. This injection comes in a vial of 20,000u/cc. What will be the amount you will administer? Dilaudid 0.25mg IV for pain. The pharmacy dispenses a carpuject/vial of Dilaudid 1mg/cc. What is the amount you will administer? Solumedrol 25mg IV. It is dispensed as a 40mg/cc vial. What is the amount you will administer? Plavix 300mg to be given now. It only comes in 75mg tablets. How many tabs will you administer to give the correct dose? This is your patient… MB, 75 yo, admitted to the step down unit with exacerbation of heart failure. She complained of SOB, 3+ pitting edema in lower legs and a weight gain of 8 lbs in 3 days. Her K+ was 3.4 mEq/L in the ED. Furosemide 40mg IV was given in the ED with 800cc urine out P-96 R-32-BP 160/90 initially in ED P-86-R-24 BP 122/78 after Lasix Physician has ordered: KCL 30 mEq po bid Pharmacy has dispensed KCL 20 meq/15cc elixir