* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Business Cycles
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
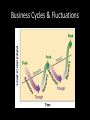
Business Cycles & Fluctuations http://www.investopedia.com/video/play/busi ness-cycle/ Business Cycles The regular ups [increases] and downs [decreases] of the Gross Domestic Product. Can interrupt the nation’s economic growth. Recession A period during which GDP declines for at least two quarters in a row [6 months] Peak A recession begins when the economy reaches a peak: the point where GDP stops going up. Trough The end of a recession. The point where GDP stops decreasing and begins to rise. Expansion A period of recovery from recession. Continues until the economy reaches a new peak. Depression If a recession is very severe, it could lead to a depression: A state of the economy with: •Large numbers of people out of work •Major shortages and •Low production [excess capacity in manufacturing plants] UNEMPLOYMENT Civilian Labor Force The sum of all people 16 years and older who are either employed or actively seeking employment. Excluded: military, imprisoned, institutionalized. Unemployed People available for and looking for work during the last 4 weeks. Unemployment rate The number of unemployed divided by the total number of people in the civilian labor force. Number of unemployed =unemployment rate Civilian labor force 15,100,000 154, 082,000 = 9.8% unemployment rate U.S. on average= 6 % Our Unemployment Rates •Philadelphia: 7.3% (Feb 2015) •Pennsylvania: 5.2% (Feb 2015) •Northeast: 5.6% April, 2014 •United States: 5.5% March, 2015 •Detroit, Michigan: 12.5% (Feb 2015) *Bureau of Labor Statistics, United States Department of Labor Underemployment Discouraged workers: people who give up and stop looking for work. [not included in the unemployment rate] Underemployed workers who would like to work more hours or prefer a job that better matches their skills. Frictional Unemployment Workers changing jobs or waiting to go to a new job Short-term unemployment that occurs while workers search for the jobs best suited for their skills and interests. Structural Unemployment Fundamental changes in the economy that reduces the demand for some workers. Arises from a mismatch of skills between job seekers and the types of jobs available. Technological Unemployment Occurs when workers are replaced by machines or automated systems that make their skills obsolete. ATMS/Bank Tellers Cyclical Unemployment Relates to a change in the business cycle. Joblessness caused by economic contraction. During contraction, production [measured as GDP] declines. Business stop hiring or lay workers off. Recession/Depression Seasonal Unemployment Results from seasonal changes in the weather or in demand for certain seasonrelated jobs. landscaping, agricultural jobs, beach resorts. • http://content.time.com/time/video/player/0, 32068,1149720836001_2092416,00.html