* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Benward Chapter 9
Microtonal music wikipedia , lookup
Consonance and dissonance wikipedia , lookup
Traditional sub-Saharan African harmony wikipedia , lookup
Figured bass wikipedia , lookup
Chord (music) wikipedia , lookup
Schenkerian analysis wikipedia , lookup
Chord names and symbols (popular music) wikipedia , lookup
Circle of fifths wikipedia , lookup
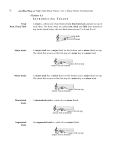
Chapter Nine Intervals: The Major Triad and the Interval of the Perfect Fifth The Triad Chord: Three or more different tones sounding together. A chord that consists of three different tones, each a third apart, is called a triad. Triads have formed the basis for the music since the beginning of the fifteenth century. Tones of the triad may be arranged in different orders or placed in different octaves, but if the names of the notes are the same, the chord preserves its identity. It is always possible to reassemble the notes in thirds to show its construction. The Major Triad A triad with a major third on the bottom and a minor third on top. Interval: The Perfect Fifth (P5) The interval between the bottom and top notes of a triad is a perfect fifth. It contains seven half steps. Songs used to identify a Perfect Fifth Ascending: do-sol, Twinkle, Twinkle Little Star, Theme from 2001, Whisper Not (Benny Golson), Bags Grove, Lavender’s Blue, Hey There Georgy Girl, Theme from Star Wars, Baa Baa Black Sheep Descending: sol-do, Feelings, 7 Steps to Heaven (Miles Davis), Have You Met Miss Jones?, Minuette in G, Flinstones, Bring a Torch Jeannette Isabella, It Don’t Mean a Thing if it Ain’t Got That Swing The Names of the Triad Tones Each member of the triad is named in relation to the tone on which the chord is constructed, which is the root of the triad. The note a third above the root is called the third of the triad. The fifth above the root is the fifth of the triad. Triads are named by the root and the quality of sound: thus, in the following example, a major triad built on C is called the C major triad. The Diminished Fifth (d5) If a fifth is built on each note of any major scale, all but one of the fifths will have seven half steps (perfect fifths). One fifth, however, has only six half steps. Its quality of sound is so totally different from that of the perfect fifth that it is called diminished. The diminished fifth has six half steps and is also referred to as a tritone. Songs Used to identify a diminished fifth Ascending: Maria (West Side Story), Simpson’s Theme Song, ti-fa Descending: European Siren, Blue Seven (Sandy Rollins), fa, ti How to Write Fifths The first harmony in Western European music was based on the interval of the perfect fifth, back in the ninth century. (organum) All fifths are perfect as long as the accidentals match. The exception is any fifth starting on a B. Music with Melodies Set with Fifths After the Middle Ages, composers avoided writing successions of perfect intervals. However, at the end of the nineteenth century, composers such as Debussy again became fascinated with the sounds of fifths.