* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Integrating Markets in Financial Instruments
Syndicated loan wikipedia , lookup
Shadow banking system wikipedia , lookup
Public finance wikipedia , lookup
Private equity secondary market wikipedia , lookup
Global saving glut wikipedia , lookup
Market (economics) wikipedia , lookup
Global financial system wikipedia , lookup
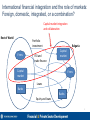
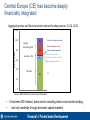
Local capital markets in internationally integrated financial systems: How can capital markets best serve domestic investors and firms? Steen Byskov Sr. Financial Sector Specialist The World Bank November 14, 2011 International financial integration and the role of markets: Foreign, domestic, integrated, or a combination? Capital market integration and collaboration Rest of World Portfolio investment Firms FDI and trade finance Bulgaria Capital market Capital market Firms Loans Banks Banks Equity and loans 2 Central Europe (CE) has become deeply financially integrated Aggregate private and financial sector external funding sources, EU 10, 2010 120 100 Foreign borrowing: 35% Securities: 8% Real sector debt securities Banks debt securities 4 60 40 Real sector foreign borrowing Banks foreign borrowing 19 80 Percent of GDP 16 Real sector equity securities Banks equity securities FDI: 63% 63 FDI 20 0 Sources: IMF BOPS, Bank for International Settlements. • • It has been FDI intense, bank centric including direct cross border lending... …but only modestly through domestic capital markets 3 CE firms get much funding from abroad, but little from capital markets compared to other regions 300 Domesticbank bank credit Domestic credit Foreign Foreignborrowing borrowing 250 FDI FDI Domesticequity equitymarket marketcapitalization capitalization Domestic Percent of GDP 200 Domestic Domesticprivate privatedebt debt 111 International Internationalprivate privatedebt debt 150 100 59 18 38 49 14 63 50 0 33 11 15 14 26 81 58 27 35 6 3 17 4 5 5 5 EU10 Europe and Central Asia Latin America East Asia and Pacific 31 Sources: IFS, BOPS, WDI, BIS. • • Bank credit is rather important in EU10 Domestic capital markets are rather unimportant 4 Central European capital markets are still mostly small and illiquid 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Turnover Ratios in Emerging Europe, 2010 percent 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 Sources: FESE for market capitalization, IMF for GDP. Turkey Hungary Poland Czech Rep. Estonia Romania Slovakia Bulgaria Slovenia Turkey Poland Czech Rep. Hungary Slovenia Bulgaria Romania 0 Slovakia Percent of GDP Equity Market Capitalizations in Emerging Europe, 2010 Source: World Development Indicators, the World Bank. 5 Firm’s raised money through the local stock market pre-crisis, but it stopped during the 2008-09 crisis Estimated net funds raised on stock exchanges markets Percent of GDP 1.0 0.9 2005-2008 0.8 2008-2010 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 Slovakia Slovenia Latvia Hungary Ukraine Estonia Lithuania Kazakhstan Turkey Poland Romania Czech Rep Croatia Bulgaria Serbia Russia 0.0 Sources: WDI, Bloomberg Note: Net funds raised are estimated as the growth in market capitalization net of the price effect as measured by the main index on the stock exchange. 6 European trend towards decreasing bank funding since 2008 increases the need for markets • Structural trend or tactical response? Trend may be accelerated by – Immediate funding pressures and higher cost of capital for parent banks – Shifting parent bank strategies – Home country supervisory actions (Austrian example) – EBA recapitalization requirements – Basel III Share of funding from banks (vs. bonds) Median among a survey of 161 EMEA corporates 60 50 Percent • 40 30 20 10 0 2007 2008 2009 2010 Source: FitchRatings, “European Corporate Funding Disintermediation”, Oct. 19, 2011 7 Why have CE markets remained small, and what is the solution? The economic and financial structure in CEE countries do not support independent local markets Markets were set up to facilitate privatizations Small economies cannot independently support liquid capital markets Alternative funding from domestic and international banks developed quickly FDI companies are not likely to use local markets HOWEVER, pressures on banks will strengthen the demand for capital markets Solution Improve investors’ and firms’ access to capital markets through market integration and collaboration EU facilitates capital market integration In Western Europe, market infrastructure has integrated, but in CEE it remains national Policy choices are interconnected -> need for cross border coordination The next presentation outlines capital market development in EU and options for CEE 8