* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Business Cycle
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
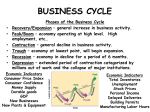
The Business Cycle • One of the major problems capitalist nations must constantly deal with is an economic event known as the business cycle • This means that the economy will go through periods of boom and bust. The Business Cycle • A free market economy does not grow at a constant rate. It goes through a series of booms and busts called the business cycle. • The following graph illustrates the business cycle: The Business Cycle Explanation A. The letter A on the graph represents a decline, sometimes calls a recession. During a decline, consumer spending decreases as consumers and investors become cautious about the future. This causes factories to slow production and lay off workers. The increased unemployment tends to reduce spending in the marketplace even further, contributing to the economy's decline. The Business Cycle B. The letter B on the map represents the lowest point of the recession. This is a period of high unemployment and low prices. Prices have dropped because there is less money being circulated in the economy. The Business Cycle C. The letter C on the map represents a boom, sometimes called prosperity. A boom is a period of prosperity. Most people have jobs. As a result they tend to be buying goods and services. This keeps the economy strong. This period will see the highest levels of inflation as producers try to slowly increase their prices in order to get a bigger share of the thriving market. The Business Cycle D. The letter D on the map represents a depression. A depression is a very big decline whereas a recession is only a small decline. It can be defined as three quarters of negative growth During a depression, unemployment is very high and there is very little money circulating in the marketplace. A depression is a serious problem for a country. The most famous depression was the Great Depression in the 1930's. The Business Cycle E. The letter E represents a recovery. During a recovery, the economy is improving. As people begin spending more, producers are encouraged to increase production. This means more jobs and, in turn, even more spending. A recovery was the intended effect of Franklin Delano Roosevelt's (FDR) New Deal in the 1930's Can you spot the recession, recovery and prosperity? The Business Cycle • The oil industry is a good example of the business cycle at work. • Fluctuating prices for (and production of) oil have occurred since the beginning of the industry. • During Rockefeller's day, the price of oil even fell below the price of water! • Nowadays, in Alberta we can see the effect that changing oil prices have on our economy. • When prices are low, we tend to have higher unemployment and a slower economy. • When they rise again, we are able to increase spending at all levels. The Business Cycle • When an economy has been prosperous for a long time, raw materials tend to get used up, skilled labourers become scarce, and stockpiles of goods in warehouses increase. • This causes some factories to lay off workers. • All these factors will eventually work together to cause a recession Classical Liberalism’s Solution • Past depressions (like in the 1870s) –let them work it out for themselves. • Leave things alone and they will return to normal because the business cycle is natural. • However the US gov’t did intervene to try to force strikes to end(i.e. the army killed 70 workers in 1877) How did classical liberalism respond to competing ideologies? • Socialism, communism, fascism and other beliefs had reasons for existing. • If there was no response, revolution or some other abandonment of capitalism might occur. Welfare Capitalism (US definition) • • In the USA, many industrialists felt the need to fend off left wing appeal by improving the lives of their workers. For example: • • Henry Ford offered his workers a comparatively high wage- $5/day George Pullman built a town for his workers (better housing, sanitation, etc.) Look at the following advertisement • It’s probably from the 1930s • It’s aimed at managers or bosses. The Great Depression • It wasn’t that great! • Seen as a failure of pure capitalist ideas • • • Keynesian Economics John Maynard Keynes was a British economist Wrote General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money Advocated interventionist policies to deal with the adverse effects of the business cycle • • • • Keynesian Economics Keynes argued that an economic slump was not a long-run phenomenon that we should all get depressed about and leave the markets to sort out. Keynes felt that a slump (or trough) was a short-run problem stemming from a lack of demand. If the private sector was not prepared to spend to boost demand, then the government should do it instead by running a budget deficit. When times were good again and the private sector was spending again, the government could trim its spending and pay off the debts they had accumulated during the slump. Keynes’ Demand Side Economics More money in your pockets: Governments should spend money in a recession to reduce its severity. It should also reduce taxes. Less money in your pockets: Governments should spend less money in boom times to soften a boom. It should also raise taxes. Demand-Side Economics • How to cool an overheated economy? • How to warm it up again? • Influence consumer demand Heat it up • Fiscal Policy • increase government spending • social assistance How could these actions stimulate • public works consumer demand? • lower taxes • Monetary Policy • lower interest rates Cool it off • • Fiscal Policy • • cut government spending • • cut spending as fewer people need social assistance limit public works raise taxes Monetary Policy • raise interest rates How could these actions slow consumer demand? Welfare State • Keynes’ theories influence a great number of liberal democracies. • In the USA president Roosevelt set up his “New Deal” which combined government intervention and freemarket principles. Economic Responses Guess what ideas the monetarists were responding to. Review What did Keynes feel the government should do during a recession/depression to: • government spending • taxes • interest rates Why? Review What about during periods of strong economic growth? • government spending • taxes • interest rates Why? Questions Page 212-213 Read FDR’s speech at the conference of Mobilization for Human Needs and answer questions 4-7 on page 213.