* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Business Cycle
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Economic growth wikipedia , lookup
Chinese economic reform wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
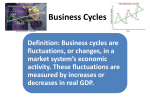
The Business Cycle Chapter 10 Economic Fluctuations, Unemployment and Inflation Business Cycle Defined as: – The pattern of rising real GDP followed by falling real GDP. Business Cycle • Pattern of the Business Cycle – The pattern is that of a period of growth, called expansion, which hits a peak. – The growth is followed by a fall in the economy, called a contraction. – The bottom of the fall is called the trough. Business Cycle • Pattern of the Business Cycle – After a period of time in the trough, the economy resumes its growth/expansion. – Later, it hits another peak, at a higher size of GDP. Changing Business Cycle Vocabulary • • • • • • Panic Crash Depression Recession Growth-Adjustment Phase Jobless Recovery Indicators • Economists use changes in a variety of activities to measure the business cycle, and to try to predict where the economy is headed. • They include: – Leading indicators – Lagging indicators LEADING INDICATORS • Variables that change before real output changes. • They include: – Unemployment claims – Manufacturers’ new orders LAGGING INDICATORS • Variables that change after real output changes. • They include: – Inventories to sales ratio – Outstanding commercial loans