* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
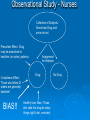
History of Medicine Body health dependent on the balance of 4 humours: Blood, phlegm, bile, and black bile Sweating, vomiting, urinating, bleeding, oozing pus were ways to restore balance Treatment linked to this theory Blood letting – cutting, cupping, leeches Induce vomiting - Ipecac, calomel Blistering – mustard pack to induce infection History of Medicine News Flash 1799! George Washington has a sore throat! Blistered throat Leeches behind ears and on throat Enema Emetic More blood letting = 5 pints! History of Medicine News Flash 1881! President Garfield Shot! Drs probed wound with fingers “Healthy pus” discharged – Whew! We thought he might die… Died of infection – strep bacteria were introduced by probing of doctors History of Medicine Rise of Thomsonians in early 1800s Less violent treatment Thought that disease was a result of cold Herbs used to purge the body Warm baths Return medicine to laypeople Others Homeopaths: Let nature do it…diet, exercise, hygiene Hydrotherapy: Diet, bathing These beat throwing up and enemas! History of Medicine Why were these therapies supported? No cures! Some benefits – diet, exercise, cleanliness Accidental successes – Many diseases are self limiting – “post hoc ergo propter hoc” Popular press Placebo effect Reason was used instead of experimentation History of Medicine New Advances…Europe 1800s Microscope, stethoscope, thermometers Study of Bacteriology Study of parasites Epidemiology: Correlation of disease and treatments - found bleeding to be ineffective – Whew! History of Medicine James Lind - 1747 In a controlled experiment, gave oranges/lemons to British sailors and they didn’t develop scurvy Joseph Lister – 1850s and 1860s Aseptic surgery Antiseptic carbolic acid 4% mortality rate Paradigm shift: Development of microscope Humours to microorganisms Claude Bernard: “Why think? Exhaustively experiment, then think.” History of Medicine Advances in U.S. Johns Hopkins dies and leaves 3.5 million to open a university/hospital Quaker trustees of estate decided on the German model Research and experimentation began with much success Immunizations – Typhoid, cholera, rabies Research Culminated In… First Cure 1891: Diphtheria “El garrotillo” Francisco de Goya 1746 - 1828 History of Medicine Sometime in the early 1900s… “a random patient, with a random disease, consulting a doctor chosen at random had, for the first time in the history of mankind, a better than fifty-fifty chance of profiting from the encounter” - Lawence Henderson, Harvard, 1964 Science Makes a Difference! Ea 18 rly 00 19 s 00 s 19 40 s N ow 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 G re M ek ed s ie va l # Years Average Life Expectancy Current Tx in Autism Field Rapid prompting Sensory integration Facilitated communication EDTA Chelation Xango juice Mega-Vitamins GFCF diet Auditory integration Relationship development intervention Psychomotor patterning Sciopathy Behavior Analysis* Current Tx in Autism Field Why are there so many? No cure for autism Accidental successes Kids may improve for unknown reasons Kids may improve due to concurrent Tx Press and internet blogs “(Child’s name) reasoning and behavior have changed for the better since drinking this juice. “ Placebo effect? Lack of appropriate experimentation – sound familiar? Reason vs experiments Current Tx in Autism Field Why are they used? (cont’d) Proponents tell us that Tx is supported by “Research” But sometimes studies don’t have objective measurement Some studies don’t establish causality Current Tx in Autism Field Should I Try This One? Is there scientific support? Make evidence-based decisions Are the studies that support it correctly done? Weigh risks/costs vs benefits Short term vs long term What about cost of not trying alternatives Beware of “Research Shows” HRT (Hormone replacement therapy during menopause) 1985: 122,000 nurses studied by Harvard Medical School HRT is effective at managing menopausal symptoms Also, concluded that nurses taking HRT during menopause had 1/3 as many heart attacks This result formed the basis of therapeutic wisdom for the next 17 years Beware of “Research Shows” 1998: Heart-Estrogen Replacement (HERS) Clinical Trial– post-menopausal women Concluded that estrogen increased frequency of heart attacks in those women who had existing heart disease. 2002: Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) Clinical Trial – post-menopausal women Concluded that HRT was a potential health risk for all post-menopausal women including heart disease, stroke, breast cancer. But may offer protection from osteoporosis and maybe colorectal cancer. 2011 – Effects of HRT less clear – short term use maybe OK Observational Study - Nurses Collection of Subjects: Some take Drug and some do not Prescriber Effect: Drug may be prescribed to healthier (or sicker) patients Compliance Effect: Those who follow Dr orders are generally healthier! BIAS!! Assignment for Analysis Drug Healthy User Bias: Those who take the drug do many things right! (diet, exercise) No Drug Observational Studies “They can distinguish associations between events…But they cannot inherently determine causation…” -Gary Taubes, New York Times, Science Journalist Controlled Experiment – HERS/WHI Subjects Random Assignment Drug No Systematic Bias Placebo