* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Open economy macroeconomics
Global financial system wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Balance of payments wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Foreign-exchange reserves wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Okishio's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Exchange rate wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate wikipedia , lookup
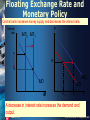
Chapter 29 Open economy macroeconomics David Begg, Stanley Fischer and Rudiger Dornbusch, Economics, 9th Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2008 PowerPoint presentation by Alex Tackie and Damian Ward ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, 2008 Open economy macroeconomics • … is the study of economies in which international transactions play a significant role – international considerations are especially important for open economies like the UK, Germany or the Netherlands • Domestic macroeconomic policy in such countries cannot ignore the influence of the rest of the world – especially via the exchange rate. ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, 2008 Floating Exchange Rate and Monetary Policy Central bank increases money supply and decreases the interest rate. İnterest rate P MS2 MS1 r1 P1 r2 AD2 MD M AD1 Y1 Y2 A decrease in interest rate increases the demand and output. 3 Y ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, 2008 Floating Exchange Rate and Monetary Policy • Monetary Policy is Effective under Floating Exchange rate. • Increase in MS →Decrease in r. – C and I increases – NX increases because the devaluation of the exchange rate. • Increases in demad and output. 4 ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, 2008 Fixed Exchange Rate and Fiscal Policy The government can use an expansionary fiscal policy to increase the demand and the output. P AD3 AD2 AD1 P1 İncrease in G Y1 5 Y2 Y3 Y ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, 2008 Fixed Exchange Rate and Fiscal Policy • When (G) increases, – National output increases. – Interest rate will also increase, – There will be capital inflow – The central bank increases the money supply to keep the exchange rate constant. – The interest rate will return to the original value. In the meantime the output will increase and a short-term economic boom will be experienced. 6 ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, 2008 Crises in Greece • Greece cannot apply its monetary policy because it is in the Euro area. • Greece cannot apply its fiscal policy because the budget deficit is already very high and the country is likely to default. • The only policy left is to decrease prices. They will be more competitive this way and will be able to export. To decrease the price level, the labor costs should decrease. 7 ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, 2008