* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Understanding the Market System
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Consumerism wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Circular economy wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
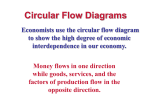
Understanding the basic operation of an economic system Allocating resources in a market economy limited resources or The Factors of Production… The root of the scarcity problem Factors of Production Groups of resources used to make all goods and services Land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship Privately owned in a market system LAND Natural resources LABOR Any effort a person devotes to a task for which that person is paid CAPITAL Any human made resource that is used to create other goods and services • Physical capital goods like building and tools for the purpose of production • Human capital is the knowledge and skills a worker gains through education and experience ENTREPRENEURSHIP A person who assembles the factors of production to create goods and services Risk-taker! Circular flow of economic activity Tying it all together… Maintaining a proper functioning a free market is not easy or simple The Pillars of Free Enterprise Pillar Explanation (From producer view & consumer view) Example Private Property For purposes of business enterprise, or as a result of consumer choice Factory owner Home owner Car owner Choice For purposes of production and profit, to fulfill consumer wants/needs open a business Choose a profession job Consumer choice Voluntary Exchange Where the producer and Places of exchange (mall, consumer come together: the internet) marketplace (willingly buy or sell) Contracts Competition Within industries –maintain quality and fair prices, As consumers (demand) push prices up Gas stations, Airline industries, Supermarkets, Stock Market Economic Incentives For purpose of profit, wage, interest, Or “get a good deal” Successful entrepreneurs make big money -profit Salary, Fringe benefits PAYMENTS: Economic Incentive RENT SALARY INTEREST PROFIT •LAND •LABOR •CAPITAL •ENTREPRENEURSHIP Why money… Government’s Role? From Res. Owners to Gov’t – – taxes Productive services From Bus. Owners to Gov’t – – taxes business services From Gov’t to Res Owners – – money payments Gov’t services From Gov’t to Bus Owners – – money payments Gov’t services Gross Domestic Product one of the primary indicators used to gauge the health of a country's economy at its most basic: a total of what everyone has earned in a year (income approach), or by a total of what everyone spent (expenditure method). what GDP represents, has a large impact on nearly everyone within that economy Adapted from: http://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/199.asp HOW DO THE FOUR FACTORS OF PRODUCTION AND THE CIRCULAR FLOW OF ECONOMIC ACTIVITY RELATE TO … UNEMPLOYMENT? GOVERNMENT SPENDING? BUSINESS GROWTH? MINIMUM WAGE?