* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Chinese economic reform wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Rostow's stages of growth wikipedia , lookup
Economic growth wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
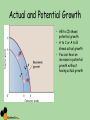
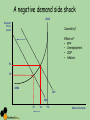
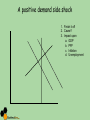
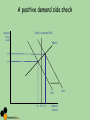
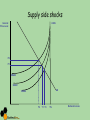
Macroeconomic Indicators The Economic Cycle and Economic Growth Cycles • • • • Peak, boom, overheating Downturn Recession, depression, trough, slump Recovery, expansion Cycles Business cycle/trade cycle/economic cycle Kondratiev Kuznets Kitchin Keynes Schumpeter Friedman K-wave Building cycle Inventory cycle Multiplier – accelerator Technology/innovation Monetary Output Gaps • The difference between actual growth and the trend rate of growth • Where would these be on your chart? • Output lost in a recession is regained in a boom but…. Hysteresis • The trend rate of growth can shift downwards if there is a deep recession due to permanent losses of human and physical capital • Loss of skills – structural change • Long term unemployed • Cut backs in investment • Outdated technology • ‘potential’ falls Hysteresis and Growth Trend Business cycle models Shocks – Demand or supply side • Exogenous shocks • Endogenous shocks • Explain how a major world recession, an exogenous shock to the UK economy, could trigger a business cycle. (10/15 marks) Shocks and ADAS • Key terms – – – – Long-term growth rate Actual growth Potential growth Trend rate of economic growth Actual and Potential Growth • AB to CD shows potential growth • A to C or A to B shows actual growth • You can have an increase in potential growth without having actual growth Task Using a PPF diagram, show the following 1. 2. 3. 4. An economy with full employment experiencing economic growth An economy initially with full employment experiencing a recession, keeping its AS capacity constant An economy in recession returning to full employment, with its AS capacity constant An economy which initially has a small and constant output gap, experiencing economic growth ADAS A negative demand side shock LRAS General Price Level Caused by? Effect on? • PPF • Unemployment • GDP • Inflation Pe P2 SRAS AD1 AD2 Y2 Ye Yfc National Income A positive demand side shock 1. Finish it off 2. Cause? 3. Impact upon a. GDP b. PPF c. Inflation d. Unemployment A positive demand side shock General Price Level LRAS = potential GDP SRAS1 P2 P1 AD1 Y1 Yfc Y2 National Income AD2 Supply side shocks • Show the effect on an ADAS diagram of the following – Increased rates of emigration – A fall in international commodity prices Supply side shocks General Price Level LRAS P2 P1 SRAS2 SRAS1 AD SRAS3 Y2 Y1 Y3 Yfc National Income Causes of economic growth • Economic stability and sound macroeconomic policies • Increased labour activity/participation • Increased labour productivity • Investment in physical capital • Improved human capital • Enterprise Is growth good? Debate • Advantages • Disadvantages Is growth good? • Advantages • Improvements in living standards: More jobs: • The accelerator effect of growth on capital investment: • Greater business confidence: • The “fiscal dividend”: • Potential environmental benefits • Benefits from growth driven by technological change • Disadvantages • Inflation • Environmental concerns • Inequality Kuznets curve - explain What would the question be? What would the question be? Applied Economics The Impact on the economy