* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Balance of payments wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Global financial system wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Okishio's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Foreign-exchange reserves wikipedia , lookup
Inflation targeting wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate wikipedia , lookup
Exchange rate wikipedia , lookup
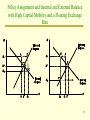
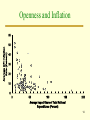
INTERNATIONAL MONETARY AND FINANCIAL ECONOMICS Third Edition Joseph P. Daniels David D. VanHoose Copyright © South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved. Chapter 14 Domestic Economic Policymaking in a Global Economy Policy Assignment Problem • Once policymakers commit to an external objective, they confront a fundamental problem: Domestic and international objectives often clash. • Assignment Problem: The problem of determining whether the central bank or the finance ministry should assume responsibility for achieving a nation’s domestic or international policy objectives. 2 Monetary and Fiscal Policy Combinations for External Balance with High Capital Mobility and a Floating Exchange Rate 3 Monetary and Fiscal Policy Combinations for Internal Balance with High Capital Mobility and a Floating Exchange Rate 4 Policy Assignment and Internal and External Balance with High Capital Mobility and a Floating Exchange Rate 5 Exchange Rate Responses • Short-run wage stickiness causes the aggregate price level to adjust less completely to changes in aggregate demand than it would otherwise. • This has an important consequence for the response of the exchange rate to policy actions that affect aggregate demand. • Exchange Rate Overshooting is a situation in which the short-run effect for an increase in aggregate demand is a rise in the nominal exchange rate above its long-run equilibrium value. 6 Long-Run Adjustment of the Exchange Rate to an Increase in the Money Stock 7 Openness and the Output-Inflation Relationship • The openness of an nation’s economy is another potentially important factor that affects the responsiveness of a nation’s real output to changes in the price level. • It turns out, however, the openness can have conflicting effects on the output –inflation relationship. • Openness is often measured using imports as a share of total expenditure. 8 Imports as a Share of Total Expenditures in Selected Nations 9 Competition in Domestic Product Markets • Many nations restrain competition through elaborate systems of domestic regulations and protect firms from competition using trade barriers. • Imperfect Competition is a market environment in which there are only a few firms, each of which individually can influence the market price by varying its production. 10 Index Measure of the Extent of Product-Market Regulation in selected Industrialized Nations 11 The Sacrifice Ratio • The Sacrifice Ratio is the short-run fall in a nation’s real output generated by a reduction in inflation divided by the associated decline in the inflation rate. • If a rise in openness in a nation is observed to be associated with a larger sacrifice ratio, this would provide evidence that greater openness raises the sensitivity of real output to a change in the price level. 12 Central Bank Independence and the Net Effect of Openness on the Sacrifice Ratio 13 Openness and Inflation 14 New Open Economy Macroeconomics • Open Economy Macroeconomics is the study of factors affecting the overall economic performance of a country that permits crossboarder exchanges of goods, services, and financial assets. • New Open Economy Macroeconomics focuses on how nominal wage stickiness, sluggish prices, and imperfect competition affect the transmission of policy actions. 15